This test is performed for the diagnosis of an autoimmune disease known as Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). This disease affects synovial joints (like joints of hands, knees, and feet) with subcutaneous nodules. The prevalence rate is 1% (women are affected 3-5% more). There are evidence of RA (Rheumatoid Arthritis) disease in smoker people than non-smokers.
Rheumatoid factor (RF) is circulating in the blood of RA patients. RF is an autoantibody which can attach to other antibodies. It is well-defined as an antibody against the Fc part of the IgG. It is not normally found in the general population (3-5% of healthy population). The rheumatoid factor is not specific for this disease and is found in other diseases both related and non-related to rheumatoid arthritis.
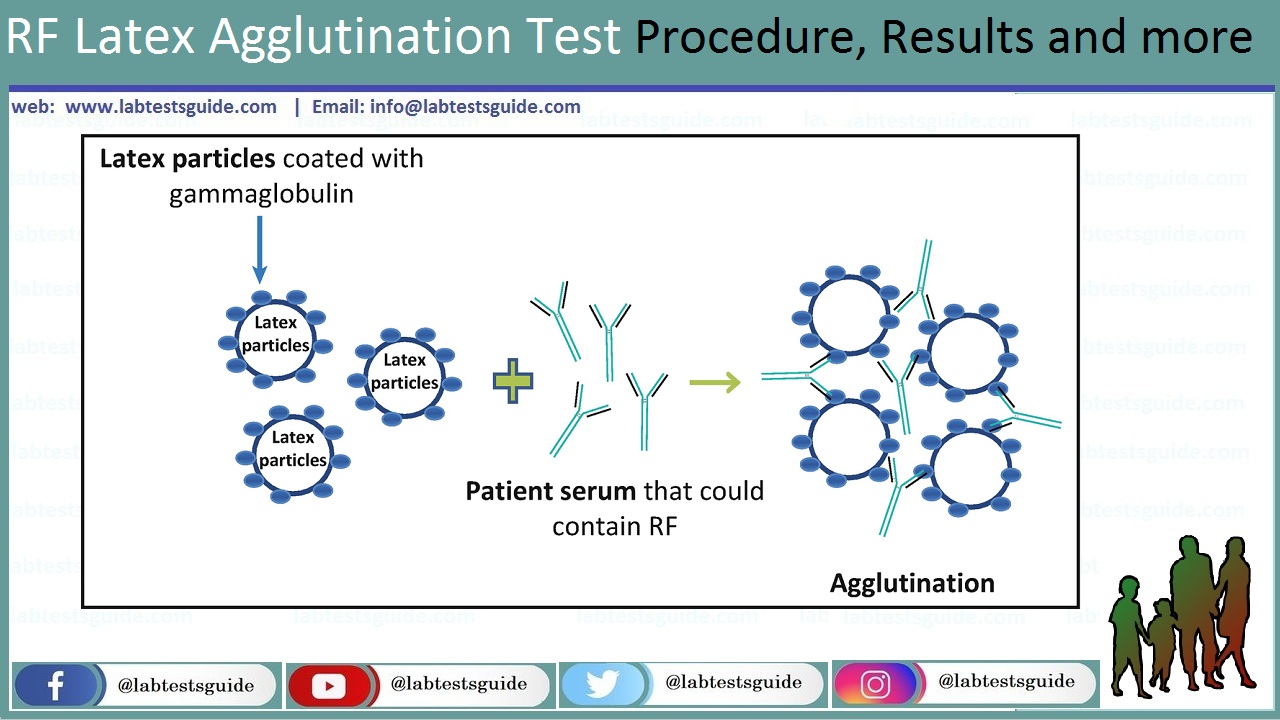
PRINCIPLE:
It is a slide agglutination test. Latex particles coated with human gamma globulins are allowed to react with test serum. Agglutination will be observed if RF is present in the serum.
REQUIREMENTS:
- Serum sample
- Latex reagent
- Positive and negative controls (PC; NC)
- Test card
- Normal saline
- Disposable mixing sticks
- Mechanical rotator (80-100 rpm)
- Test tubes
PROCEDURE:
- Bring the kit reagents and sample to room temperature.
- Place 0.05 ml of the serum into one circle of slide.
- Place similar quantities of positive and negative controls in separate circles.
- Gently mix the latex reagent vial (to ensure homogeneity) and place one drop to each of the circle.
- Mix the contents of each circle evenly with disposable sticks and spread over the complete area of the circle.
- Place the slide on mechanical rotator (80-100 rpm) for 2 minutes.
- Examine for agglutination macroscopically.
- Compare the results with positive and negative controls.
RESULTS:
- Agglutination indicates a positive reaction.
- If the RA test is positive, the amount of RF will be equal to 8 IU/ml or above
- In case of a negative reaction (no agglutination) less than 8 IU/ml.
SEMI QUANTITATIVE TEST:
If RF test is positive, serial dilutions of the serum are tested. The highest dilution factor of the serum producing positive result will be the titre. Prepare double dilutions of serum as follows:
| Tube No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | – |
| Serum (ml) | 0.5 | 0.5 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Saline (ml) | – | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | – |
| 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5Discarded | |
| Dilutions | 1/1 | 1/2 | 1/4 | 1/8 | 1/16 | 1/32 | – |
| Concentration IU/ml | 0.3 | 0.6 | 1.2 | 2.4 | 4.8 | 9.6 | – |
QUALITY CONTROL:
Positive and negative controls in the kit must be run to the parallel with every test which is being performed.
INTERPRETATION OF RF TEST:
- The test is not entirely specific and false positive results are seen commonly (3-5%).
- RF test can become false positive in following diseases:
- Chronic liver infection
- Leukemia
- Infectious mononucleosis
- Systemic Lupus erythematosus
- Bacterial endocarditis
- Systemic sclerosis
NOTE:
- Negative results do not rule out the possibility of RA as up to 20% of rheumatoid arthritis patients remain negative for rheumatic factor (Sero-negative rheumatoid arthritis).
- It is recommended to make the final diagnosis with clinical examination and Rose Waaler test.



