The Anti B titer test is a blood test used to measure the levels of antibodies to the B antigen in the blood. It helps determine an individual’s blood type and compatibility for blood transfusions.
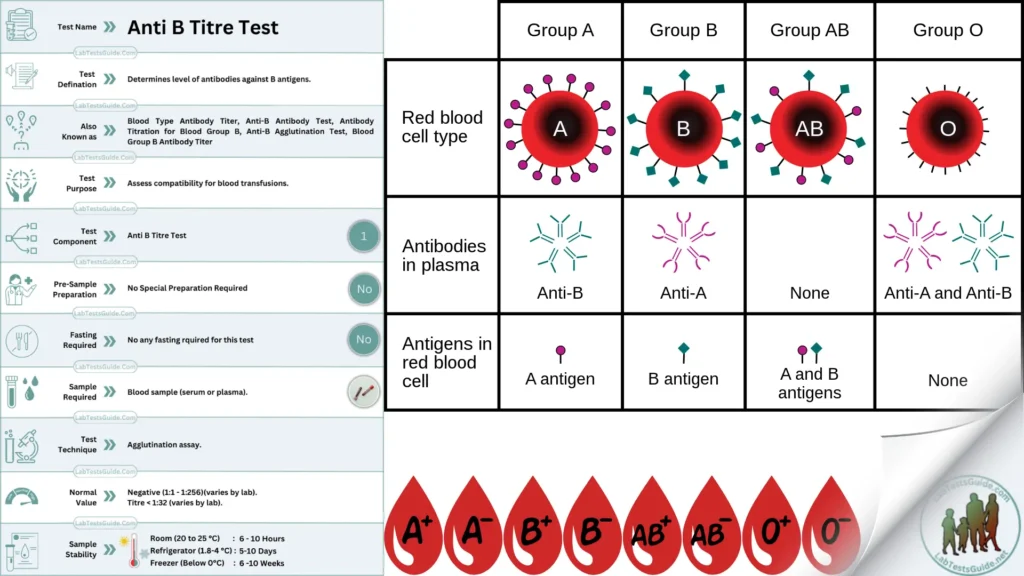
Understanding the levels of these antibodies is important for many reasons, particularly in the fields of blood transfusion and organ transplantation. An accurate Anti B titer can help ensure compatibility between donors and recipients, reducing the likelihood of a harmful immune reaction. During pregnancy, this test is also important to evaluate the risks of Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn (HDN).
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
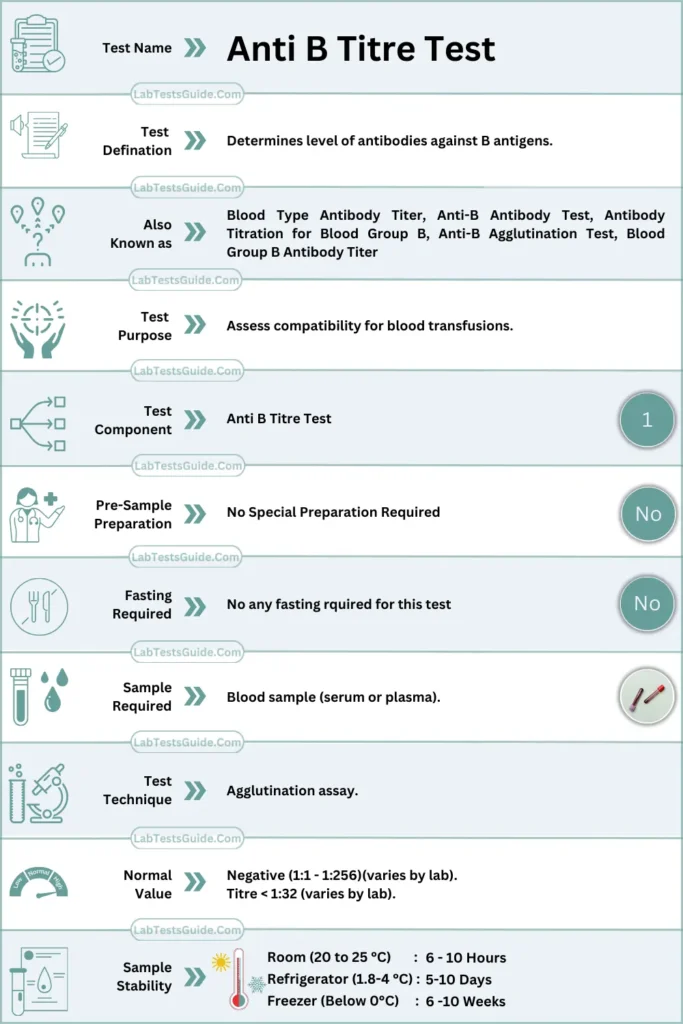
| Test Name | Anti B Titre Test For Blood Transfusions |
| Test Definition | Determines level of antibodies against B antigens. |
| Test Purpose | Assess compatibility for blood transfusions. |
| Other Names | Blood Type Antibody Titer, Anti-B Antibody Test. |
| Test Components | Blood sample, reagents for agglutination. |
| Pre-Sample Prep | None required. |
| Fasting Required | Not necessary. |
| Required Sample | Blood sample (serum or plasma). |
| Test Technique | Agglutination assay. |
| Normal Values | Titre < 1:32 (varies by lab). |
| Sample Stability | Room Temperature (20 – 25 °C): 6 – 10 Hours Refregerator (1.8 – 4 °C): 5-10 Days Freezer (Below 0 °C): 6 -10 Weeks |
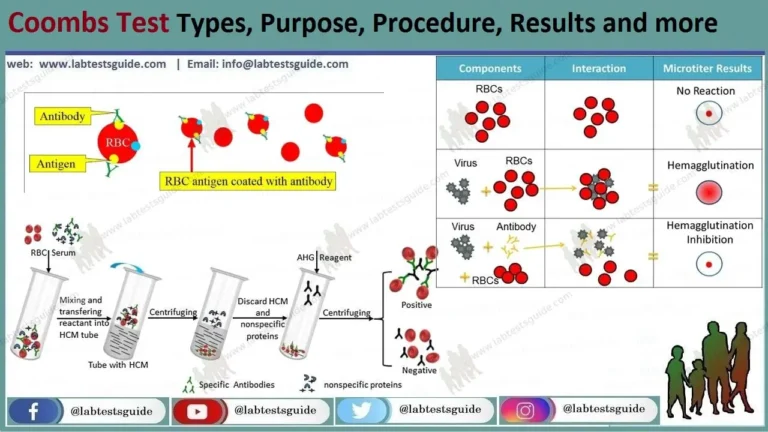
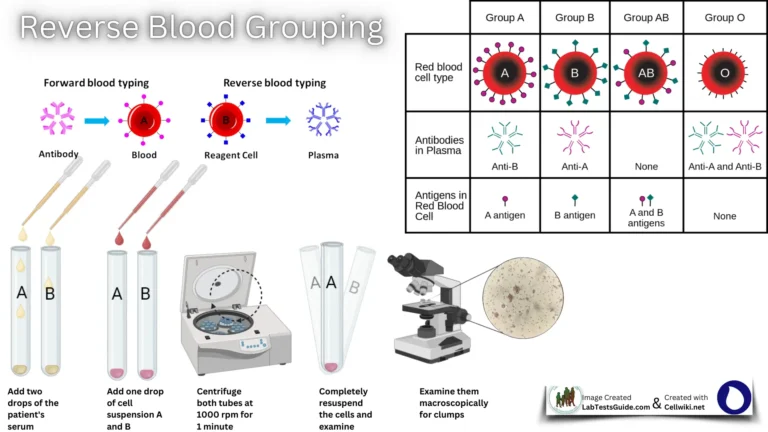
What is the Anti B Titre Test?
The Anti B Titre Test is a blood test that checks for antibodies against B antigens in the blood. These antibodies can cause serious reactions if a person receives blood with B antigens they’re allergic to.
Test Purpose:
The test measures the anti-B titer to determine whether the body’s immune system responds to foreign antigens.
The objective of the Anti B titer test is to:
- Evaluate compatibility for blood transfusions.
- Determine the presence and concentration of anti-B antibodies.
- Prevent adverse reactions in recipients.
- Ensure safe blood group matching.
- Guide clinical decisions regarding transfusions.
- Verify suitability for organ transplants.
Who should take the Anti B-Titre test?
- People who are scheduled to receive a blood transfusion
- Pregnant women with blood type A or AB, especially when the father has blood type B
- People with suspected B antigen exposure who are looking for blood typing confirmation
Anti B Titer Test Preparation:
Here is the basic preparation for the Anti B titer test.
- Before the test:
No specific dietary or medication restrictions.
Make sure your healthcare provider is aware of any medications or medical conditions.
Understand the purpose and possible results of the test. - During the test: No specific actions are required during the test.
- After the test: Follow the post-test instructions provided by your healthcare provider.
- Discuss the results and their implications with the healthcare provider.
Anti B Titre Test Normal Range
Here is the normal range of the Anti B Titre Test (varies by lab)
| Test Result Range | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Negative | Insufficient immunity |
| Positive | Sufficient immunity |
| Normal Range | 1:1 – 1:256 |
Anti B Titre Test Interpretation
Here is the Interpretation of the Anti B Titre Test.
| Test Result | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Positive | Sufficient immunity against B antigen |
| Negative | Insufficient immunity against B antigen |
- Positive results typically indicate that the individual has a level of immunity against the B antigen, which is important for protection against certain infections or blood type compatibility.
- Negative results on the “Anti B Titre” test may have implications for blood compatibility and susceptibility to certain infections, and further evaluation may be necessary, especially in medical contexts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the Anti B Titre test?
The Anti B Titre test is a blood test designed to quantify the concentration of Anti-B antibodies in your blood. These antibodies are produced by your immune system to combat foreign antigens, such as the B antigens found on certain red blood cells.
Why is the Anti B Titre test performed?
The Anti B Titre test is essential in determining compatibility in cases of blood transfusion or organ transplantation. It helps to prevent harmful immune responses by identifying potential mismatches. The test also serves to assess risks of Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn during pregnancy.
How is the Anti B Titre test performed?
The Anti B Titre test involves a standard blood draw. A healthcare professional will collect a blood sample from your vein, typically from your elbow crease or the back of your hand.
Are there specific preparations needed for the test?
There is no specific preparation required for the Anti B Titre test. However, it’s crucial to stay hydrated and disclose any medications, supplements, or treatments you are currently using to your doctor.
What do the results of the Anti B Titre test signify?
Results are given as titres, which reflect the concentration of Anti-B antibodies in your blood. Higher titres might suggest an increased risk of immune reactions during blood transfusion, organ transplantation, or a higher likelihood of HDN during pregnancy.
How frequently should I take this test?
Your doctor will determine the frequency of this test based on your specific situation and health history.
What should I do if my Anti B Titre test results are high?
If your Anti B Titre results are high, it’s important to consult with your doctor. They might suggest additional testing or modifications to your treatment plans based on these results.
Are there risks associated with the Anti B Titre test?
The risks associated with the Anti B Titre test are minimal and are similar to those of any blood draw. These might include slight pain or bruising at the site of the needle insertion, or feeling faint or lightheaded.
Can medications affect the results of the Anti B Titre test?
Yes, certain medications might impact the results of the Anti B Titre test. Always inform your doctor of any medication or supplements you are currently taking.
What factors can influence the Anti B Titre test results?
Several factors, including your current health status, medications you’re taking, or recent immunizations, can influence the test results. Always discuss these factors with your doctor prior to the test.
Who should get an Anti B Titre test?
Those needing a blood transfusion or organ transplant may require an Anti B Titre test to ensure compatibility. Pregnant women, especially those with O blood type carrying a fetus with B or AB blood type, might also need this test to assess risk of HDN.
How can I lower my Anti B Titre?
The level of Anti B Titre in your blood is not something you can typically control or lower with lifestyle modifications. If you have concerns, it’s best to consult with your doctor.
Are there alternatives to the Anti B Titre test?
While there are other tests that assess blood compatibility and risk of hemolytic disease, the Anti B Titre test is unique in its specific measurement of Anti-B antibodies.
Which doctor should I consult if my Anti B Titre test results are abnormal?
Abnormal Anti B Titre test results should be discussed with your primary care doctor or a hematologist, depending on the reason for the test.
Are there different types of Anti-B antibodies?
Yes, there are two types of Anti-B antibodies: IgM and IgG. IgM antibodies are typically involved in immediate reactions to blood group incompatibilities, while IgG antibodies can cross the placenta and potentially cause HDN.
Anti B Titre test results is crucial in ensuring the safety of procedures like blood transfusions and organ transplants, and in predicting risks during pregnancy. Always discuss your results and potential next steps with your doctor. This test is a tool aiding medical professionals in making informed decisions regarding your health care but does not independently diagnose or rule out specific conditions.