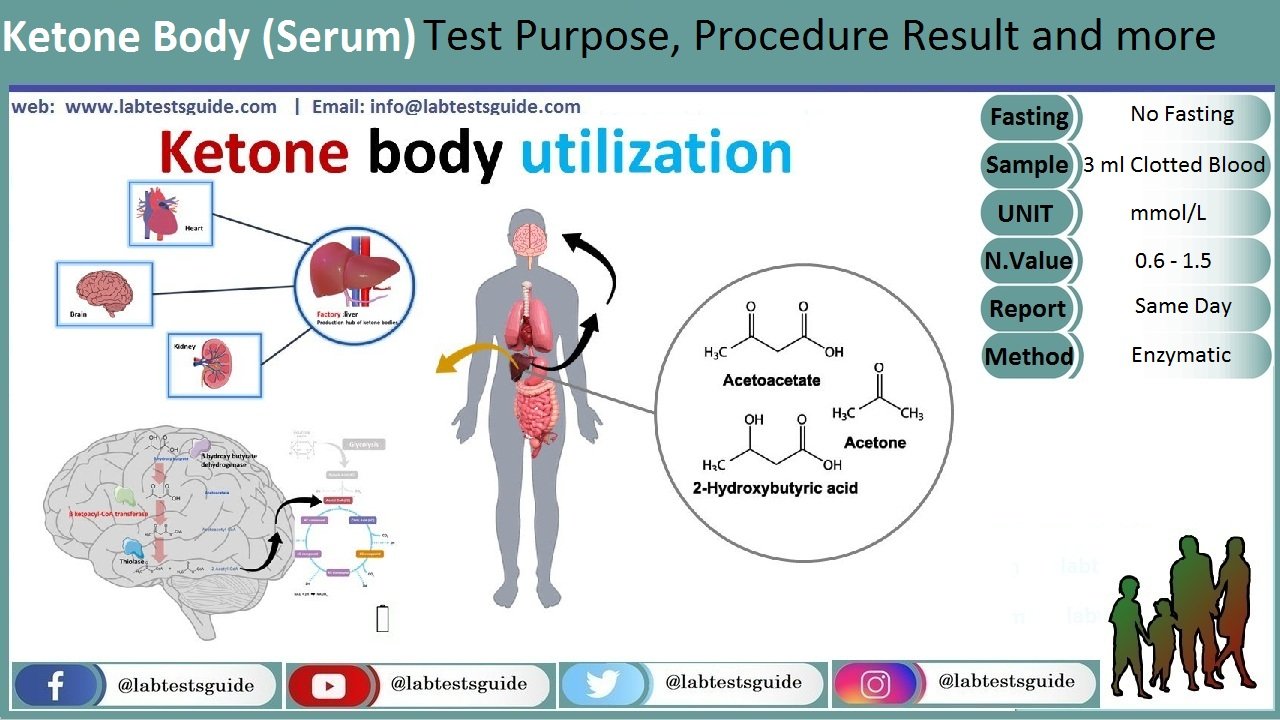
Ketones (ketone bodies) are by-products of fat metabolism, and ketone blood tests are primarily used to detect, and monitor a serious, sometimes life-threatening condition called diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA).
| Also Known as | Serum Ketones, Plasma Ketones, Beta-hydroxybutyrate, Ketone Bodies, Beta-hydroxybutyric Acid , Acetoacetate, Acetoacetic Acid, Acetone, Ketone Body, Blood Ketone |
| Test Purpose | |
| Test Preparations | No Special Preparation Required |
| Test Components | Keytone Body |
| Specimen | 2 ML (0.5 ML Min.) Serum From 1 SST. Ship Refrigerated Or Frozen. |
| Stability Room | 6 Hrs |
| Stability Refrigerated | 12 Hrs |
| Stability Frozen | 4 Weeks |
| Method | Enzymatic |
| Download Report | Not Available |
Why get tested:
To determine the amount of ketones (ketones, acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone) in your blood to help diagnose life-threatening problems such as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) or alcoholic ketoacidosis (AKA)
When to get tested:
When you have symptoms associated with ketoacidosis, such as increased urination, excessive thirst, dehydration, rapid breathing, and shortness of breath.
Normal Value:
Blood Ketone Bodies: 0.6 – 1.5 mmol/l
Signs And Symptoms
- This condition is seen in carbohydrates deficiency or starvation or frequent vomiting.
- The patient will have a thirst and a dry mouth.
- Increased frequency of urine.
- There is easy fatigue.
- There may be nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
- There is a fruity odor breath.
- Difficult in concentration and confusion.
- This condition may become very serious if not treated in time.
Laboratory Diagnosis
- Blood glucose: level is 300 to 500 mg/dL or higher.
- Ketones bodies: These are positive in the urine and their level in the blood is increased.
- Electrolytes: Sodium is decreased.
- Potassium is increased.
- Blood gasses: There is metabolic acidosis.
- The pH is low.
- Bicarbonate markedly decreased.
Increased Ketones In:
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis
- Acute illness, especially in children (febrile illness, Gastroenteritis, dehydration)
- Alcoholic Ketoacidosis (similar to Starvation Ketosis)
- Starvation Ketosis
- Ketoacids increase 10 fold to >1 mmol/L after 3 days of Fasting
- Type I Glycogen Storage Disease (Von Gierke’s Disease)
- Isopropanol Ingestion (Isopropyl Alcohol or Rubbing Alcohol)
- Only found on acetone testing
- Does NOT raise serum Beta-Hydroxybutyrate levels (most common modern day testing modality)
- Does not result in a Metabolic Acidosis with Anion Gap
Keywords: Bodies, Ketone, Ketone Bodies, ketone body, Ketone bodies (substance), Ketone bodies, Ketone body, Ketone body (substance), Ketone Bodies [Chemical/Ingredient], body ketone, bodies ketones, ketone bodies, body ketones, Ketone body analyte
Possible References Used