Aerobic Wound Culture Test – Procedure, Results, Interpretation & Uses
An aerobic wound culture test identifies specific bacteria causing an infection in a wound by collecting a sample (swab, fluid, tissue), culturing the organisms in a laboratory with oxygen (aerobic conditions), and then performing sensitivity tests to find the best antibiotics, helping doctors choose the appropriate treatment.

Quick Facts:
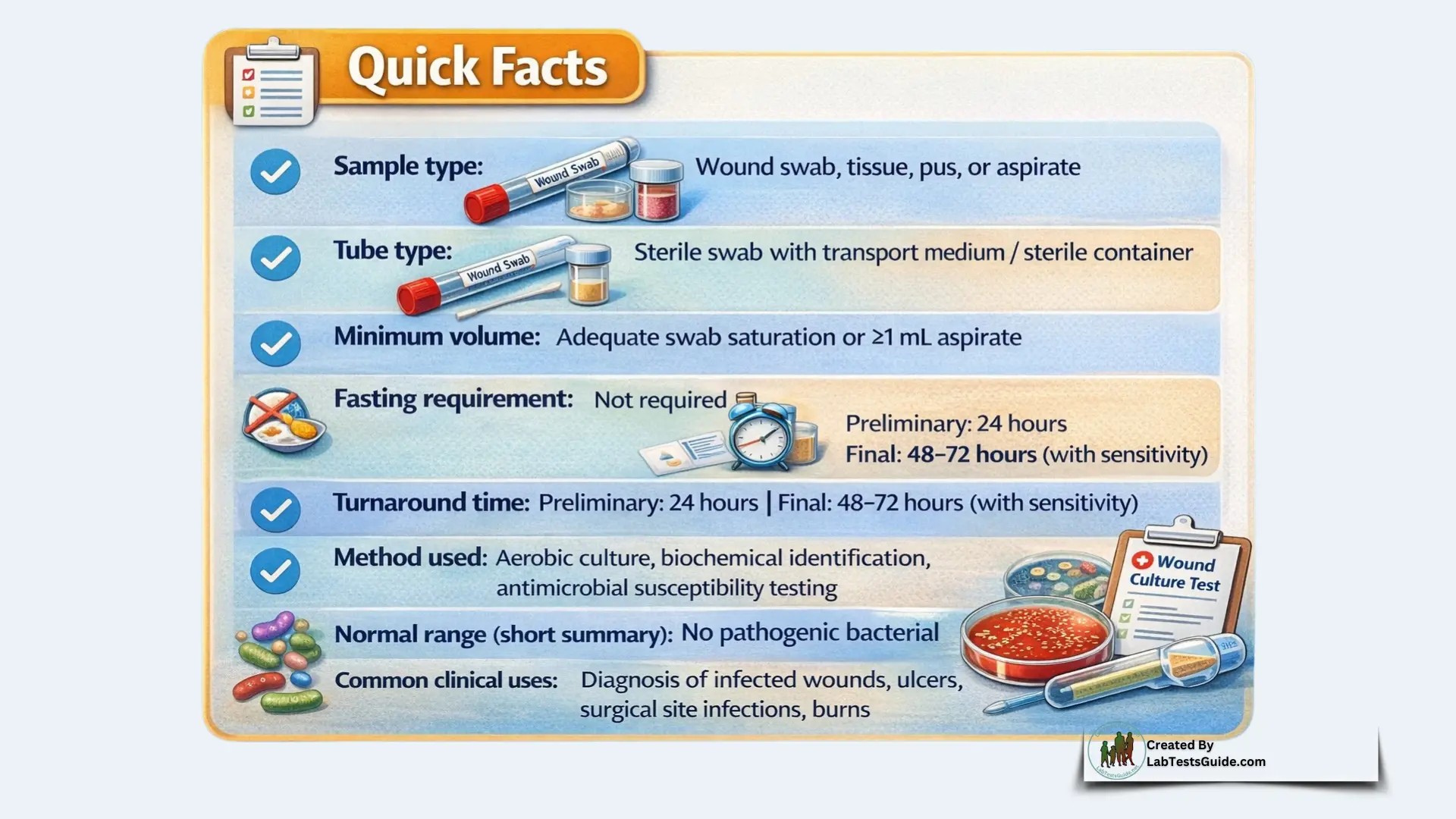
- Sample type: Wound swab, tissue, pus, or aspirate
- Tube type: Sterile swab with transport medium / sterile container
- Minimum volume: Adequate swab saturation or ≥1 mL aspirate
- Fasting requirement: Not required
- Turnaround time: Preliminary: 24 hours | Final: 48–72 hours (with sensitivity)
- Method used: Aerobic culture, biochemical identification, antimicrobial susceptibility testing
- Normal range (short summary): No pathogenic bacterial growth
- Common clinical uses: Diagnosis of infected wounds, ulcers, surgical site infections, burns
What is Aerobic Wound Culture Test?
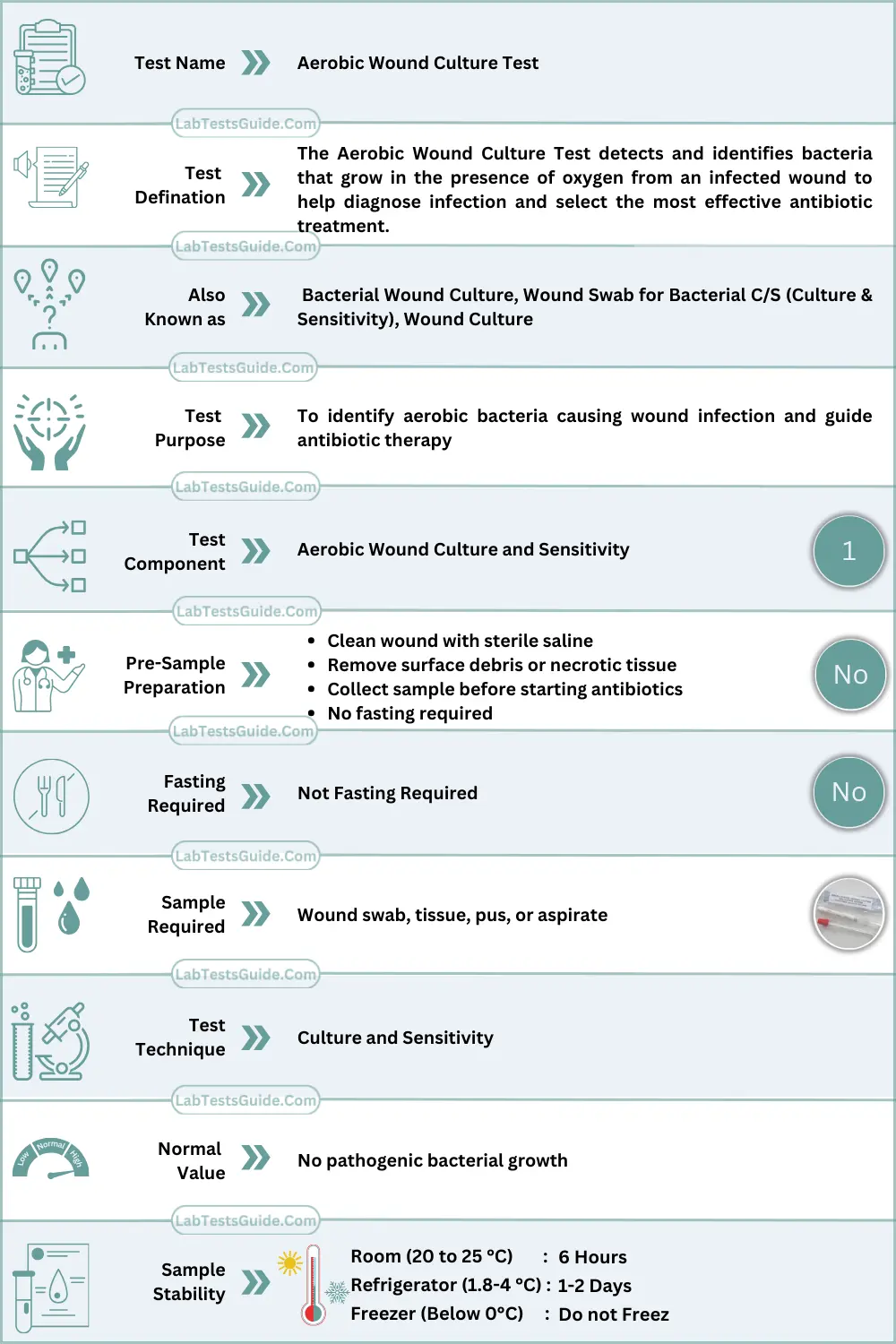
The Aerobic Wound Culture Test detects and identifies bacteria that grow in the presence of oxygen from an infected wound to help diagnose infection and select the most effective antibiotic treatment.
Why is Aerobic Wound Culture Test Done? (Indications)
For Patients / General Use
- Non-healing wounds
- Pus or discharge from a wound
- Redness, warmth, swelling, or pain
- Fever with an open wound
- Diabetic foot ulcers or pressure sores
For Doctors / Clinical Use
- Identify causative aerobic bacteria
- Guide antibiotic selection (culture & sensitivity)
- Monitor treatment response
- Diagnose surgical site or burn wound infections
- Differentiate colonization vs. true infection
How the Aerobic Wound Culture Test Works (Principle / Methodology)
The specimen is inoculated onto aerobic culture media such as blood agar and MacConkey agar and incubated in the presence of oxygen. Bacterial growth is identified using colony morphology, Gram staining, and biochemical tests. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) is performed to determine effective antibiotics.
Aerobic Wound Culture Test Specimen Requirements & Collection:

- Specimen type: Wound swab, tissue biopsy, pus, or aspirate
- Tube type: Sterile swab with transport medium / sterile container
- Volume: Adequate sample; ≥1 mL for aspirates
- Patient preparation: Clean wound surface before sampling
- Collection steps:
- Clean wound with sterile saline
- Collect deep tissue or exudate (avoid surface contamination)
- Place swab immediately in transport medium
- Transport & storage:
- Transport within 2 hours
- Room temperature preferred
- Avoid refrigeration unless delayed
Aerobic Wound Culture Test Interpretation of Results
Positive Growth (Abnormal Findings)
Causes
- Bacterial wound infection
- Surgical site infection
- Diabetic foot infection
- Traumatic or burn wound contamination
Common Organisms
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Streptococcus pyogenes
- Escherichia coli
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Clinical Relevance
- Confirms infection
- Guides targeted antibiotic therapy
- Prevents complications like sepsis
No Growth / Normal Findings
Causes
- No aerobic bacterial infection
- Prior antibiotic therapy
- Inadequate specimen
Clinical Relevance
- Consider anaerobic culture or repeat sampling if suspicion remains
🧠 AI-Powered Test Result Analysis:
Understand your Aerobic Wound Culture Test – Procedure, Results, Interpretation & Uses Results
AI-powered Lab Test Results Meaning tool 🤖
📥 Download Aerobic Wound Culture Lab Report Format
Get the demo report format for Aerobic Wound Culturein your preferred format. These templates are fully editable and professional.
How to Download?
| File Description | Format |
|---|---|
Aerobic Wound Culture Test No Growth (Negative) Demo Report Format (Image) | .PNG |
Aerobic Wound Culture Test No Growth (Negative) Demo Report Format (MS Word) | .DOCX |
Aerobic Wound Culture Test No Growth (Negative) Demo Report Format (MS Excel) | .XLSX |
Aerobic Wound Culture Test No Growth (Negative) Demo Report Format (PDF) |
| File Description | Format |
|---|---|
Aerobic Wound Culture Test Staph Aureus Growth (Positive) Demo Report Format (Image) | .PNG |
Aerobic Wound Culture Test Staph Aureus Growth (Positive) Demo Report Format (MS Word) | .DOCX |
Aerobic Wound Culture Test Staph Aureus Growth (Positive) Demo Report Format (MS Excel) | .XLSX |
Aerobic Wound Culture Test Staph Aureus Growth (Positive) Demo Report Format (PDF) |
Aerobic Wound Culture Test Interfering Factors / Pre-Analytical Errors
- Medications: Prior antibiotic use may suppress growth
- Sample handling: Delayed transport reduces recovery
- Biological variation: Colonizing flora vs. true pathogens
- Improper collection: Surface swabs may give misleading results
Nursing / Phlebotomy Notes
- Use sterile swab with transport medium
- Label specimen correctly (site, date, time)
- Collect before starting antibiotics
- Transport promptly
- Use standard infection control precautions
Lab Student Key Points
- Collect deep wound samples, not surface contaminants
- Proper transport is critical for accuracy
- Always correlate with clinical findings
- Perform sensitivity testing on significant isolates