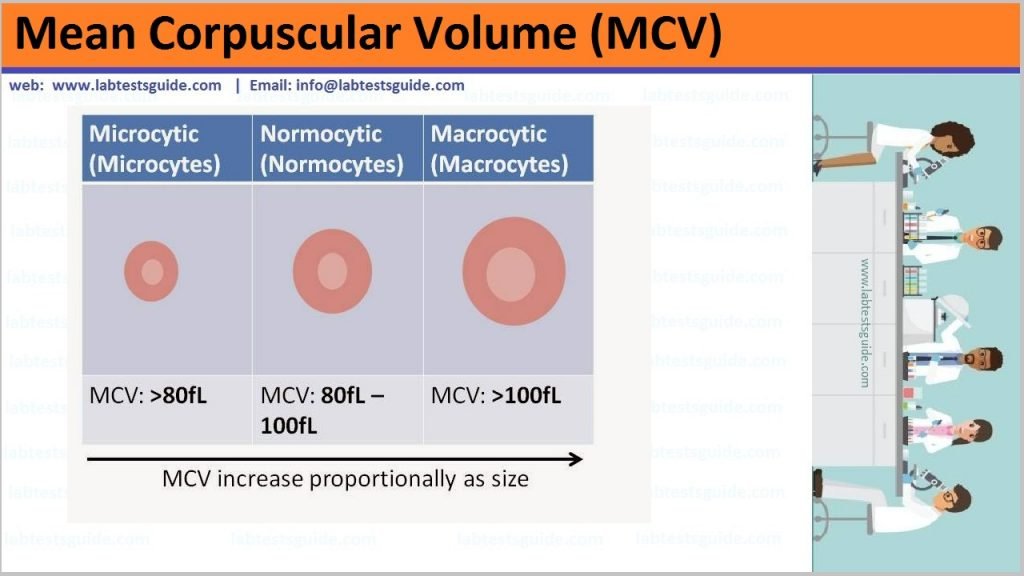
The mean corpuscular volume, or mean cell volume (MCV), is a measure of the average volume of a red blood corpuscle (or red blood cell). The measure is attained by multiplying a volume of blood by the proportion of blood that is cellular (the hematocrit), and dividing that product by the number of erythrocytes (red blood cells) in that volume. The mean corpuscular volume is a part of a standard complete blood count.
Test Panel: Hemoglobin, Red Blood Cells (RBC), HCT, MCV, MCH, MCHC, Platelets Count, White Blood Cells (WBC), DLC, ESR
Why Get Tested:
- This is one of the blood indices.
- This is done to diagnose the anemia.
When to get tested
- when you have signs and symptoms of anemia (weakness, fatigue).
- when you have signs and symptoms of polycythemia (dizziness, headache)
- At regular intervals to monitor a disorder that affects RBCs and to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment
Sample Required:
- The best sample is EDTA blood.
- Stable 6 hours at 25 °C and 24 hours at 4 °C.
- Fetal blood collected percutaneous from the umbilical area.
Normal Value:
| Test Name | Male | Female |
| MCV | 75 – 95 fl | 75 – 95 fl |
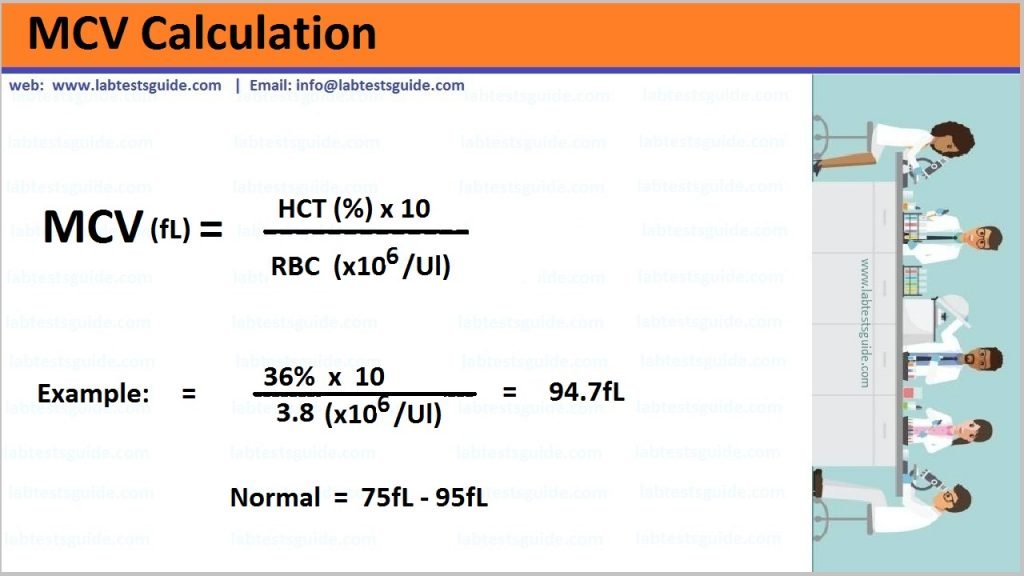
Test Procedure or calculation
MCV Result will be detect with Calculation.
Calculation Formula
MCV increased in:
- Pernicious anemia (vit.B12 deficiency).
- Folic acid deficiency.
- Liver diseases.
- Alcoholism.
- Antimetabolic therapy.