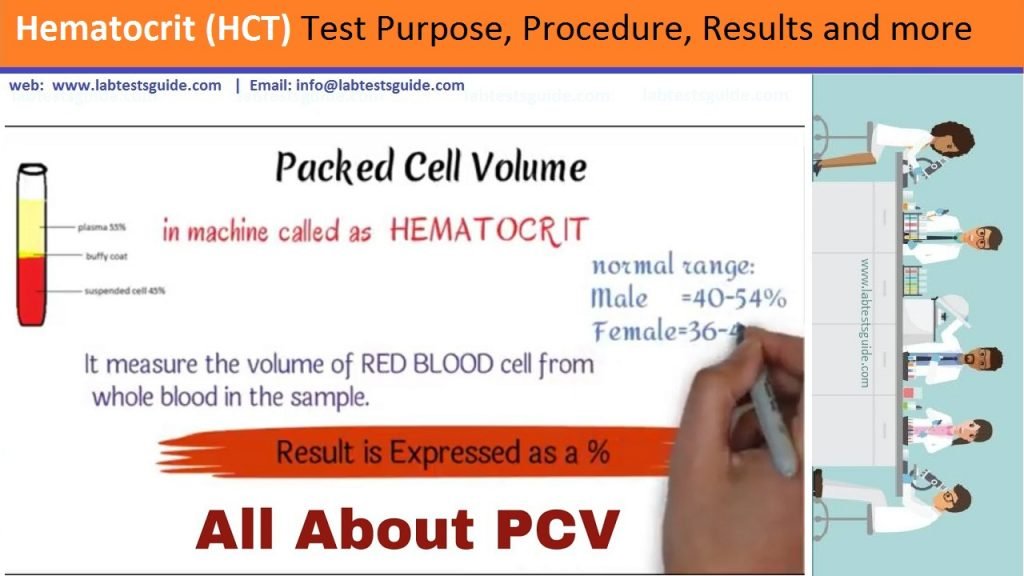
Hematocrit is the percentage of red blood cells in the total blood volume. Red blood cells are vital to your health. Imagine them as the subway system of your blood. They transport oxygen and nutrients to various locations in your body. For you to stay healthy, your body needs to have the correct proportion of red blood cells.
Also Known as: Hct, Crit, Packed Cell Volume, PCV, H and H (Hemoglobin and Hematocrit)
Test Panel: Hemoglobin, Red Blood Cells (RBC), HCT, MCV, MCH, MCHC, Platelets Count, White Blood Cells (WBC), DLC, ESR
Why Get Tested:
- It is used to diagnose anemia.
- It is used to diagnose leukemia
- It is used to diagnose dehydration
- It is used to diagnose dietary deficiencies
- Hct is done in the patients with bleeding or blood loss.
- It is part of complete blood count.
When to Get Tested:
- when you have signs and symptoms of anemia (weakness, fatigue).
- when you have signs and symptoms of polycythemia (dizziness, headache)
- At regular intervals to monitor a disorder that affects RBCs and to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment
Sample Required:
- The patient blood is taken in EDTA.
- It is stable for 48 hours at 4 °C and 6 hours at 23 °C.
- Fetal blood: Collected by percutaneous blood sampling.
Precautions for Sample:
- Perform the test within 6 hours of the blood collection.
- EDTA is the choice of blood anticoagulant.
- Avoid hemolysis.
- Avoid clotting of the blood.
- Centrifugation must be adequate. This will give the high result.
- The buffy coat is not included in the hematocrit.
- Avoid excess of the EDTA.
- Avoid overdilution of the blood sample by the anticoagulant.
- Avoid Prolonged tourniquet, it can lead to hemoconcentration and error in the Hct.
- Drugs like penicillin and chloramphenicol decrease the Hct level.
Method to estimate the Hct:
- Microhematocrit tube method.
- Wintrobe hematocrit method is the macro method.
- Automated method.
Normal Value:
| Test Name | Male | Female |
| HCT | 38 – 52 % | 38 – 52 % |
Critical value of Hct = <15 % or >60 %
Increased Hct is seen in:
- Polycythemia Vera.
- Erythrocytosis.
- Extreme physical exercise or excitement.
- High Altitude.
- Dehydration leading to Hemoconcentration e.g. diarrhea, burns, and vomiting.
- Congenital heart failure.
- Severe chronic pulmonary obstructive disease (COPD).
Decreased Hct is seen in:
- Anemia.
- Hemoglobinopathies.
- Cirrhosis.
- Hemolytic anemia (Erythroblastosis fetalis, drug-induced hemolytic anemia, and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria.
- Hemorrhage.
- Bone marrow failure
- Renal diseases.
- Normal pregnancy.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- malignancies like lymphoma, leukemia, multiple myeloma, and Hodgkin’s diseases.
- Normal pregnancy.
- Bone marrow failure.
CBC (Complete blood count) includes:
This is the measure of:
- Red blood cells.
- White blood cells.
- Platelet Count
- Hemoglobin
- Hematocrit (HCT)
- RBC indices.
- Mean corpuscular volume (MCV).
- Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH).
- Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC)
- Red blood cell distribution width (RDW).
- White cell differential count (DLC) includes.
- Peripheral blood smear study.