HbA1c Test Purpose, Procedure, Result Interpretation, Report Format etc
Glycated hemoglobin is a form of hemoglobin that is chemically linked to a sugar. Most monosaccharides, including glucose, galactose and fructose, spontaneously bond with hemoglobin, when present in the bloodstream of humans.
| Test Name | HbA1c; GLYCOSYLATED HEMOGLOBIN |
| Test Purpose | This assay is useful for diagnosing Diabetes and evaluating long term control of blood glucose concentrations in diabetic patients. It reflects the mean glucose concentration over the previous period of 8 to 12 weeks and is a better indicator of long term glycemic control as compared with blood glucose levels due to lesser day to day variation. |
| Pretest Preparations | No special preparation required |
| Category | Diabetes |
| Specimen | 3 mL (2 mL min.) whole blood in 1 Lavender Top (EDTA) tube. Ship refrigerated. DO NOT FREEZE. |
| Stability Room | 6 hrs |
| Stability Refrigerated | 1 week |
| Stability Frozen | NA |
| Method | High Performance Liquid Chromatography, NGSP certified |
Also Known as: A1c, HbA1c, Glycohemoglobin, Glycated Hemoglobin, Glycosylated Hemoglobin,Hemoglobin A1C, HgbA1c
Test Purpose:
- This test is used to monitor diabetes control.
- This test tells us the patient average glucose index over a long period of time (2 to 3 months).
- It tracks glucose in the milder form of diabetes.
- It helps to determine which type of drugs may be needed.
- Its measurement is of value in a specific group of patients like:
- Diabetic children
- Diabetic patients whose renal threshold for glucose is abnormal.
- Unstable diabetes type I, taking insulin.
- Type II diabetic women who become pregnant.
- Patients with changing dietary or other habits.
- It should be repeated every 3 to 4 months.
eAG & HbA1c Calculator:
eAG & HbA1c Converter
• HbA1c to eAG (mg/dL): (28.7 × A1c) – 46.7
• HbA1c to eAG (mmol/L): (1.59 × A1c) – 2.59
• eAG (mg/dL) to A1c: (Glucose + 46.7) ÷ 28.7
• eAG (mmol/L) to A1c: (Glucose + 2.59) ÷ 1.59
• mg/dl to mmol/L Formula mg/dL /18
• mmol/L to mg/dl Formula mmol/L x 18
*Interpretation is based on standard clinical ranges. Single readings (Fasting/Random) may vary from actual A1c lab results.
Sample Required:
- The blood sample is taken in the EDTA 3 to 4 ml.
- Washed RBC or hemolysate is prepared and this is stable for 4 to 7 days at 4 °C.
- A blood sample can be drawn at any time.
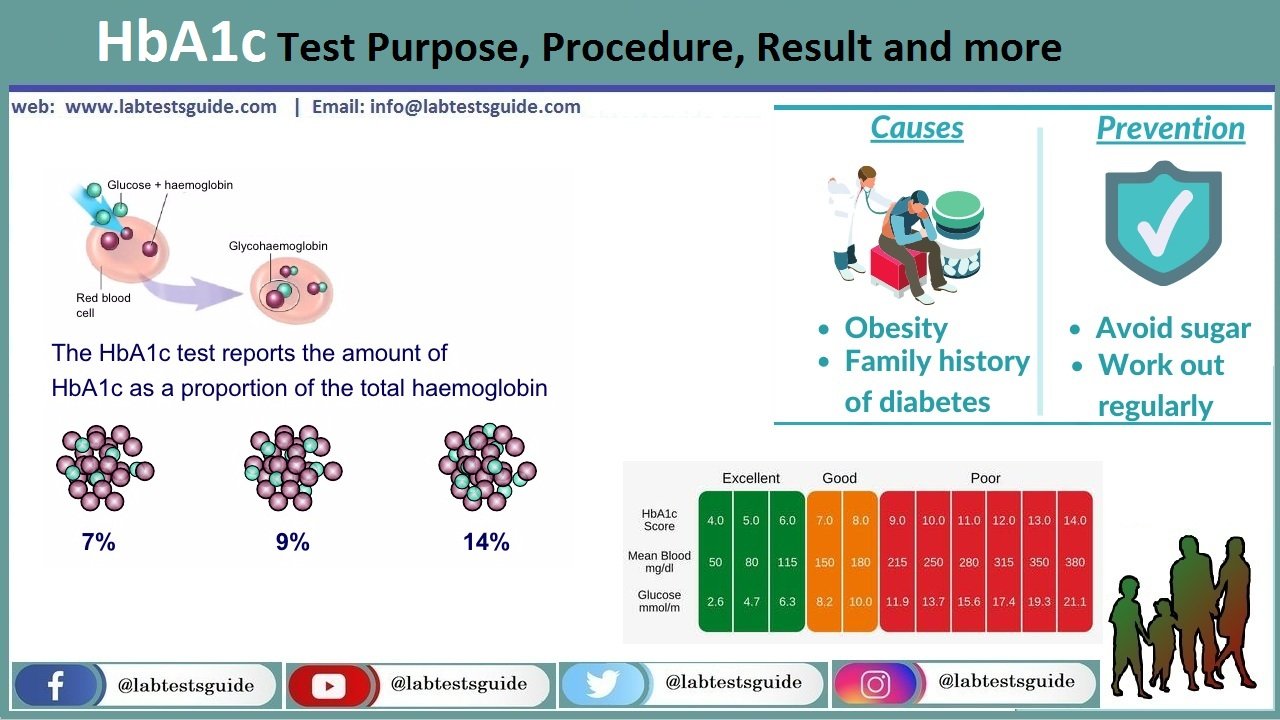
HbA1c Normal Values:
Source 1
- HbA1 c (% of total Hb) = 4.0 to 5.2
- Hb A1 (% of total Hb) = 5.0 to 7.5
Source 2
- Non Diabetic adult = 2.2 to 4.8 %.
- Non Diabetic child = 1.8 to 4.0 % .
- Prediabetic = 5.7 to 6.4 %
- Diabetics = >6.5 %
- Diabetic HbA1c = > 8.1 % = corresponds with glucose >200 mg/dl.
Diabetic Control And HbA1c
- Good diabetic control = 2.5 to 5.9 %.
- Fair diabetic control = 6 to 8 %.
- Poor diabetic control = > 8 %.
- (Values may vary according to the lab)
The following table gives a recommendation for the treatment:
| HbA1c level | mg/dL | mmol/L | Interpretation |
| 4 | 68 | 3.8 | non-diabetic |
| 5 | 97 | 5.4 | non-diabetic |
| 6 | 125 | 7.0 | non-diabetic |
| 7 | 154 | 8.5 | ADA target |
| 8 | 183 | 10.1 | treatment needed |
| 9 | 212 | 11.7 | treatment needed |
| 10 | 240 | 13.3 | treatment needed |
| 11 | 269 | 14.9 | treatment needed |
| 12 | 298 | 16.5 | treatment needed |
| 13 | 326 | 18.0 | treatment needed |
| 14 | 355 | 19.7 | treatment needed |
HbA1c And Estimated Blood Glucose Level:
| HbA1c level | Glucose level mg/dL |
| 4% | 68 |
| 5% | 97 |
| 6% | 125 |
| 7% | 154 |
| 8% | 183 |
| 9% | 212 |
| 10% | 240 |
| 11% | 269 |
| 12% | 298 |
| 15% | 384 |
| 18% | 470 |
| 20% | 527 |
| 25% | 671 |
mg/dl to mmol/L Formula = mg/dL /18
mmol/L to mg/dl Formula = mmol/L x 18
Increased Level Is Seen In:
- Newly diagnosed diabetic patient.
- Uncontrolled diabetic patient.
- Nondiabetic hyperglycemia is seen in:
- Cushing’s syndrome.
- Acromegaly.
- Corticosteroids therapy.
- Pheochromocytoma.
- Acute stress.
- Glucagonoma.
- Patient with splenectomy.
- Alcohol toxicity.
- Iron deficiency anemia.
- Lead toxicity.
Decreased HbA1c Level Is Seen In:
- Hemolytic anemia.
- Chronic blood loss.
- Chronic renal failure.
- Pregnancy.
🧠 AI-Powered Test Result Analysis:
Understand your HbA1c Test Results
AI-powered Lab Test Results Meaning tool 🤖
📥 Download HbA1c Test Lab Report Format
Get the demo report format for HbA1c Test in your preferred format. These templates are fully editable and professional.
How to Download?
| File Description | Format |
|---|---|
Glycated Hemoglobin (HbA1c) Test Report Format (Image) | .PNG ⬇️ |
Glycated Hemoglobin (HbA1c) Test Report Format (MS Word) | .DOCX ⬇️ |
Glycated Hemoglobin (HbA1c) Test Report Format (MS Excel) | .XLSX ⬇️ |
Glycated Hemoglobin (HbA1c) Test Report Format (PDF) | .PDF ⬇️ |