Blood plasma is a yellowish liquid component of blood that holds the blood cells in whole blood in suspension. It is the liquid part of the blood that carries cells and proteins throughout the body. It makes up about 55% of the body’s total blood volume. It is the intravascular fluid part of extracellular fluid (all body fluid outside cells). It is mostly water (up to 95% by volume), and contains dissolved proteins (6–8%) (e.g. serum albumins, globulins, and fibrinogen), glucose, clotting factors, electrolytes (Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, HCO3−, Cl−, etc.), hormones, carbon dioxide (plasma being the main medium for excretory product transportation) and oxygen. It plays a vital role in an intravascular osmotic effect that keeps electrolyte concentration balanced and protects the body from infection and other blood disorders.
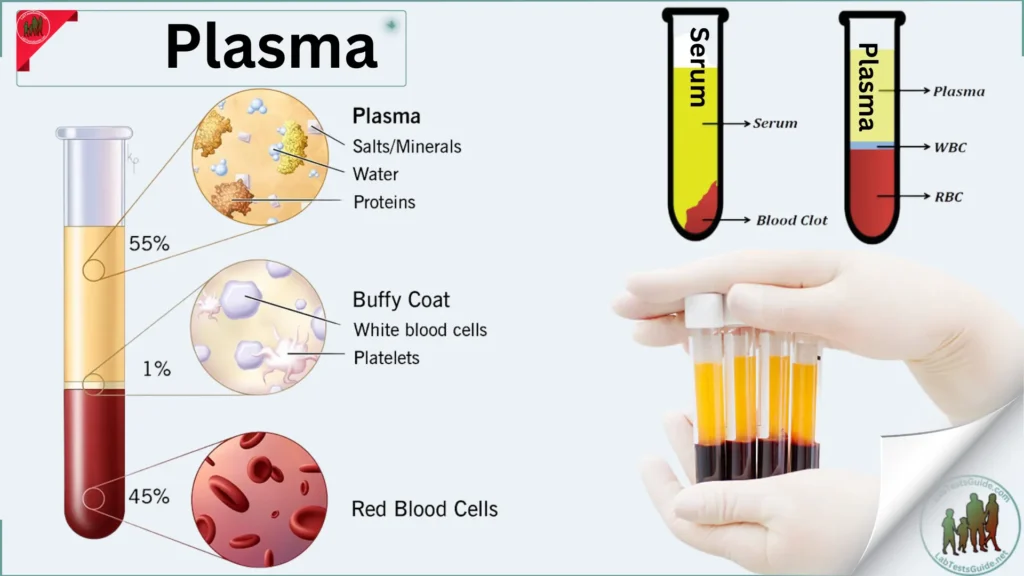
- Serum Received from Clotted Blood.
- Plasma Received from anticoagulant blood
Plasma preparation
Collect whole blood into commercially available anticoagulant-treated tubes e.g., EDTA-treated (lavender tops) or citrate-treated (light blue tops). Heparinized tubes (green tops) are indicated for some applications; however, heparin can often be contaminated with endotoxin, which can stimulate white blood cells to release cytokines. Cells are removed from plasma by centrifugation for 10 minutes at 1,000–2,000 x g using a refrigerated centrifuge. Centrifugation for 15 minutes at 2,000 x g depletes platelets in the plasma sample.
Specimen Containers
- Red-top tube: Contains no anticoagulant or preservative.
- Mottled red/gray-top, gold-top, or cherry red-top (gel-barrier) tube: Contains clot activator and gel for separating serum from cells, but not anticoagulant. Do not use gel-barrier tubes to submit specimens for therapeutic drug monitoring. Always check the test description to determine whether a gel-barrier tube is acceptable.
- Lavender-top tube: Contains K2 EDTA.
- Gray-top tube: Contains sodium fluoride (a preservative) and potassium oxalate (an anticoagulant).
- Blue-top tube (also light blue-top tube): Contains sodium citrate. Be sure to use only tubes with a 3.2% sodium citrate concentration. These are easily identified by the yellow diagonal stripes on the label.
- Green-top tube: Contains sodium heparin or lithium heparin.
- Yellow-top tube: Contains acid citrate dextrose (ACD) solution.
- Royal blue-top tube: Contains sodium EDTA for trace metal studies. Some royal blue-top tubes do not contain EDTA.
- Tan-top tube: Contains sodium EDTA for blood lead analysis.
- Plasma Preparation Tube (PPT™): Contains EDTA.