Wright’s stain is a histologic stain that facilitates the differentiation of blood cell types. It is classically a mixture of eosin (red) and methylene blue dyes. It is used primarily to stain peripheral blood smears, urine samples, and bone marrow aspirates which are examined under a light microscope.
Reagents
The dye may be purchased as a powder which is then mixed to methanol or a ready-made solution may be obtained.
- Staining Solution
Wright’s stain powder = 1.0 gm
Water free methanol = 400 ml - Phosphate buffer (0.15M, ph 6.5/6.8)
Potassium dihydrogen phosphate, anhydrous = 0.663 gm
Disodium hydrogen phosphate, anhydrous = 0.256 gm
Distilled water = 100 ml
Storage and Shelf life:
Wright’s Stain should be stored at room temperature and protected from light. Under these conditions it has a shelf life of 52 weeks from the date of manufacture.
Procedure:
- Dip slide for a few seconds in methanol as a fixative step and allow slide to air dry completely.
- Place slide on a level staining rack and place 1.0 ml of the Wright Stain Solution upon the smear 1 – 3 minutes.
- Add 2.0 ml distilled water or Phosphate buffer pH 6.5 and let stand twice as long as 1-3 minuts.
- Rinse stained smear with water or the Phosphate buffer pH 6.5 until the edges show faintly pinkish-red.
- Wipe the underside of the slide and let the slide air dry in a vertical position.
- Examine the slide under the microscope.
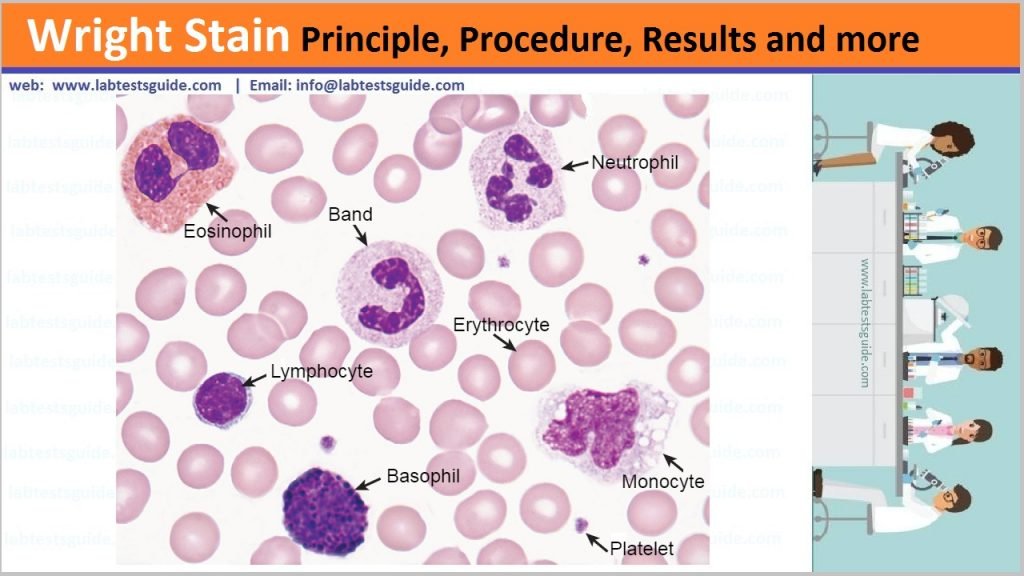
Results:
| Erthrocytes | yellowish-red |
| Polymorphonuclears: Nucleus | dark purple |
| Polymorphonuclears: Granules | reddish-lilac |
| Polymorphonuclears: Cytoplasm | pale-pink |
| Eosinophiles: Nuclei | blue |
| Eosinophiles: Granules | red to orange-red |
| Eosinophiles: Cytoplasm | blue |
| Basophiles: Nucleus | purple to dark blue |
| Basophiles: Granules | very dark purple |
| Lymphocytes: Nuclei | dark purple |
| Lymphocytes: Cytoplasm | sky blue |
| Platelets | violet to purple granules |






One Comment