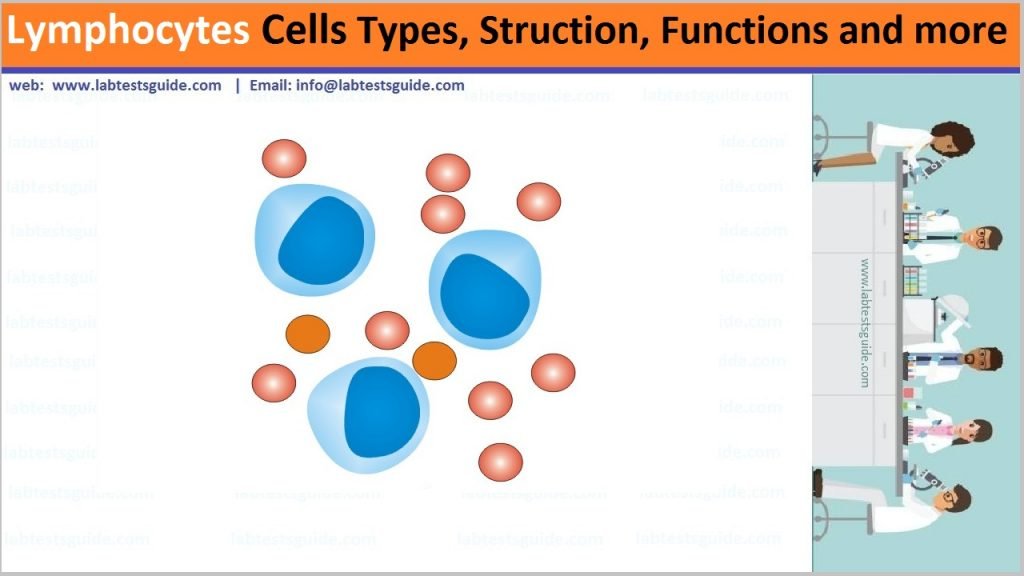
Lymphocytes are white blood cells that are also one of the body’s main types of immune cells. They are made in the bone marrow and found in the blood and lymph tissue. The immune system is a complex network of cells known as immune cells that include lymphocytes.
Also Known as: Lymphocytes, Lympho
Cells Panel: Neutrophils, Lymphocytes, Monocytes, Eosinophils, Basophils
Types of Lymphocytes:
- T Cells (B Lymphocytes)
- B Cells (T Lymphocytes)
- Natural Killer (NK)
B-cells develop in the bone marrow. T cells are born in the bone marrow, but are matured in the Thymus. There will be more on this in the section on the immune system.
Structure of Lymphocytes:
- The large cells are 10–14 µm and have a smaller nucleus-to-cytoplasm ratio and more granules.
- The smaller cells are typically 6–9 µm with a larger volume of nucleus to cytoplasm, creating a “halo” effect.
- A few cells may fall outside these ranges, at 14–17 µm.
- Neucleus: Larg Neucleus round to idented fill the cells , Clumped with chromatin
- Cytoplasm: Peripheral rim of basophilic cytoplasm , no granules
Function of Lymphocytes
The B-cells develop into plasma cells which make antibodies, The T-cells attack viruses, cancer cells, and transplants.
Referance Ranges:
| Test Name | Male | Female |
| Lymphocytes | 20 – 50 % | 20 – 50 % |
Lymphocytes increased in:
Lymphocyte Decreased in:
- Chronic debilitating illness.
- Immune-deficiency.
Related Articles:
Possible References Used