The inhibin A test is indeed conducted to measure the levels of inhibin A in a pregnant woman’s blood. It’s utilized as part of the maternal serum quadruple screening test to assess the risk of Down syndrome in the fetus. Inhibin A is indeed produced by the placenta during pregnancy, and deviations from normal levels can indicate a higher risk of chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome.
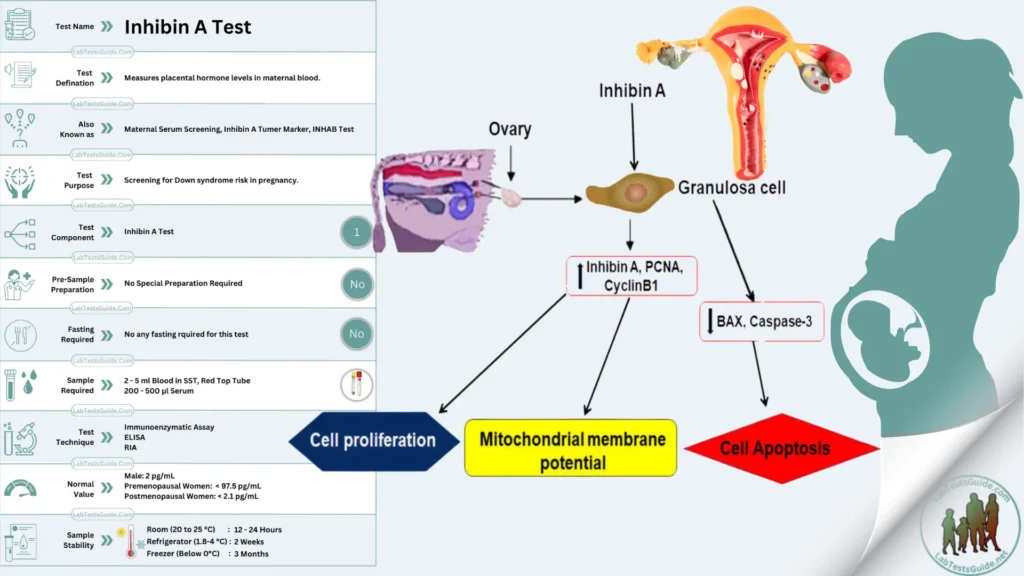
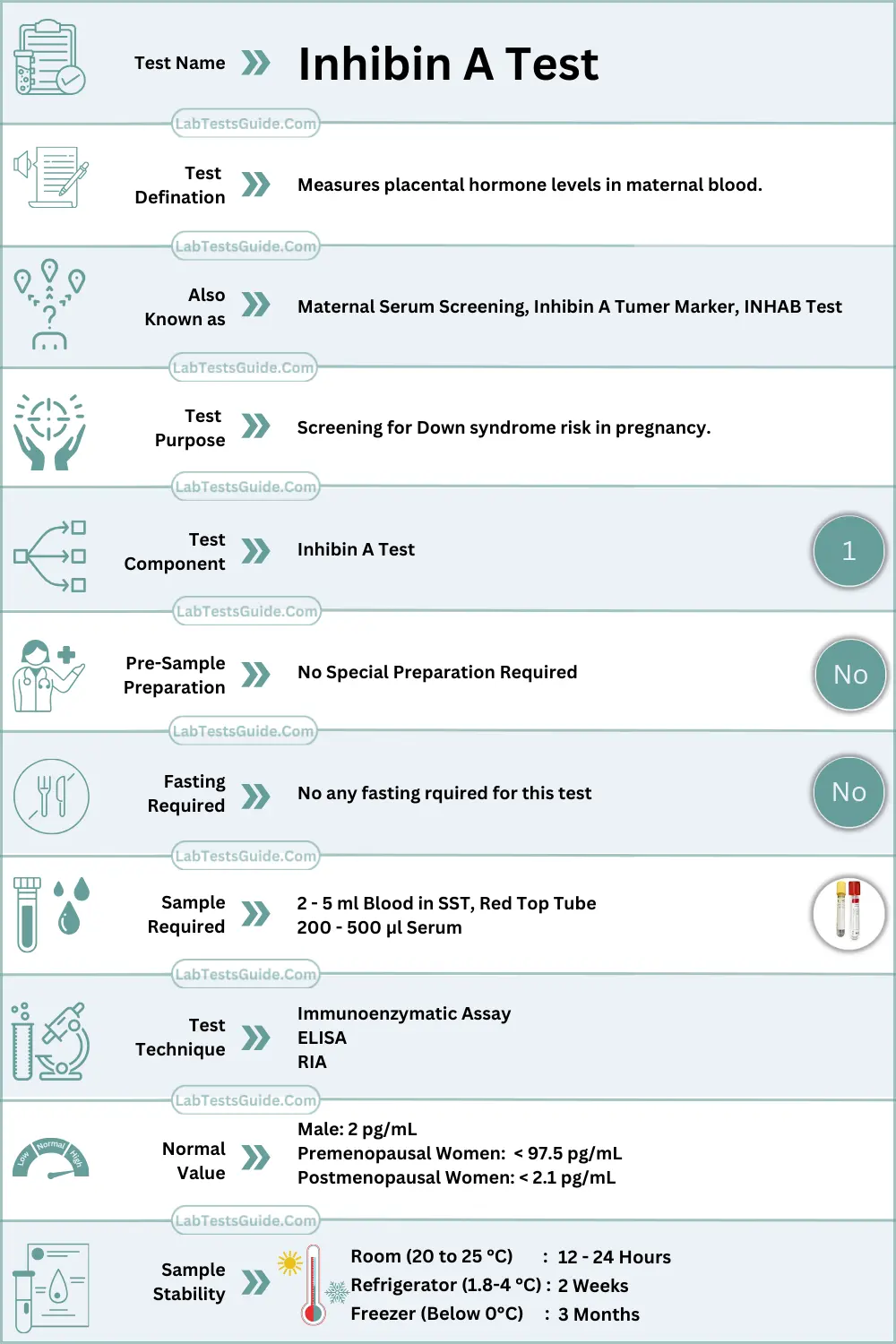
| Test Name | Inhibin A Test |
|---|---|
| Test Definition | Measures placental hormone levels in maternal blood. |
| Test Purpose | Screening for Down syndrome risk in pregnancy. |
| Also Known As | Maternal Serum Screening, Inhibin A Tumer Marker, INHAB Test |
| Test Components | Inhibin A Test |
| Pre-Sample Prep | No special preparation required. |
| Fasting Requirement | Not required |
| Required Sample | 2 – 5 ml Blood in SST, Red Top Tube 200 – 500 μl Serum |
| Test Technique | Immunoenzymatic Assay ELISA RIA |
| Normal Values | Varies with gestational age and reference range. (See Below) |
| Sample Stability | Room Temperature (20 – 25 °C): 12-24 Hours Refregerator (2-8 °C): 2 weeks Freezer (Below 0 °C): 3 Months |
Understand Your Test Results:
Understand your Inhibin A Test Results
AI-powered Lab Test Results Meaning tool 🤖
What is Inhibin A Test ?
Inhibin is a dimeric glycoprotein complex that suppresses the secretion of FSH by the pituitary gland. Inhibin is produced by the gonads; by Sertoli cells in particular in men and by granulosa cells in women. Inhibin plays a vital role in controlling gamete production and embryonic and fetal development. There are two types of inhibin found in the blood; Inhibin A and Inhibin B.
Why Get Tested Inhibin A Test ?
- To aid in the diagnosis of ovarian tumors, often in conjunction with a CA-125 test.
- To assist in diagnosing rare ovarian granulosa cell tumors and occasionally mucinous epithelial ovarian tumors.
- To evaluate the efficacy of treatment for ovarian tumors.
- To monitor for recurrence of ovarian tumors after treatment.
When to get Tested ?
- When there’s suspicion of an ovarian tumor, especially if there’s a pelvic mass detected.
- After receiving a diagnosis of granulosa cell tumor or mucinous epithelial tumor, before initiating treatment.
- At various intervals during and after treatment to monitor the progress and potential recurrence of the tumor.
Purpose of Inhibin A Test:
The purpose of the Inhibin A test is:
Part of prenatal screening involves estimating the likelihood of Down syndrome and certain birth defects in developing fetuses.
This test helps evaluate prenatal health and identify potential risks.
Measures inhibin A levels to assist in risk assessment.
Normally, no special fasting is needed before the test.
Ensures a healthy pregnancy by identifying potential risks and guiding further evaluation.
Pre-Sample Preparation:
No any special preparation required. No specific fasting or dietary restrictions.
Required Sample:
A blood sample will be drawn from a vein.
- 2 – 5 ml Blood in SST, Red Top Tube
- 200 – 500 μl Serum
Normal / Reference Values:
The normal range for inhibin A levels varies depending on sex and menopausal status:
Source 1:
- Males: <5.0 pg/mL
- Females:
- <11 years: <5.0 pg/mL
- 11-17 years: <98 pg/mL
- Premenopausal: <98 pg/mL
- Postmenopausal: <5.0 pg/mL
Source 2:
- The Inhibin A normal range for men across all age groups is < 2pg/ml.
- The Inhibin A normal range for premenopausal women is < 97.5 pg/ml
- The Inhibin A normal range for postmenopausal women is < 2.1 pg/ml
Source 3:
- Men:Less than 2 pg/mL
- Premenopausal Women:Less than 97.5 pg/mL
It’s important to note that premenopausal inhibin A levels can fluctuate throughout the menstrual cycle, being lower in the follicular phase (when eggs mature) and higher in the luteal phase (after ovulation). - Postmenopausal Women:Less than 2.1 pg/mL
Inhibin A Test Result
- Normal result: Low or negative Inhibin A level.
- Abnormal result: High or positive Inhibin A level; further evaluation may be needed.
Discuss results with your doctor for appropriate guidance.
Result Interpretation:
Here is the Interpretation of the Inhibin A Test.
- High levels: May suggest potential risks during pregnancy or birth defects.
- Within normal range: Typically indicates a lower chance of certain problems occurring.
- Healthy pregnancy: Typically seen in uncomplicated pregnancies.
- Low risk of birth defects: Often indicates a lower risk of birth defects.
- Normal Ovarian Function: Suggests healthy ovarian function in women.
- Low levels: This may raise concerns about pregnancy-related risks or conditions.
Understand Your Test Results:
Understand your Inhibin A Test Results
AI-powered Lab Test Results Meaning tool 🤖
FAQs:
What is an inhibin A test?
An inhibin A test is a blood test used to measure the levels of inhibin A hormone in the body.
What is inhibin A hormone?
Inhibin A is a hormone produced by the ovaries in females and the testes in males. In females, it plays a role in regulating the menstrual cycle and fertility.
Why is an inhibin A test done?
It is primarily done as part of fertility testing in women to evaluate ovarian function and to help diagnose certain reproductive disorders.
When is an inhibin A test usually performed?
It is often performed during the early follicular phase of the menstrual cycle, typically on days 2-4.
How is the test performed?
A blood sample is taken, usually from a vein in the arm, and then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
What do the results of an inhibin A test indicate?
Elevated or decreased levels of inhibin A can indicate various reproductive issues such as ovarian dysfunction, ovarian tumors, or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
What are normal inhibin A levels?
Normal ranges can vary depending on the laboratory and the stage of the menstrual cycle, but generally, levels are higher in the follicular phase and lower in the luteal phase.
Are there any risks associated with the test?
The test is generally safe, with minimal risks such as slight discomfort or bruising at the site where the blood is drawn.
Can inhibin A levels be affected by medications or other factors?
Yes, certain medications, such as hormonal contraceptives, can affect inhibin A levels. Pregnancy and menopause can also influence results.
What should I do if my inhibin A levels are abnormal?
If your inhibin A levels are abnormal, your healthcare provider may recommend further testing or treatment depending on the underlying cause. It’s important to discuss the results with your doctor to understand their implications for your health and fertility.