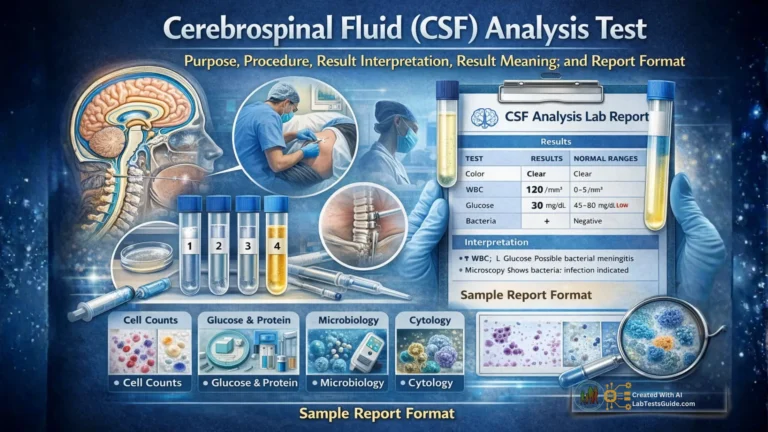
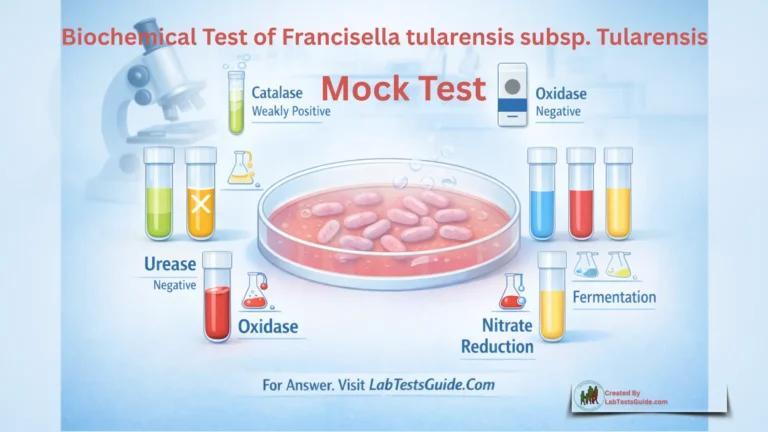
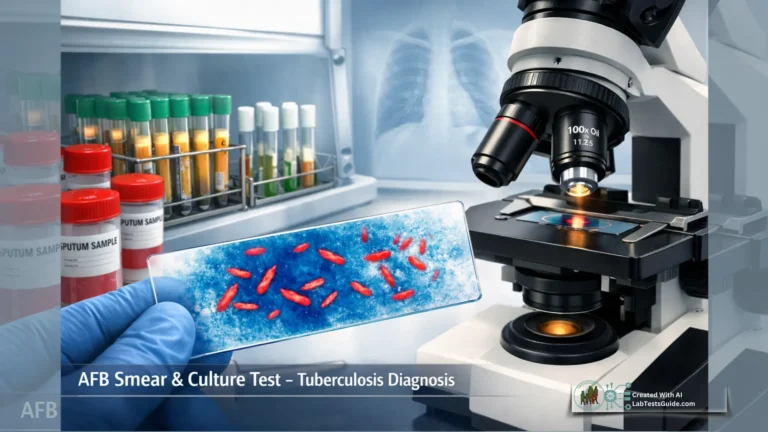
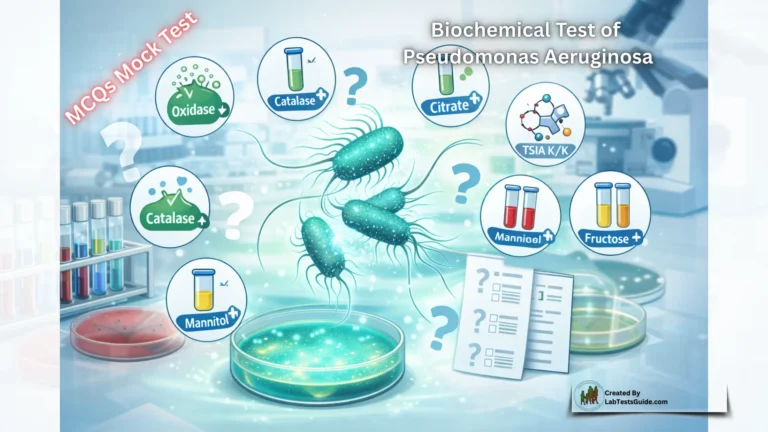
Microbiology
 Microbiology is the branch of biology that deals with the study of microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa, and algae. It is a vast field that encompasses several sub-disciplines, including medical microbiology, environmental microbiology, industrial microbiology, and microbial ecology.
Microbiology is the branch of biology that deals with the study of microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa, and algae. It is a vast field that encompasses several sub-disciplines, including medical microbiology, environmental microbiology, industrial microbiology, and microbial ecology.Microbiology is a broad scientific discipline that encompasses various subfields. Here are some of the major fields of microbiology:
- Bacteriology: the study of bacteria, including their identification, classification, physiology, ecology, and pathogenesis.
- Virology: the study of viruses, including their structure, replication, evolution, and interaction with host cells.
- Mycology: the study of fungi, including their identification, classification, physiology, ecology, and pathogenesis.
- Parasitology: the study of parasites, including protozoa and helminths, their identification, classification, physiology, ecology, and pathogenesis.
- Immunology: the study of the immune system, including the mechanisms of host defense against infectious agents, autoimmune diseases, and immunodeficiencies.
- Microbial physiology: the study of the metabolic and physiological processes of microorganisms.
- Microbial ecology: the study of the interactions between microorganisms and their environment.
- Applied microbiology: the use of microorganisms in biotechnology, industry, agriculture, and medicine.
- Microbial genetics: the study of the genetics of microorganisms, including the mechanisms of genetic variation, gene expression, and gene transfer.
- Environmental microbiology: the study of the microbial communities in various environmental niches, including soil, water, and air.