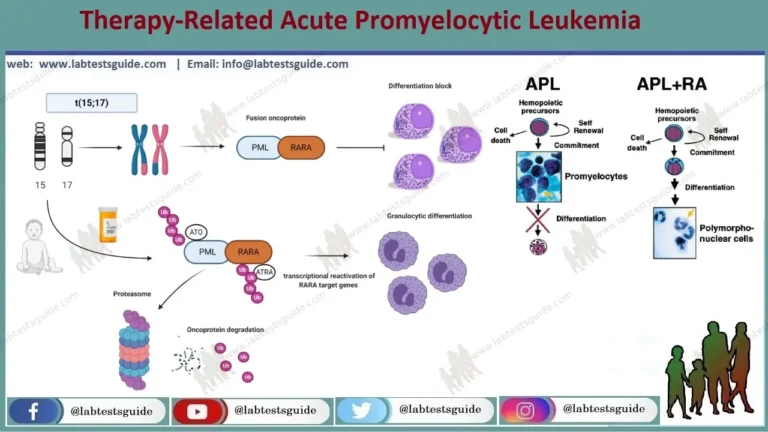
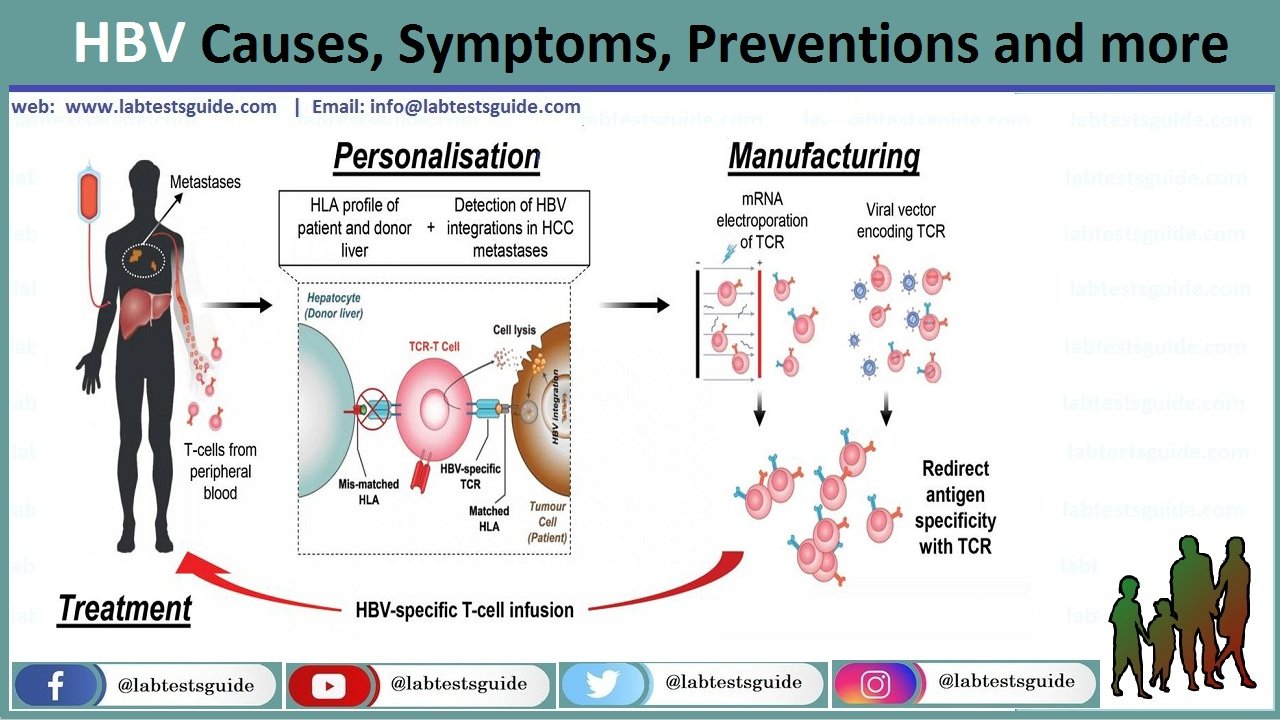
Hepatitis B is an infection of your liver. It can cause scarring of the organ, liver failure and cancer. It can be fatal if left untreated.
For some people, hepatitis B infection is chronic, meaning it lasts more than six months. Chronic hepatitis B increases the risk of liver failure, liver cancer, or cirrhosis.
Most adults with hepatitis B have complete recovery, even if their symptoms and symptoms are severe. Hepatitis B infection is more likely to be chronic in infants and children.
Also Known as: HBV Tests. Hep B, anti-HBs, Hepatitis B Surface Antibody, HBsAg, Hepatitis B Surface Antigen, HBeAg, Hepatitis B e Antigen, anti-HBc, Hepatitis B Core Antibody, anti-HBc IgM, anti-HBe, Hepatitis B e Antibody, HBV DNA
A vaccine can prevent hepatitis B, but there is no cure if you have a condition. If you are infected, taking some precautions can help prevent the virus from spreading to others.
Acute Vs Chronic HBV:
- Acute hepatitis B infection: lasts less than six months. Your immune system can clear hepatitis B from your body, and you should make a full recovery within a few months. Most people who get hepatitis B as an adult have severe infections, but they can lead to chronic infections.
- Chronic hepatitis B infection: lasts six months or longer. It has been delayed because your immune system cannot fight infection. Chronic hepatitis B infection can last a lifetime, potentially leading to coronary diseases such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Symptoms:
When you’re first infected, the warning signs include:
- Jaundice.- Your skin or the whites of the eyes turn yellow, and your pee turns brown or orange.)
- Light-colored poop
- Fever
- Fatigue that persists for weeks or months
- Stomach trouble like loss of appetite, nausea, and vomiting
- Belly pain
Causes:
It’s caused by the hepatitis B virus
The most common ways to get hepatitis B include:
- Sex: If you have unprotected sex with someone you can have it and your partner’s blood, sputum, sperm or vaginal discharges enter your body.
- Sharing needles: The virus spreads easily through injected needles and syringes.
- Accidental puncture: health workers and anyone else who comes in contact with human blood can do so.
- Mother to Childrens: Pregnant women with hepatitis B can reach their babies during delivery. But newborn babies can avoid infection. There is a vaccine.
Risk Factors:
Hepatitis B is transmitted to an affected person by contact with blood, semen or other body fluids. If you are at increased risk of hepatitis B infection:
- Have unprotected sex with multiple sexual partners or anyone affected by HBV
- Distribute needles during IV drug use
- They are men who have sex with other men
- Stay with someone who has chronic HBV infection
- There are newborn babies born to an infected mother
- Have a job that will make you bloody human
- Travel with areas with high HBV infection rates, such as Asia, the Pacific, Africa and Eastern Europe.
Complications:
Chronic HBV infection can cause serious complications, such as:
- Liver scars (cirrhosis). Inflammation associated with hepatitis B infection can lead to extensive liver lesions (cirrhosis), which can affect the liver’s ability to function.
- Liver cancer: increases the risk of liver cancer in people with chronic hepatitis B infection.
- Liver failure: Severe liver failure is a condition in which the major functions of the liver are stopped. When this happens, a liver transplant is necessary to maintain life.
- Other conditions: Individuals with chronic hepatitis B can develop kidney disease or inflammation in the blood vessels.
Precautions to Prevent HBV:
Other ways to reduce the risk of HBV include:
- Know the HBV status of any sexual partner: Don’t engage in unprotected sex unless you are absolutely sure that your partner is not affected by HBV or any other sexually transmitted infection.
- When you do not know your partner’s health, use a new latex or polyurethane condom each time you have sex. Remember that while condoms can reduce the risk of contracting your HBV, they do not eliminate the risk.
- Do not use illegal drugs. If you use illegal drugs, get help to stop. If you can’t stop it, use a sterile injection every time you apply illicit drugs. Never distribute needles.
- Be careful of tattoos and body piercing. If you find a drilling or tattoo, look for a popular store. Ask about how clean the equipment is. Make sure employees use sterile needles. If you can’t find answers, look for another store.
- Ask about hepatitis B vaccine before traveling. If you travel to an area where hepatitis B is common, ask your doctor about the hepatitis B vaccine. It is usually given in a series of three injections over a period of six months.
Preventions:
The hepatitis B vaccine is usually given in three to four injections in six months. You cannot get hepatitis B with the vaccine.
Hepatitis B vaccine is recommended.
- Newborn
- Children and adolescents are not vaccinated at birth
- People who work or live in a center for people with developmental disabilities.
- People who live with someone who has hepatitis B
- Health workers, emergency workers and others who come in contact with blood.
- Anyone who has a sexually transmitted infection, including HIV.
- Men who have sex with men.
- People who have more than one sexual partner.
- A sexual partner with someone who has hepatitis B
- People who use illegal drugs or distribute needles and syringes
- People with chronic liver disease.
- People with end stage renal disease
- The highest rate of hepatitis B infection in the world is high
Diagnosis:
The tests that can help diagnose hepatitis B or its complications are:
- Blood tests. Blood tests can detect the symptoms of hepatitis B virus in your body and tell your doctor if it is severe or chronic. A simple blood test can also determine if you are immune to this condition.
- Liver ultrasound A special ultrasound called transient allergy can show the amount of liver damage.
- Liver biopsy. Your doctor may remove a small sample (liver biopsy) from your liver for analysis to check for liver damage. During this test, your doctor inserts a thin needle into your skin and your liver and removes tissue samples for laboratory analysis.
Hepatitis B Screening:
Talk to your doctor about detecting hepatitis B infection if you:
- Are pregnant
- Stay with someone who has hepatitis B
- There were many sexual partners
- You have had sex with someone who has hepatitis B
- You are a man who has sex with men
- Having a history of sexually transmitted disease.
- HIV or hepatitis C
- Have a liver enzyme test with unknown results.
- Receive kidney dialysis
- Take medicines that suppress the immune system, such as those used to prevent rejection after organ transplantation.
- Use illegal injection drugs
- They are in jail
- He was born in a country where hepatitis B is common, including Asia, the Pacific, Africa, and Eastern Europe.
- Hepatitis B is common for adoptive parents or children from places such as Asia, the Pacific, Africa, and Eastern Europe.
Treatment:
Please Contact to your Healthcare Provider.