T3 Resin Uptake Test Purpose, Procedure, Results Interpretation and Analyze your Results
The T3 uptake test, also called the T3 resin uptake test, indirectly measures the binding capacity of TBG. Does not measure T3, despite the name.
TBG, short for thyroxine binding globulin, is a protein that can bind to T4 and T3. The T3 uptake test reports the percentage of TBG that is bound to thyroid hormones: a higher percentage of T3 uptake means more TBG bound to T4 or T3. This test can be useful when abnormalities in thyroid-binding proteins make total T4 levels misleading.
Understand Your Test Results:
Understand your T3 Resin Uptake Test Results
AI-powered Lab Test Results Meaning tool 🤖
| Also Known as | T3, FT3, Total T3, Free T3, Triiodothyronine, Free Triiodothyronine, Total Triiodothyronine, T3 Radioimmunoassay, TT3, T3 Uptake, T3RU, T3 Resin Uptake |
| Test Purpose | 1. To help evaluate thyroid gland function 2. To diagnose thyroid disease, including hyperthyroidism, and determine the cause 3. To monitor effectiveness of treatment of a thyroid disorder |
| Test Preparations | No Special Preparation Required |
| Test Components | Total Triiodothyronine (T3) Free Triiodothyronine (FT3) T3 resin uptake (T3RU) |
| Specimen | 3 ML (1.5 ML Min.) Serum From 1 SST Tube |
| Stability Room | 2 Hrs |
| Stability Refrigerated | 1 Week |
| Stability Frozen | 4 Weeks |
| Method | Chemiluminescent Immunoassay |
| Download Report | Download Report |
The T3 hormone comes in two forms:
- Bound T3, which attaches to protein
- Free T3, which does not attach to anything
The vast majority of thyroid hormones are in the bound form, but it is generally more useful to measure the free form because it is the one that has a clinical effect. This is where the T3 uptake test comes into play. This test provides a way to indirectly measure free T4 levels.
T3 Uptake: The T3 uptake test, also called the T3 resin uptake (T3RU) test, indirectly measures the binding capacity of thyroxine binding globulin TBG. It does not measure T3, despite the name
T3 Uptake Test:
The T3 uptake test, also called the T3 resin uptake test, indirectly measures the binding capacity of TBG. Does not measure T3, despite the name.
TBG, short for thyroxine binding globulin, is a protein that can bind to T4 and T3. The T3 uptake test reports the percentage of TBG that is bound to thyroid hormones: a higher percentage of T3 uptake means more TBG bound to T4 or T3. This test can be useful when abnormalities in thyroid-binding proteins make total T4 levels misleading.
But % T3 uptake is not very useful by itself. The T3 uptake test should be done in conjunction with a total T4 test to calculate free T4, also called the free T4 index. A high level of free T4 can indicate hyperthyroidism, while low levels can indicate hypothyroidism.
Difference between T3 and FT3
T3 has 2 forms: bound and free. Bound T3 is attached to a protein and free T3 is not attached to anything. The free T3 test measures only the amount of free T3. The total T3 test measures both free and bound T3 in your blood.
Defination:
T3:
The thyroid is a small butterfly-shaped gland present in the neck region and is responsible for various functions of the body, including metabolism and growth. Triiodothyronine (T3) is one of the hormones produced by the thyroid gland. This test is done to assess thyroid function and measures the blood level of the T3 hormone. T3 is four times more powerful than T4. Being secreted by the thyroid gland, T3 and T4 play an important role in the growth of the human body.
Free T3:
Free Triiodothyronine test measures the amount of T3 in the blood. Blood levels of T3 are higher or lower because of inadequate or uncontrolled production of the hormone by the thyroid gland because of thyroid dysfunction or pituitary dysfunction. Abnormal levels of T3 in the blood are related tp hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, and slow metabolism.
What other tests might I have along with this test?
You may also need these tests:
- T3 uptake.
- Free T3.
- Total T3.
- Total T4.
- Free T4.
- Free thyroxine index.
- TSH.
- Thyroglobulin (Tg)
- Thyroid scan
- Radioactive iodine uptake test
- Thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI) test
Why Get Tested:
- Triiodothyronine is given to detect thyroid dysfunction.
- It helps diagnose hyperthyroidism, a condition in which the thyroid produces excess hormones.
- This test helps detect infertility in women.
- This test is not affected by protein level and is therefore more accurate.
- An overactive thyroid (overactive thyroid gland function), underactive thyroid (low thyroid gland function), and hypopituitarism (underactive pituitary gland) are some of the disorders that affect the thyroid gland.
When to Get Tested :
You may need a T3 or Ft3 test if you have symptoms of hyperthyroidism. These include:
- Anxiety
- Weightloss
- Tremors in the hands
- Incrise of Cardiac frecuency
- Bulging eyes
- Sleeping problems
- Fatigue
- Low heat tolerance.
- More frequent bowel movements
Sample Required:
3 ML (1.5 ML Min.) Serum From 1 SST Tube
Preparation for Sample:
No need any Preparation for this test
Before the test
Drugs that can increase T3 measurements include:
- Birth control pills
- Clofibrate
- Estrogens
- Methadone
- Certain herbal remedies
Drugs that can decrease T3 measurements include:
- Amiodarone
- Anabolic steroids
- Androgens
- Antithyroid drugs (for example, propylthiouracil and methimazole)
- Lithium
- Phenytoin
- Propranolol
Normal Values
Source 1:
- Total T3 : 0.7 to 2.0 nmol/L
- Free T3 : 2.0 to 7.0 pmol/L
- T3 Uptake: 25 – 50 %
Source 2:
- Triiodothyronine (T3): 80-180 ng/dl
- Free T3: 230-619 pg/dl
Sourse 2 T3 resine Uptake :
| Age | Male (%) | Female (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 to 11 m | 23−34 | 23−36 |
| 1 to 3 y | 24−35 | 24−36 |
| 4 to 6 y | 24−34 | 24−35 |
| 7 to 11 y | 24−33 | 22−35 |
| 12 to 15 y | 25−37 | 23−37 |
| 16 to 18 y | 24−38 | 23−35 |
| >18 y | 24−39 | 24−39 |
Source 3 (T3):
- 0-5 days: 73-288 ng/dL
- 6 days-2 months: 80-275 ng/dL
- 3-11 months: 86-265 ng/dL
- 1-5 years: 92-248 ng/dL
- 6-10 years: 93-231 ng/dL
- 11-19 years: 91-218 ng/dL
- Adult (> or =20 years): 80-200 ng/dL
Source 3 (F T3):
- Cord blood (>37 weeks ) = 15 to 391 pg/dL
- Child and adult = 260 to 480 pg/dL (4.0 to 7.4 pmol/L)
- Pregnancy
- First trimester = 211 to 383 pg/dL
- Second and third trimester = 196 to 338 pg/dL
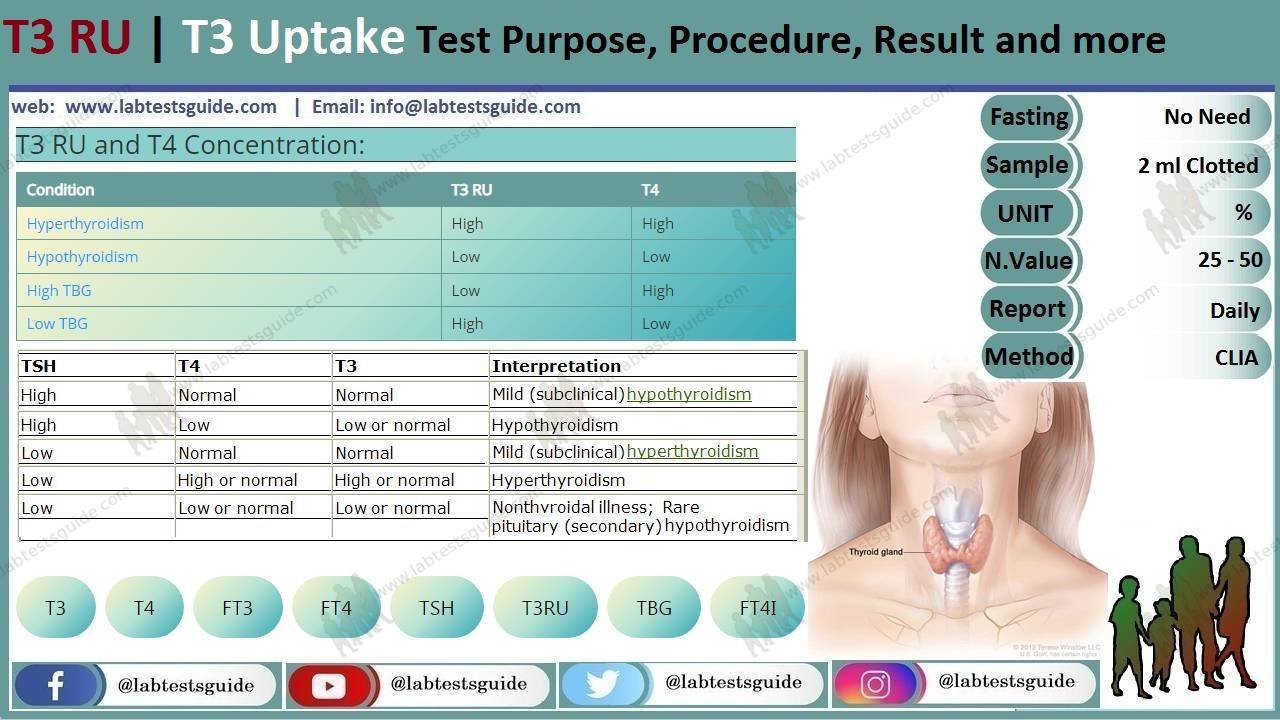
T3 RU and T4 Concentration:
| Condition | T3 RU | T4 |
|---|---|---|
| Hyperthyroidism | High | High |
| Hypothyroidism | Low | Low |
| High TBG | Low | High |
| Low TBG | High | Low |
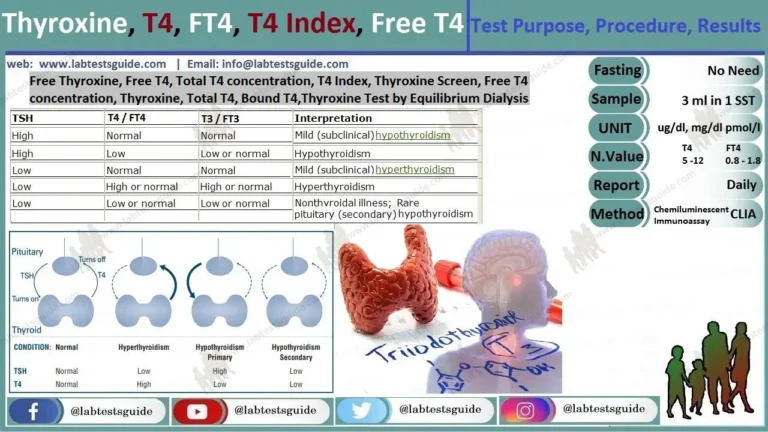
| TSH | Total and Free T4 | Total and Free T3 | MOST LIKELY DIAGNOSIS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal thyroid function (e.g., “euthyroid”) |
| Normal or decreased | Normal or decreased | Decreased | Normal adjustment in thyroid function due to illness (nonthyroidal illness or sick euthyroid syndrome) |
| Increased | Normal | Normal | Subclinical hypothyroidism1; in a person with hypothyroidism on treatment, not enough thyroid hormone is being given |
| Increased | Decreased | Normal of decreased | Hypothyroidism resulting from a problem with the thyroid gland itself (primary hypothyroidism) |
| Normal or increased | Increased | Increased | Hyperthyroidism resulting from a problem with the pituitary gland signals (central hyperthyroidism) or from a problem with the thyroid hormone receptor (thyroid hormone resistance) |
| Decreased | Normal | Normal | Subclinical Hyperthyroidism; in a person with hypothyroidism, too much thyroid hormone is being given |
| Decreased | Normal | Increased | Hyperthyroidism resulting from the thyroid gland making too much active thyroid hormone T3 (uncommon, also known as T3 toxicosis) |
| Decreased | Increased | Increased | Hyperthyroidism resulting from the gland making too much thyroid hormones (primary hyperthyroidism) |
| Decreased | Decreased | Decreased | Hypothyroidism resulting from a problem with the hypothalamus or pituitary signals that govern the thyroid gland (central hypothyroidism) |
Increased Level Of T3:
- Primary Hyperthyroidism like :
- grave’s disease.
- Toxic thyroid adenoma.
- Acute thyroiditis. In the early stages, the thyroid produces more T3.
- Ectopic thyroid tissue e.g. Struma ovarii.
- Increased Thyroid binding globulin, seen in pregnancy, Hepatitis, and congenital hyperproteinemia.
Decreased Level Of T3:
- Hypothyroidism is seen in :
- Cretinism.
- Surgical ablation.
- Myxedema.
- Hypothalamic Failure.
- Nephrotic Syndrome.
- Iodine Insufficiency.
- Pituitary insufficiency.
- Renal failure.
- Cirrhosis.
- Advanced Cancer.
- Hepatic Diseases.
Increased Level of Free T3 :
- T3 toxicosis.
- Hyperthyroidism.
- Peripheral resistance syndrome.
Decreased Level of Free T3 :
- Hypothyroidism.
- Pregnancy in the third trimester.
Understand Your Test Results:
Understand your T3 Resin Uptake Test Results
AI-powered Lab Test Results Meaning tool 🤖