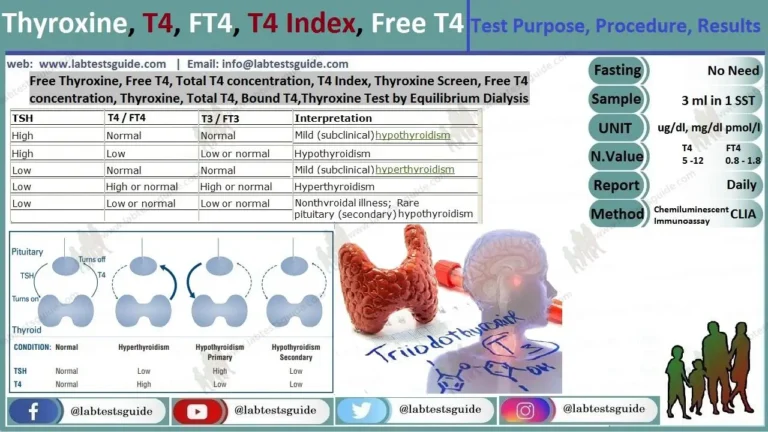
This test measures the amount of very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) in your blood. VLDL cholesterol is a type of blood fat. It’s considered one of the “bad” forms of cholesterol, along with LDL cholesterol and triglycerides. This is because high levels cholesterol can clog your arteries and lead to a heart attack.
Also Known As: VLDL-C, VLDL, Very Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol
Test Panel: Cholesterol, HDL Cholesterol, LDL Cholesterol, Triglycerides, VLDL Cholesterol, Non-High Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol
Why Get Tested:
- Advised to evaluate the coronary artery disease risk.
- This can be advised as the part of a lipid profile.
When to Get Tested:
- Screening: as part of a regular health exam with a lipid profile.
- when no risk factors for heart disease are present.
- once every four to six years in adults.
- children should have a lipid profile screening at least once between the ages of 9 and 11 and then again between the ages of 17 and 21.
Sample Required:
- This test is done on the serum.
- Fasting sample is preferred. Advised the patient to fast for 12 to 14 hours.
- This test can be done on plasma as well.
- Can store serum or plasma at 4 °C for 4 days (can keep for 5 to 7 days).
Normal Value:
- 7 to 32 mg/dL.
Calculation of VLDL
The VLDL can be calculated by the following formula:
- VLDL = Triglycerides ÷ 5
Increased VLDL is seen in:
- Nephrotic syndrome.
- Glycogen storage diseases.
- Familial LDL lipoproteinemia.
- Hypothyroidism.
- Chronic liver disease.
- Liver cell carcinoma.
- Gammopathies.
- Cushing syndrome.
- Familial hypercholesterolemia.
Decreased VLDL is seen in:
- Hypoproteinemia.
- Hyperthyroidism.
- Familial hypolipoproteinemia.
Table showing the summary of characteristics of the lipoproteins
| Characteristics | Chylomicron | HDL | LDL | VLDL |
| PLasma appearance | Creamy layer, slightly turbid | Clear | Clear, or yellow-orange tint | Turbid to opaque |
| Size (diameter nm) | >70.0 | 4 to 10 | 19.6 to 22.7 | 25 to 70 |
| Electrophoretic mobility | Origin | α – region | β – region | Pre – β region |
| Molecular weight | 0.4 to 30 x 109 | 3.6 x 109 | 2.75 x 109 | 5 to 10 x 109 |
| Synthesized in (Tissue of origin) | Intestine | Intestine and liver | Intravascular | Liver and intestine |
| Composition by weight in % | ||||
| Cholesterol esterified | 5 | 38 | 49 | 11 to 14 |
| Cholesterol unesterified | 2 | 10 | 13 | 5 to 8 |
| Triglycerides | 84 | 9 | 11 | 44 to 60 |
| Phospholipids | 7 | 22 | 27 | 20 to 23 |
| Proteins | 2 | 21 | 23 | 4 to 11 |
| Triglycerides | Markedly raised | Normal | Normal/ Raised | Moderately to Markedly raised |
| Clinical significance of | Pancreatitis and acute abdomen | Decreased risk of CAD | Increased risk of CAD | Increased risk of CAD |
| Functions | Transport dietary lipids to tissue | Carry cholesterol from tissue to liver | Carries cholesterol to tissue | Transport endogenous TG from liver to adipose tissue |