Lab Test Abbreviations, Acronyms and Definitions
Lab test abbreviations and acronyms are essential components of medical and scientific communication, providing concise representations of complex diagnostic procedures and analyses.
| 17-OHP | 17-Hydroxyprogesterone |
| 3-ANCA | Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies (c-ANCA / p-ANCA) |
| 5-HIAA | 5-Hydroxyindoleacetic Acid |
| 5-HT | 5-Hydroxytryptamine (Serotonin) |
| A/G Ratio | Albumin/Globulin Ratio |
| A1A | Alpha-1 Antitrypsin |
| A1AT | Alpha-1 Antitrypsin |
| A1c | Hemoglobin A1c |
| AB | Antibody |
| ABG | Arterial Blood Gas |
| AB | ABO Group and Rh Type |
| ABT | Antibody Titer |
| ACA | Anti-Cardiolipin Antibodies |
| ACE | Angiotensin Converting Enzyme |
| ACID PHOS | Acid Phosphatase |
| ACP | Acid Phosphatase |
| ACT | Activated Clotting Time |
| ACTH | Adrenocorticotropic Hormone |
| ADA | Adenosine Deaminase |
| AFB | Acid-Fast Bacillus |
| AFP | Alpha Fetoprotein |
| AG | Antigen |
| ALA | Aminolevulinic Acid |
| Alb | Albumin |
| Alk Phos | Alkaline Phosphatase |
| ALP | Alkaline Phosphatase |
| ANA | Antinuclear Antibody |
| Anti-HBc | Hepatitis B Core Antibody |
| Anti-HBe | Hepatitis Be Antibody |
| Anti-HBs | Hepatitis B Surface Antibody |
| Anti-HCV | Hepatitis C Antibody |
| APT | Stool for Fetal Hemoglobin |
| aPTT | Activated Partial Thrombin Time |
| ASN | Antibody Screen |
| ASO | Antistreptolysin-O |
| ASP | Aspirin Resistance |
| AT III | Antithrombin-III Activity |
| B12 | Vitamin B12 |
| BMP | Basic Metabolic Panel |
| BNP | Brain Natriuretic Peptide |
| BUN | Blood Urea Nitrogen |
| C1 | Complement C1, Functional |
| C1Q | C1Q Binding Assay |
| C2 | Complement C2 |
| C3 | Complement C3 |
| C4 | Complement C4 |
| Ca | Calcium |
| CBC | Complete Blood Count |
| CBCD | Complete Blood Count with Differential |
| CEA | Carcinoembryonic Antigen |
| CH50 | Complement Immunoassay, Total |
| CK | Creatine Kinase |
| Cl | Chloride |
| CMB | CKMB Panel |
| CMP | Comprehensive Metabolic Panel |
| CMV | Cytomegalovirus |
| CMV Ag | CMV Antigenemia |
| CO | Carbon Monoxide |
| CO2 | Carbon Dioxide |
| COHB | Carboxyhemoglobin |
| CONABO | Confirmatory Type |
| CPK | Creatine Phosphokinase (Creatine Kinase) |
| Cr | Creatinine |
| CRCL, CrCl | Creatinine Clearance |
| CRD | Cord Type and DAT |
| CREAT | Creatinine |
| CRP | C-Reactive Protein |
| Cu | Copper |
| D Bil | Direct Bilirubin |
| DAT | Direct Antiglobulin (Coombs) Test |
| DCAS | DAT and AB Screen |
| DHEA | Dehydroepiandrosterone |
| DHEAS | Dehydroepiandrosterone-Sulfate |
| DIFM | Differential |
| Dig | Digoxin |
| EOS | Eosinophils |
| EPO | Erythropoietin |
| ERA | Estrogen Receptor Assay |
| ESR | Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate |
| ETOH | Ethanol |
| FBS | Fasting Blood Sugar (Glucose) |
| Fe | Total Iron |
| FEP | Free Erythrocyte Protoporphyrin |
| FFN | Fetal Fibronectin |
| FFQ | Fecal Fat |
| Fol | Folate |
| FSH/LH | FSH/LH Evaluation |
| FT3 | Free T3 |
| FT4 | Free Thyroxine |
| G2PP | 2 Hour Postprandial Glucose |
| G-6-PD | Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase |
| Gamma GT | Gamma Glutamyl Transferase |
| GCT | Glucose Challenge Test |
| GDS | Gestational Diabetes Screen |
| GGT | Gamma Glutamyl Transferase |
| GH | Growth Hormone |
| Glu | Glucose |
| H&H (or H/H) | Hemoglobin and Hematocrit |
| Hapto | Haptoglobin |
| HbA1c | Hemoglobin A1c |
| HBeAb | Hepatitis Be Virus Antibody |
| HBeAg | Hepatitis Be Virus Antigen |
| HBsAb | Hepatitis B Surface Antibody |
| HBsAg | Hepatitis B Surface Antigen |
| hCG | Human Chorionic Gonadotropin |
| hCG (urine) | Urine Pregnancy Test |
| HCT | Hematocrit |
| HDL | High Density Lipoprotein |
| HFP | Hepatic Function Panel |
| HGB | Hemoglobin |
| HgbA1c | Hemoglobin A1c |
| HGH | Human Growth Hormone |
| HIAA | 5-Hydroxyindoleacetic Acid |
| HIV | Human Immunodeficiency Virus |
| HPV | Human Papilloma Virus |
| HSV | Herpes Simplex Virus |
| iCa | Ionized Calcium |
| IFE | Immunofixation Electrophoresis |
| IgA | Immunoglobulin A |
| IgE | Immunoglobulin E |
| IGF | Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I |
| IgG | Immunoglobulin G |
| IgM | Immunoglobulin M |
| INR | Prothrombin Time |
| Jo-1 | Jo-1 Antibody |
| KB | Kleihauer-Betke |
| K | Potassium |
| Lact(o) | Lactoferrin |
| LD | Lactate Dehydrogenase |
| LDH | Lactate Dehydrogenase |
| LFT | Liver Function Tests |
| LH | Luteinizing Hormone |
| Li+ or Li | Lithium |
| MetHb/MetHgb | Methemoglobin |
| Mg, Mag | Magnesium |
| MIC | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration |
| MMA | Methylmalonic Acid |
| Mn | Manganese |
| Mono | Mononucleosis |
| NA | Sodium |
| NEOTY | Neonate Type and DAT |
| NEOXM | Neonate Type and XM |
| NH3 | Ammonia |
| NTR | Newborn Type and Rh |
| PAP | Pap Smear OR Pap Smear & HPV DNA Test OR Prostatic Acid Phosphatase |
| Pb | Lead |
| PBG | Porphobilinogen |
| PCP | Phencyclidine |
| PEP | Protein Electrophoresis |
| PHOS | Phosphorus |
| PKU | Phenylketonuria |
| PLT or PLT Ct | Platelet Count |
| PO4 | Phosphorus |
| PRL | Prolactin |
| PRU | P2Y12 |
| PSA | Prostate Specific Antigen |
| PT | Prothrombin Time |
| PTH | Parathyroid Hormone |
| PTT | Partial Thromboplastin Time |
| QIG | Quantitative Immunoglobulins |
| RBC | Red Blood Cell |
| RET | Reticulocyte Count |
| RF | Rheumatoid Factor |
| RFP | Renal Function Panel |
| RhIG (Eval) | RhIG Evaluation |
| RPR | Rapid Plasma Reagin |
| RSV | Respiratory Syncytial Virus |
| Scl-70 | Scleroderma Antibody |
| SHBG | Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin |
| SIFE | Serum Immunofixation Electrophoresis |
| Siro | Sirolimus |
| SPEP | Serum Protein Electrophoresis |
| SSA | Sjögren’s Syndrome A Antibody |
| SSB | Sjögren’s Syndrome B Antibody |
| SSDNA | Single Stranded DNA |
| T Bil | Total Bilirubin |
| T3 | Triiodothyronine |
| T4 | Thyroxine |
| Tacro | Tacrolimus |
| TBG | Thyroxine Binding Globulin |
| TGL | Triglycerides |
| Theo | Theophylline |
| TIBC | Total Iron Binding Capacity |
| TP | Total Protein |
| TREP | Treponemal Antibodies |
| Trep Ab | Treponemal Antibodies |
| TRH | Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone |
| Trig | Triglycerides |
| TRXN | Transfusion Reaction Evaluation |
| TSH | Thyroid Stimulating Hormone |
| TSI | Thyroid Stimulating Immunoglobulin |
| TT | Thrombin Time |
| TYSC | Type and Screen |
| UIFE | Urine Immunofixation Electrophoresis |
| UPE, UPEP or | |
| Ur Prot Elect | Urine Protein Electrophoresis |
| VCA | Viral Capsid Antigen |
| VDRL | Venereal Disease Reference Lab (Syphilis Test, CSF) |
| Vit A | Vitamin A (Retinol) |
| Vit B1 | Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) |
| Vit B12 | Vitamin B12 |
| Vit B2 | Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) |
| Vit B6 | Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) |
| Vit C | Vitamin C |
| Vit D | 25-Hydroxy Vitamin D |
| VLDL | Very Low Density Lipoprotein |
| VMA | Vanillylmandelic Acid |
| VZG | Varicella zoster IgG |
| WBC | White Blood Cell Count |
| Xa | LMW Heparin |
| XM | Type and Crossmatch |
| Zn | Zinc |
| ZPP | Zinc Protoporphyrin |

Tests Abbreviations, Acronyms, Definitions and Short Brief :
Tests Starting from 0-9
17-OHP > 17-Hydroxyprogesterone (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: 17-Hydroxyprogesterone
Alternative Names: 17-OHP, OHP, 17-OH Progesterone, 17OHP, 17-OH Progesterone, 17-Alpha-Hydroxyprogesterone, OH-Progesterone, 17-alpha hydroxyprogesterone, Progesterone – 17-OH, 17-Hydroxyprogesterone, 17-Hydroxyprogesterone (Neonatal Screen)
Category: Endocrinology / Hormone Test
Purpose:
This test measures the amount of 17-hydroxyprogesterone (17-OHP) in a sample of your blood. 17-OHP is a substance produced by the adrenal glands. These glands are two small organs located above each kidney. They produce different types of hormones necessary for maintaining life and health. Hormones are chemical messengers circulating in the blood that control the actions of certain cells or organs.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Newborn screening for CAH
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Infertility evaluation
- Signs of excess androgens
Typical Normal Range:
- Newborn: < 630 ng/dL
- Adult Men: < 200 ng/dL
- Adult Women (follicular phase): < 80 ng/dL
Related Tests: Cortisol, ACTH Stimulation Test, DHEA-S
Notes:
Usually performed in the morning; levels can vary with menstrual cycle phase and stress.
3-ANCA > Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies (c-ANCA / p-ANCA) (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies
Alternative Names: c-ANCA, p-ANCA, PR3-ANCA (Proteinase 3), MPO-ANCA (Myeloperoxidase), ANCA Test, ANCA Screen, c-ANCA/p-ANCA Test, ANCA Antibody Test, ANCAs, Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody Test, Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies Test, ANCA Blood Test, Vasculitis ANCA Test, Autoimmune Vasculitis Test
Category: Immunology / Autoimmune Test
Purpose:
An ANCA test can determine whether you have one or both pANCA and cANCA antibodies. ANCA or MPO and PR3 tests are ordered if you have signs and symptoms suggestive of systemic autoimmune vasculitis.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA)
- Microscopic polyangiitis (MPA)
- Autoimmune vasculitis symptoms (sinusitis, lung/kidney involvement)
Typical Normal Range:
Negative (no detectable ANCA)
Negative: Less than 2 IU/mL.
Equivocal: 2-3 IU/mL (may require further testing).
Positive: Greater than 3 IU/mL.
Related Tests: ANA, ESR, CRP, Renal Function Tests
Notes:
Pattern differentiation (c-ANCA vs p-ANCA) can guide diagnosis; positive results require correlation with clinical findings.
5-HIAA – 5-Hydroxyindoleacetic Acid (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: 5-Hydroxyindoleacetic Acid
Alternative Names: 5-Hydroxy-3-indoleacetic acid, Urinary 5-HIAA, HIAA Test, 5-HIAA Urine Test, Serotonin Metabolite Test, 24-Hour Urine 5-HIAA
Category: Biochemistry / Tumor Marker
Purpose:
5-HIAA is a urine test that measures the amount of 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA). 5-HIAA is the hormone serotonin’s breakdown product. 5-HIAA, a marker of serotonin levels, is produced by the body and measured by this test. 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) is used to identify and monitor carcinoid tumors. Either a blood test for serotonin and/or chromogranin A or a separate one can be ordered.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected carcinoid syndrome (flushing, diarrhea, wheezing)
- Monitoring treatment of carcinoid tumors
- Evaluation of serotonin metabolism disorders
Typical Normal Range:
Urine (24-hour): 2–9 mg/24 hr or (10.4 to 46.8 µmol/24h) (may vary by lab)
Related Tests: Serum Chromogranin A, Serotonin, Urinary Catecholamines
Notes:
Patients are advised to avoid foods high in serotonin (bananas, nuts, tomatoes, avocados) and certain medications before the test to avoid false results.
5-HT – 5-Hydroxytryptamine (Serotonin) (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: 5-Hydroxytryptamine
Alternative Names: Serotonin, Enteramine, Serotonin Test. Serotonin Blood Test, 5-Hydroxytryptamine Level, 5-HT Levelc, Serum Serotonin
Category: Biochemistry / Neurotransmitter Test
Purpose:
Measures serotonin levels in blood, urine, or cerebrospinal fluid to assess serotonin metabolism and detect related disorders.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected carcinoid syndrome
- Evaluation of serotonin-producing tumors
- Research/clinical studies of psychiatric or neurological conditions
- Monitoring therapy in serotonin-related disorders
Typical Normal Range:
- Serum/Plasma: 50–200 ng/mL (varies by lab)
- Urine (24-hour): <10 mg/24 hr
Related Tests: 5-HIAA (5-Hydroxyindoleacetic Acid) Test, Chromogranin A (CgA) Test, Imaging Studies (CT Scan, MRI, PET Scan, Octreoscan, Platelet Serotonin
Notes:
Levels can be influenced by medications, diet, and stress. Avoid serotonin-rich foods before testing.
Tests Starting from A
A/G Ratio – Albumin/Globulin Ratio (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Albumin/Globulin Ratio
Alternative Names: A/G Ratio, Serum Albumin to Globulin Ratio, Albumin-Globulin Ratio, Alb/Glob Ratio, A/G Ratio, Total Protein with A/G Ratio
Category: Biochemistry / Liver & Kidney Function Test
Purpose:
Evaluates the balance between albumin and globulin proteins in the blood to assess liver function, kidney disease, and immune disorders.
The total protein level and the albumin-to-globulin (A/G) ratio determine the amount of protein in the blood. The body uses protein for various essential functions, such as energy production, muscle repair, and strengthening the immune system. The amount of protein in the blood is determined by a total protein level. Excess or deficiency of protein can be a sign of liver or kidney disease, infection, inflammation, malnutrition, and cancer.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Chronic liver disease (cirrhosis, hepatitis)
- Kidney disease (nephrotic syndrome)
- Nutritional status assessment
- Autoimmune or immune system disorders
Typical Normal Range:
- A/G Ratio: 1.0 – 2.1 (may vary slightly by lab)
Related Tests: Total Protein, Albumin, Globulin, Liver Function Tests (LFTs), Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP), Kidney Function Tests, Protein Electrophoresis, Immunoglobulins (IgG, IgA, IgM, IgE) Studies
Notes:
A low A/G ratio may indicate chronic illness, liver disease, or autoimmune disorder; a high ratio may suggest genetic conditions or decreased globulin production.
A1A – Alpha-1 Antitrypsin (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Alpha-1 Antitrypsin
Alternative Names: Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Test, Serum AAT Test, AAT Level Test, AAT Deficiency Test, Alpha-1 Protease Inhibitor Test, A1AT Test, AATD Test, α1-Antitrypsin
Category: Biochemistry / Genetic & Liver Function Test
Purpose:
Alpha-1 antitrypsin (A1AT or A1A), a protein produced by the liver, protects the lungs against harm brought on by inflammation. Its absence can lead to emphysema and early liver damage. This test measures alpha-1 antitrypsin, a protein that protects tissues from enzymatic damage. It is diagnosed with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, which can lead to lung and liver problems.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Early-onset emphysema or COPD
- Unexplained chronic liver disease
- Family history of Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency
- Evaluation of neonatal jaundice or hepatitis
Typical Normal Range:
Serum: 100 – 300 mg/dL (may vary by lab)
Related Tests: Liver Function Tests (LFTs), Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs), Genetic Testing for AAT mutations, Chest X-ray / CT Scan, Liver Biopsy, Genetic Testing (Phenotyping/Genotyping)
Notes:
Low levels suggest genetic deficiency; patients may require genetic confirmation. Smoking accelerates lung damage in deficiency cases.
A1AT – Alpha-1 Antitrypsin (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Alpha-1 Antitrypsin
Alternative Names: Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Test, Serum AAT Test, AAT Level Test, AAT Deficiency Test, Alpha-1 Protease Inhibitor Test, A1A Test, AATD Test, α1-Antitrypsin
Category: Biochemistry / Genetic & Liver Function Test
Purpose:
Alpha-1 antitrypsin (A1AT or A1A), a protein produced by the liver, protects the lungs against harm brought on by inflammation. Its absence can lead to emphysema and early liver damage. This test measures alpha-1 antitrypsin, a protein that protects tissues from enzymatic damage. It is diagnosed with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, which can lead to lung and liver problems.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Early-onset emphysema or COPD
- Unexplained chronic liver disease
- Family history of Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency
- Evaluation of neonatal jaundice or hepatitis
Typical Normal Range:
Serum: 100 – 300 mg/dL (may vary by lab)
Related Tests: Liver Function Tests (LFTs), Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs), Genetic Testing for AAT mutations, Chest X-ray / CT Scan, Liver Biopsy, Genetic Testing (Phenotyping/Genotyping)
Notes:
Low levels suggest genetic deficiency; patients may require genetic confirmation. Smoking accelerates lung damage in deficiency cases.
A1c – Hemoglobin A1c (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Hemoglobin A1c
Alternative Names: HbA1c, Glycated Hemoglobin, Glycosylated Hemoglobin, Glycohemoglobin, A1c
Category: Biochemistry / Diabetes Test
Purpose:
Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) determines average blood glucose levels over the past 2 to 3 months by detecting the amount of hemoglobin bound to glucose in red blood cells. It is an essential tool for monitoring and diagnosing diabetes. It determines the proportion of glycated (glucose-bound) hemoglobin to assess long-term glycemic control over the past two to three months.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Screening and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus
- Monitoring long-term glycemic control in diabetic patients
- Assessing the risk of diabetic complications (kidney, eye, and heart disease)
- Differentiating between short-term and chronic hyperglycemia
Typical Normal Range:
Normal: < 5.7%
Prediabetes: 5.7 – 6.4%
Diabetes: ≥ 6.5%
Related Tests: Fasting Blood Glucose, Random Blood Glucose, Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT), Fructosamine, Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM), Autoantibody Tests, C-Peptide Test
Notes:
It is not affected by daily blood sugar fluctuations. However, it may be unreliable in patients with anemia, hemoglobin fluctuations, or recent bleeding.
AAT – Alpha-1 Antitrypsin (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Alpha-1 Antitrypsin
Alternative Names: Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Test, Serum AAT Test, AAT Level Test, AAT Deficiency Test, Alpha-1 Protease Inhibitor Test, A1A Test, AATD Test, α1-Antitrypsin
Category: Biochemistry / Genetic & Liver Function Test
Purpose:
Alpha-1 antitrypsin (A1AT or A1A), a protein produced by the liver, protects the lungs against harm brought on by inflammation. Its absence can lead to emphysema and early liver damage. This test measures alpha-1 antitrypsin, a protein that protects tissues from enzymatic damage. It is diagnosed with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, which can lead to lung and liver problems.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Early-onset emphysema or COPD
- Unexplained chronic liver disease
- Family history of Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency
- Evaluation of neonatal jaundice or hepatitis
Typical Normal Range:
Serum: 100 – 300 mg/dL (may vary by lab)
Related Tests: Liver Function Tests (LFTs), Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs), Genetic Testing for AAT mutations, Chest X-ray / CT Scan, Liver Biopsy, Genetic Testing (Phenotyping/Genotyping)
Notes:
Low levels suggest genetic deficiency; patients may require genetic confirmation. Smoking accelerates lung damage in deficiency cases.
AB – Antibody (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Antibody
Alternative Names: Immunoglobulin Test, Ig, Serology Test, Specific Antibody Test, Antigen-Antibody Test, Immune Status Test, Titer Test
Category: Immunology / Serology
Purpose:
The immune system produces proteins called antibodies, or immunoglobulins, to recognize and eliminate pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and poisons. Antibody screening tests can identify immune deficiencies, autoimmune diseases, and previous infections. Testing for antibodies in the blood can diagnose infections, autoimmune diseases, immune disorders, or vaccine responses.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Diagnosis of acute or past infections (viral, bacterial, parasitic)
- Evaluation of autoimmune diseases
- Determining immune response after vaccination
- Monitoring immunodeficiency disorders
Typical Normal Range:
- Depends on antibody type (IgG, IgA, IgM, IgE, IgD) and test method
- Generally: Negative (non-reactive) in absence of disease
| Antibody | Function | Normal Range (Blood) |
|---|---|---|
| IgG | Long-term immunity (most abundant) | 700–1600 mg/dL |
| IgA | Protects mucous membranes (gut, respiratory tract) | 70–400 mg/dL |
| IgM | First responder to new infections | 40–230 mg/dL |
| IgE | Allergic reactions & parasitic infections | <100 IU/mL (varies by lab) |
| IgD | Role unclear (rarely tested) | <10 mg/dL |
Related Tests: Immunoglobulin Panel, Antigen Tests, Autoantibody Profiles (ANA, ANCA, RF), PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) Tests, CBC Test, Immunoglobulin (Ig) Levels, Autoantibody Tests
Notes:
Presence of antibodies indicates exposure or immune response; type and level help differentiate acute vs chronic conditions.
ABG – Arterial Blood Gas (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Arterial Blood Gas
Alternative Names: Blood Gas Analysis, Arterial Blood Gasometry, Blood Gas Test, Arterial Blood Gas Analysis, Arterial Puncture, PaO2/PaCO2 Test
Category: Clinical Pathology / Critical Care
Purpose:
The main objectives of arterial blood gas testing are to assess acid-base balance, ventilation, and oxygenation by measuring oxygen (PaO₂), carbon dioxide (PaCO₂), and blood pH in an arterial blood sample. It is used to diagnose and treat lung, heart, and kidney conditions, such as respiratory failure, heart failure, diabetes, and sepsis, and is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of treatments.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Critically ill patients in ICU or ER
- Respiratory failure, COPD, asthma, pneumonia
- Monitoring patients on mechanical ventilation
- Suspected metabolic acidosis or alkalosis
- Assessment of oxygen therapy effectiveness
Typical Normal Range:
- pH: 7.35 – 7.45
- PaO₂: 75 – 100 mmHg
- PaCO₂: 35 – 45 mmHg
- HCO₃⁻: 22 – 26 mEq/L
- O₂ Saturation: 95 – 100%
Related Tests: Pulse Oximetry, Serum Electrolytes, Lactate, Spirometry, Venous Blood Gas (VBG), Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP), Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP), Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs)
Notes:
Requires arterial sample (commonly radial artery). Must be analyzed quickly; improper handling affects results.
ABRH – ABO Group and Rh Type (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: ABO Blood Group and Rh (Rhesus) Type
Alternative Names: Blood Grouping, Blood Typing, ABO/Rh Test
Category: Immunohematology / Blood Bank
Purpose:
The ABRH (ABO/Rh) blood typing test is designed to determine a person’s blood type and Rh factor, thereby ensuring the safety of blood transfusions and organ transplants and preventing pregnancy-related complications such as hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn (HDN). It identifies the presence or absence of specific antigens on red blood cells, which is crucial for matching blood donors and recipients and therefore for avoiding severe immune reactions.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Blood transfusion compatibility testing
- Organ or tissue transplantation
- Prenatal and antenatal screening (to prevent Rh incompatibility)
- Emergency and routine blood typing
Typical Normal Range:
- ABO Group: A, B, AB, or O
- Rh Factor: Positive (+) or Negative (–)
Related Tests: Antibody Screen, Crossmatch, Antibody Screen (Indirect Coombs Test), Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT) / Direct Coombs Test, Blood Transfusion
Notes:
Critical for transfusion safety; mismatched transfusions can cause life-threatening reactions. In pregnancy, Rh-negative mothers may require Rh immunoglobulin (RhIg) if carrying an Rh-positive baby.
ABT – Antibody Titer (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Antibody Titer
Alternative Names: Antibody Level Test, Serologic Titer, Antibody Serology Test, Immunization Test, Serological Antibody Testing, Antibody Serum Test, Red Cell Antibody Titration
Category: Immunology / Serology
Purpose:
The main purposes of an antibody titer test are to detect previous infections, assess the immune response in autoimmune diseases, and determine the effectiveness of vaccines and the need for booster doses. This test measures the amount of antibodies in a blood sample to assess the body’s exposure to specific antigens and the subsequent immune response against the disease or its own tissues.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Checking immunity after vaccination (e.g., Hepatitis B, Measles, Rubella)
- Detecting current or past infections
- Monitoring autoimmune conditions
- Assessing need for booster vaccines
Typical Normal Range:
- Reported as titer ratios (e.g., 1:20, 1:80, 1:160)
- Protective or abnormal levels vary by disease/test
Related Tests: Immunoglobulin Panel, Antigen Test, Neutralizing Antibody Test, Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) Test, C-Reactive Protein (CRP) Test, Antibody Screen and Identification
Notes:
A rising titer in paired samples (acute & convalescent) usually indicates recent infection. Protective thresholds differ by disease.
ACA – Anti-Cardiolipin Antibodies (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Anti-Cardiolipin Antibodies
Alternative Names: aCL Antibodies, Cardiolipin Antibody Test, Antiphospholipid Antibody Test
Category: Immunology / Autoimmune Testing
Purpose:
The anti-cardiolipin antibody (ACA) test determines the presence of specific autoantibodies in the blood that increase the risk of blood clots, recurrent miscarriages, and certain autoimmune conditions like antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). The test helps doctors investigate unexplained clotting, recurring pregnancy loss, and symptoms suggestive of APS and other autoimmune diseases, such as lupus.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Recurrent blood clots (DVT, PE)
- Recurrent miscarriages or pregnancy complications
- Evaluation of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and related autoimmune disorders
- Suspected antiphospholipid antibody syndrome
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (non-reactive)
- May be reported as IgG, IgM, IgA levels in GPL/MPL units
- Low/negative = normal; Moderate/high = abnormal, linked to APS
Related Tests: Lupus Anticoagulant, Anti-β2 Glycoprotein I Antibodies, ANA Test, Complete Blood Count (CBC), Partial Thromboplastin Time (PTT) / Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (aPTT)
Notes:
Persistent positivity (≥12 weeks apart) is required for APS diagnosis. May be transiently positive after infections or medications.
ACE – Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Angiotensin Converting Enzyme
Alternative Names: Serum ACE, Serum Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (SACE)
Category: Biochemistry / Enzymology
Purpose:
An ACE blood test measures the level of angiotensin-converting enzyme in the blood and is primarily used to help diagnose and monitor sarcoidosis by detecting elevated enzyme levels caused by granulomas in the body. It can also help in monitoring the effectiveness of corticosteroid treatment for sarcoidosis, as levels should decrease with effective treatment. The test is also helpful in diagnosing Gaucher disease and can be elevated in other conditions, but sarcoidosis is its main application.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected sarcoidosis
- Monitoring disease activity in sarcoidosis
- Evaluation of granulomatous diseases (e.g., tuberculosis, leprosy)
- Rarely for hypertension-related studies
Typical Normal Range:
- Adults: 8 – 52 U/L (may vary by lab)
- Children may have higher levels
Related Tests: Serum Calcium, Chest X-ray/CT, Pulmonary Function Tests, Lysozyme, Biopsy, CBC
Notes:
Elevated ACE supports but does not confirm sarcoidosis. Levels may also be raised in liver disease, diabetes, and infections. Some patients with sarcoidosis may have normal ACE.
ACL – Anterior Cruciate Ligament (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Anterior Cruciate Ligament
Alternative Names: Cruciate Ligament of Knee (Anterior), ACL Injury Test, Lachman Test, Anterior Drawer Test, Pivot Shift Test, Lever Sign Test
Category: Orthopedics / Sports Medicine
Purpose:
The primary purpose of Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) (ACL) tests, such as the Lachman and Anterior Drawer tests, is to assess the integrity of the ACL and diagnose an injury by evaluating the forward movement of the tibia (shin bone) relative to the femur (thigh bone). A positive test result, indicating excessive anterior translation or a lack of a firm “end feel,” suggests a torn or unstable ACL, which often leads to knee instability and requires further evaluation.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Sports injuries (football, basketball, soccer, skiing)
- Knee instability or “giving way”
- Suspected ligament tear or rupture
- Pre- and post-surgical assessment
Typical Normal Range:
- Intact ligament with no laxity on physical exam
- Negative Lachman test / Anterior drawer test
- MRI shows intact ligament fibers
Related Tests: MRI Knee, X-ray (to rule out fractures), Arthroscopy, Lachman & Pivot-Shift Test, Instrumented Laxity Testing
Notes:
ACL injuries are common in athletes; may require surgical reconstruction for full function. Early rehab and strengthening reduce re-injury risk.
ACID PHOS – Acid Phosphatase (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Acid Phosphatase
Alternative Names: Serum Acid Phosphatase (SAP), Prostatic Acid Phosphatase (PAP), Tartrate-Resistant Acid Phosphatase (TRAP), Seminal Acid Phosphatase (SAP)
Category: Enzyme Test
Purpose:
The acid phosphatase test is used to diagnose diseases such as hairy cell leukemia, characterized by an elevation of a specific type of acid phosphatase. It can also be used as a marker to monitor the progression and response to treatment of prostate cancer and other diseases affecting the liver, bones, or blood.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Prostate cancer detection (historical use, less common now)
- Monitoring prostate carcinoma treatment
- Investigating metastatic prostate disease
- Certain bone or liver diseases
Typical Normal Range:
- 0–5.5 U/L (may vary by lab and method)
Related Tests: Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA), Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP), Bone Scan, Digital Rectal Exam (DRE), Prostate Biopsy, TRAP Stain/Test (Tartrate-Resistant Acid Phosphatase), Bone Turnover Markers, Complete Blood Count (CBC)
Notes:
Largely replaced by PSA for prostate cancer screening; still occasionally used in specific clinical cases.
ACP – Acid Phosphatase (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Acid Phosphatase
Alternative Names: Serum Acid Phosphatase (SAP), Prostatic Acid Phosphatase (PAP), Tartrate-Resistant Acid Phosphatase (TRAP), Seminal Acid Phosphatase (SAP)
Category: Enzyme Test
Purpose:
The acid phosphatase test is used to diagnose diseases such as hairy cell leukemia, characterized by an elevation of a specific type of acid phosphatase. It can also be used as a marker to monitor the progression and response to treatment of prostate cancer and other diseases affecting the liver, bones, or blood.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Prostate cancer detection (historical use, less common now)
- Monitoring prostate carcinoma treatment
- Investigating metastatic prostate disease
- Certain bone or liver diseases
Typical Normal Range:
- 0–5.5 U/L (may vary by lab and method)
Related Tests: Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA), Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP), Bone Scan, Digital Rectal Exam (DRE), Prostate Biopsy, TRAP Stain/Test (Tartrate-Resistant Acid Phosphatase), Bone Turnover Markers, Complete Blood Count (CBC)
Notes:
Largely replaced by PSA for prostate cancer screening; still occasionally used in specific clinical cases.
ACT – Activated Clotting Time(Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Activated Clotting Time
Alternative Names: Activated Coagulation Time, Whole Blood Clotting Time (Activated), Whole-blood coagulation time
Category: Coagulation Test
Purpose:
The main objective of the coagulation activation test (TCA) is to monitor the effectiveness of anticoagulation with unfractionated heparin (HNF) in real time at the patient’s bedside. Esta prueba rápida, utilizado junto a la cama durante invasive procedures como la derivación cardiopulmonar, el cateterismo cardiací y las intervenciones coronaryias percutaneas, ayuda a garantiar que la sangre del paciente no coagule en exceso ni en defecto cuando se requiere terapia intensiva con heparina.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Prostate cancer detection (historical use, less common now)
- Monitoring prostate carcinoma treatment
- Investigating metastatic prostate disease
- Certain bone or liver diseases
Typical Normal Range:
- ~70–120 seconds (varies by method and device)
Related Tests: Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time(APTT), Prothrombin Time (PT/INR), Anti-Xa Assay, Thrombin Time,
Notes:
Less sensitive than aPTT; primarily used for point-of-care monitoring when rapid results are critical.
ACTH – Adrenocorticotropic Hormone(Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Adrenocorticotropic Hormone
Alternative Names: Corticotropin, Adrenocorticotropic hormone blood test
Category: Endocrine/Hormone Test
Purpose:
The ACTH test is used to diagnose and monitor conditions that affect cortisol levels. These conditions include disorders of the pituitary and adrenal glands. High cortisol levels may be due to Cushing’s disease, a pituitary gland tumor that is usually benign (not cancerous).
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected Cushing’s syndrome
- Suspected Addison’s disease (primary adrenal insufficiency)
- Secondary adrenal insufficiency (pituitary cause)
- Monitoring ectopic ACTH production (e.g., tumors)
Typical Normal Range:
- ~10–60 pg/mL (morning sample; varies by lab and time of day)
Related Tests: Cortisol Test, Dexamethasone Suppression Test, Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone (CRH) Stimulation Test, Aldosterone, ACTH Stimulation Test, 24-Hour Urine Free Cortisol Test
Notes:
Levels show diurnal variation—highest in the morning, lowest at night; must be interpreted alongside cortisol.
ADA– Adenosine Deaminase(Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Adenosine Deaminase
Alternative Names: ADA Activity Test, ADA level, ADA enzyme activity, Adenosine deaminase assay
Category: Enzyme/Diagnostic Test
Purpose:
Adenosine deaminase (ADA) is an enzyme whose primary function is to remove toxic byproducts of DNA degradation, particularly deoxyadenosine. It converts deoxyadenosine and adenosine into harmless deoxyinosine and inosine, respectively. This crucial function protects lymphocytes and other cells from the accumulation of toxic metabolites, which is essential for the development and function of the immune system.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected tuberculous pleural effusion
- Differentiation of TB from other causes of pleural effusion
- Supportive diagnosis in peritoneal or pericardial effusions
- Monitoring certain hematologic malignancies or immune disorders
Typical Normal Range:
- <40 U/L in pleural fluid (cut-off may vary by lab and specimen type)
Related Tests: Pleural Fluid Analysis, Acid-Fast Bacillus (AFB) Smear and Culture, Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) for Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Interferon-Gamma Release Assays, ADA Deficiency
Notes:
Elevated ADA is suggestive but not diagnostic of TB; must be interpreted with clinical and microbiological findings.
AFB – Acid-Fast Bacillus(Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Acid-Fast Bacillus
Alternative Names: Ziehl-Neelsen Stain, Auramine-Rhodamine Stain, Mycobacterial Smear, Acid-fast stain, TB culture and sensitivity, TB smear and culture, AFB smear and culture
Category: Microbiology/Diagnostic Test
Purpose:
What are acid-fast bacilli (AFB) tests? Acid-fast bacilli (AFB) are bacteria that cause tuberculosis and other mycobacterial infections, such as leprosy (Hansen’s disease). AFB tests are often ordered for people with symptoms of active tuberculosis, commonly known as TB.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected pulmonary tuberculosis (sputum samples)
- Extrapulmonary TB (pleural fluid, CSF, urine, tissue biopsy)
- Monitoring response to anti-TB therapy
- Detection of nontuberculous mycobacterial infections
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (no acid-fast bacilli seen)
Related Tests: Mycobacterial Culture, GeneXpert MTB/RIF, PCR for Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Chest X-ray, Nucleic Acid Amplification Test (NAAT), Tuberculin Skin Test (TST) or Interferon-Gamma Release Assay (IGRA)
Notes:
Smear sensitivity is lower than culture or PCR; at least 3 early morning sputum samples recommended for diagnosis.
AFP – Alpha Fetoprotein(Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Alpha Fetoprotein
Alternative Names: α-Fetoprotein, Maternal Serum AFP (MSAFP), AFP Maternal, Quad screen (when part of a larger panel), AFP tumor marker
Category: Tumor Marker / Prenatal Screening Test
Purpose:
An alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) test measures AFP levels in the blood to detect potential problems during pregnancy, such as neural tube defects and chromosomal abnormalities, and to diagnose and monitor certain types of cancer and liver disorders in adults.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Screening for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
- Monitoring treatment/recurrence in liver cancers and germ cell tumors
- Prenatal screening for neural tube defects (spina bifida, anencephaly)
- Prenatal screening for chromosomal abnormalities (e.g., Down syndrome, when combined in triple/quad screen)
Typical Normal Range:
- Adults: <10 ng/mL (non-pregnant)
- Pregnancy: Varies with gestational age (normally elevated)
Related Tests: β-hCG, Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH), Ultrasound, Triple/Quad Screen, Liver Function Tests, Tumor markers, Imaging Tests, Biopsy,
Notes:
Elevated AFP can indicate liver disease, tumors, or fetal abnormalities; interpretation requires clinical context (especially in pregnancy).
AG – Antigen(Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Antigen
Alternative Names: Immunogen, Surface Marker (context-specific, e.g., HBsAg, p24 Ag), Rapid Antigen Test (RAT), Antigen Rapid Test (ART), Rapid Antigen Detection Test (RADT), Lateral Flow Test (a common type of antigen test)
Category: Immunology / Infectious Disease Marker
Purpose:
Antigen tests analyze blood, sputum, urine, stool, or other body fluids to detect specific disease markers. They are often used to determine if you have a viral illness, such as the flu or COVID-19, or to monitor cancer treatment. They can also help evaluate organ donors and recipients.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Diagnosis of viral infections (e.g., HBsAg for hepatitis B, HIV p24 antigen)
- Bacterial antigen detection (e.g., Streptococcus pneumoniae, Legionella in urine)
- Tumor marker assays (certain cancer antigens)
- Monitoring response to treatment or vaccination
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (antigen not detected)
Related Tests: Antibody Tests (Ab), PCR/NAAT, Culture, Serology Panels, Molecular Test (PCR)
Notes:
“Ag” is a general term; interpretation depends on the specific antigen test ordered. Usually paired with antibody testing for comprehensive evaluation.
AIDS – Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (Click here for Detail)
(Click here for Detail)Full Form: Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome
Alternative Names: HIV/AIDS (advanced stage of HIV infection), Antibody Tests, HIV Antibody Test, Enzyme Immunoassay (EIA), Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
Category: Infectious Disease / Immunodeficiency Disorder
Purpose:
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) occurs in the most advanced stage of the infection. HIV attacks white blood cells, weakening the immune system. This makes it easier to contract diseases such as tuberculosis, infections, and certain types of cancer.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Confirming HIV infection (ELISA, Western Blot, HIV RNA PCR)
- Monitoring CD4+ T-cell count
- Monitoring HIV viral load
- Evaluating opportunistic infections or related malignancies
Typical Normal Range:
- Not applicable (syndrome, not a laboratory “normal” test); diagnostic definition includes CD4 <200 cells/µL or AIDS-defining illness.
Related Tests: HIV Antibody/Antigen Test, HIV RNA PCR, CD4 Count, Viral Load, Opportunistic Infection Panels, Western Blot,
Notes:
AIDS is the clinical end stage of HIV infection, not a single test; diagnosis requires confirmed HIV infection plus immunologic or clinical criteria.
ALA – Aminolevulinic Acid (Click here for Detail)
(Click here for Detail)Full Form: Aminolevulinic Acid
Alternative Names: δ-Aminolevulinic Acid, 5-ALA, Delta-ALA, Delta-Aminolevulinic Acid, Aminolevulinic Acid (ALA), Urine or Plasma, ALA, Delta, Random Urine, ALA, Delta, 24-Hour Urine
Category: Metabolic / Porphyrin Pathway Test
Purpose:
It acts as a crucial precursor to porphyrins (such as chlorophyll and heme) and as a growth regulator in plants, while in medicine it is used for the detection and treatment of tumors using photodynamic therapy (PDT) and to treat certain skin conditions.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Screening and diagnosis of acute intermittent porphyria (AIP)
- Differentiation of porphyrias from other causes of abdominal/neurologic symptoms
- Suspected lead poisoning (interferes with ALA dehydratase)
- Monitoring therapy in porphyria patients
Typical Normal Range:
- Urine: <4.5 mg/L (may vary by lab)
Related Tests: Porphobilinogen (PBG), Porphyrins (Urine, Feces, and Blood), Lead Level, Erythrocyte Protoporphyrin, Hereditary Tyrosinemia Type 1 Testing, Genetic Testing
Notes:
Elevated urinary ALA is a hallmark of acute porphyric attacks and lead toxicity; results should be interpreted with clinical context and other porphyrin studies.
Alb – Albumin (Click here for Detail)
(Click here for Detail)Full Form: Albumin
Alternative Names: Serum Albumin, Urine Albumin, Microalbumin Test, Albumin-Creatinine Ratio (ACR)
Category: Protein / Liver & Kidney Function Test
Purpose:
The main functions of albumin are to maintain fluid balance in the blood vessels and to transport various substances, such as fatty acids, hormones, and medications, through the bloodstream. This is achieved by regulating plasma oncotic pressure, which prevents fluid leakage into the tissues. The liver produces albumin, and its levels are a key indicator of liver and kidney health.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of liver disease (cirrhosis, hepatitis)
- Assessment of kidney disease (nephrotic syndrome, proteinuria)
- Monitoring nutritional status and malnutrition
- Investigation of edema or ascites
Typical Normal Range:
- Serum: 3.5 – 5.0 g/dL
- Urine: <30 mg/day (microalbuminuria: 30–300 mg/day)
Related Tests: Total Protein, Globulin, A/G Ratio, Liver Function Tests, Microalbumin/Creatinine Ratio, Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP), Urine Protein Test
Notes:
Hypoalbuminemia may result from liver disease, nephrotic syndrome, malnutrition, or chronic illness; hyperalbuminemia is rare and usually due to dehydration.
Alk Phos – Alkaline Phosphatase (Click here for Detail)
(Click here for Detail)Full Form: Alkaline Phosphatase
Alternative Names: ALP, Serum Alkaline Phosphatase, Alkp, Alk Phos
Category: Enzyme / Liver & Bone Function Test
Purpose:
The alkaline phosphatase test is often used to detect or diagnose liver or bone diseases. It can also help diagnose or monitor other health problems.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected liver disease (hepatitis, cirrhosis)
- Suspected bile duct obstruction or cholestasis
- Bone disorders (rickets, osteomalacia, Paget’s disease)
- Monitoring cancer with bone or liver involvement
Typical Normal Range:
- ~44 – 147 U/L (varies by lab; higher in children and pregnancy)
Related Tests: Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase (GGT), Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT), Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST), Bilirubin, Calcium, Phosphate, ALP Isoenzyme Test,
Notes:
Elevated ALP may indicate liver or bone disease; isoenzyme testing (ALP fractionation) helps identify the source. Physiologically elevated in children (growth) and pregnancy.
ALP – Alkaline Phosphatase (Click here for Detail)
(Click here for Detail)Full Form: Alkaline Phosphatase
Alternative Names: ALP, Serum Alkaline Phosphatase, Alkp, Alk Phos
Category: Enzyme / Liver & Bone Function Test
Purpose:
The alkaline phosphatase test is often used to detect or diagnose liver or bone diseases. It can also help diagnose or monitor other health problems.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected liver disease (hepatitis, cirrhosis)
- Suspected bile duct obstruction or cholestasis
- Bone disorders (rickets, osteomalacia, Paget’s disease)
- Monitoring cancer with bone or liver involvement
Typical Normal Range:
- ~44 – 147 U/L (varies by lab; higher in children and pregnancy)
Related Tests: Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase (GGT), Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT), Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST), Bilirubin, Calcium, Phosphate, ALP Isoenzyme Test,
Notes:
Elevated ALP may indicate liver or bone disease; isoenzyme testing (ALP fractionation) helps identify the source. Physiologically elevated in children (growth) and pregnancy.
ALT– Alanine aminotransferase(Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Alanine Aminotransferase
Alternative Names: Serum Glutamic Pyruvic Transaminase (SGPT), Alanine Transaminase (ALT), GPT
Category: Enzyme / Liver Function Test
Purpose:
The main function of the enzyme alanine aminotransferase (ALT) is to help the liver metabolize amino acids and convert food into energy. An ALT blood test measures the amount of this enzyme in the blood to assess liver health, as high ALT levels can indicate liver damage or inflammation.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of liver disease (hepatitis, cirrhosis)
- Monitoring hepatotoxicity from drugs or toxins
- Assessment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
- Workup of jaundice or abnormal liver function tests
Typical Normal Range:
- ~7 – 56 U/L (varies by lab)
Related Tests: Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST), ALP, Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase (GGT), Bilirubin, Albumin, PT/INR, Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP), Liver Function Tests (LFTs),
Notes:
ALT is more liver-specific than AST; elevated levels usually indicate hepatocellular damage, though mild increases can occur in muscle injury.
ANA – Antinuclear Antibody(Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Antinuclear Antibody
Alternative Names: Antinuclear Factor (ANF), ANA panel, Fluorescent antinuclear antibody (FANA), ANA reflexive panel, Systemic lupus erythematosus – ANA (SLE-ANA)
Category: Autoimmune / Immunology Test
Purpose:
The ANA test is used to diagnose autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), the most common form of lupus. Lupus is a chronic (long-term) disease that affects many parts of the body, including the joints, skin, heart, lungs, blood vessels, kidneys, and brain.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Evaluation of other autoimmune disorders (scleroderma, Sjögren’s syndrome, mixed connective tissue disease)
- Workup of unexplained arthritis, rash, or systemic symptoms
- Monitoring disease activity in autoimmune conditions
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (no detectable ANA; reported as titer and pattern if positive)
Related Tests: ENA Panel (Extractable Nuclear Antigens), Anti-dsDNA (anti-double-stranded DNA) Test, Anti-Smith Antibody, Rheumatoid Factor (RF), Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide (anti-CCP) Tests, C-Reactive Protein (CRP) , Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR),
Notes:
A positive ANA is not diagnostic alone—seen in healthy individuals and multiple autoimmune diseases; interpretation requires clinical correlation and antibody pattern.
Anti-HBc – Hepatitis B Core Antibody(Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Hepatitis B Core Antibody
Alternative Names: HBcAb, Total Anti-HBc, Anti-Hepatitis B core antigen
Category: Infectious Disease / Hepatitis B Serology
Purpose:
The HBsAg antibody test is a blood test used to detect the presence of antibodies, or markers, developed by the body in response to hepatitis B virus infection. It identifies and monitors treatment progress and diagnoses past, current, and future infections.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Diagnosis of acute or past hepatitis B infection
- Differentiating between acute, chronic, and resolved HBV status
- Screening in patients with unexplained liver disease
- Pre-transplant or pre-immunosuppressive therapy screening
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (non-reactive)
Related Tests: Hepatitis B Surface Antigen (HBsAg), Hepatitis B Surface Antibody (Anti-HBs), Hepatitis B e-antigen (HBeAg), Anti-HBe, HBV DNA PCR, Liver Function Tests, Hepatitis B Core Antibody, IgM (IgM Anti-HBc),
Notes:
IgM anti-HBc → indicates recent/acute infection
Total anti-HBc (IgG + IgM) → indicates past or chronic infection
Not present after vaccination (only appears with natural infection)
Anti-HBe – Hepatitis B “e” Antibody(Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Hepatitis B “e” Antibody
Alternative Names: HBeAb, Hepatitis B e-Antibody, Anti-Hepatitis B e-antigen, HEAB
Category: Infectious Disease / Hepatitis B Serology
Purpose:
A reactive (positive) anti-HBe test when HBeAg levels have fallen below the detection threshold indicates the beginning of recovery in a person with hepatitis B. A nonreactive (negative) anti-HBe test may mean that the infection is very recent and that viral replication has not yet peaked.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Monitoring progression of chronic hepatitis B infection
- Evaluating infectivity and likelihood of viral replication
- Assessing response to antiviral therapy
- Differentiating between active replication and inactive carrier state
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (non-reactive)
Related Tests: Hepatitis B Surface Antigen (HBsAg), Hepatitis B Surface Antibody (Anti-HBs), Hepatitis B Core Antibody (Anti-HBc), Hepatitis B “e” Antigen (HBeAg), Hepatitis B Viral DNA (HBV DNA), Liver Function Tests,
Notes:
Positive Anti-HBe with negative HBeAg → usually indicates lower infectivity and reduced viral replication
Seroconversion from HBeAg to Anti-HBe is a favorable response in chronic HBV treatment
Must be interpreted with HBV DNA levels for accurate infectivity statusIgM anti-HBc → indicates recent/acute infection
Total anti-HBc (IgG + IgM) → indicates past or chronic infection
Not present after vaccination (only appears with natural infection)
Anti-HBs – Hepatitis B Surface Antibody(Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
Alternative Names: HBsAb, Hepatitis B Surface Antibody, Quantitative, Antibody to Hepatitis B Surface Antigen
Category: Infectious Disease / Hepatitis B Serology
Purpose:
The anti-HBs test is designed to determine whether a person is immune to the hepatitis B virus (HBV) following vaccination or a previous infection. A positive or “reactive” result indicates immunity, meaning the person is protected and cannot transmit the virus. The presence of these antibodies is a key indicator of an effective immune response, confirming protection against future exposure to HBV.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Determining immunity after hepatitis B vaccination
- Identifying past, resolved hepatitis B infection
- Screening before immunosuppressive therapy or organ transplantation
- Assessing response to HBV vaccine in healthcare workers or high-risk individuals
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (non-reactive); Protective immunity: ≥10 mIU/mL
Related Tests: Hepatitis B Surface Antigen (HBsAg), Hepatitis B Core Antibody (Anti-HBc), Hepatitis B e-antigen (HBeAg), Anti-HBe, HBV DNA PCR, Liver Function Tests, Hepatitis B Core Antibody, IgM (IgM Anti-HBc)
Notes:
Positive Anti-HBs with negative Anti-HBc → immunity from vaccination
Positive Anti-HBs with positive Anti-HBc → immunity from past infection
Lack of Anti-HBs after vaccination may indicate vaccine non-response
Anti-HCV – Hepatitis C Antibody(Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Hepatitis C Virus Antibody
Alternative Names: HCV Antibody Test, Hepatitis C Antibody Test, Anti-Hepatitis C Virus, Antibody to HCV, Hepatitis C Ab
Category: Infectious Disease / Hepatitis C Serology
Purpose:
HCV antibody testing is an essential tool for the early detection, diagnosis, and treatment of hepatitis C virus infections. Whether used for routine screening or to diagnose an active infection, this test helps healthcare professionals understand the virus status and determine appropriate action.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Screening individuals at risk for HCV (blood transfusion history, IV drug use, hemodialysis)
- Evaluation of abnormal liver function tests
- Prenatal HCV screening in high-risk mothers
- Pre-surgical or pre-transplant infectious disease workup
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (non-reactive)
Related Tests: Hepatitis C RNA Test (HCV RNA), HCV Genotype Test, Liver Function Tests, Liver Biopsy or Non-Invasive Fibrosis Tests, Qualitative HCV RNA Test, Quantitative HCV RNA Test (Viral Load)
Notes:
Positive Anti-HCV indicates exposure but does not distinguish between past, resolved, or active infection.
Confirmatory testing with HCV RNA PCR is required to determine active infection.
Antibodies usually appear 8–12 weeks after exposure.
APT – Stool for Fetal Hemoglobin(Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Alkali Denaturation Test (APT Test for Fetal Hemoglobin)
Alternative Names: APT Test, Apt-Downey Test, Alkali Denaturation Test, Fetal Hemoglobin Test
Category: Hematology / Gastrointestinal Test (Neonatal)
Purpose:
The APT test is used to differentiate neonatal blood from maternal blood in meconium. This test requires a sufficient amount of blood to be detectable with the naked eye.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of blood in stool or vomitus of newborns
- Distinguishing maternal blood swallowed during delivery from true neonatal GI bleeding
- Assessment of suspected neonatal upper GI hemorrhage
- Clarification of unclear neonatal rectal bleeding
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (no fetal hemoglobin detected in stool/vomitus)
Related Tests: Occult Blood Test, Hemoglobin Electrophoresis, Complete Blood Count (CBC), Kleihauer-Betke (KB) Test, Coagulation Studies
Notes:
Based on resistance of fetal hemoglobin (HbF) to alkali denaturation, unlike adult hemoglobin.
Useful only in neonatal period; not recommended for older infants or adults.
aPTT – Activated Partial Thrombin Time(Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time
Alternative Names: Partial Thromboplastin Time (PTT), Partial Thromboplastin Time (Activated), Intrinsic Pathway Coagulation Factor Profile, APTT
Category: Coagulation Test
Purpose:
The purpose of an aPTT test is to evaluate the intrinsic and common pathways of the coagulation cascade, measure the time it takes for a blood clot to form, and monitor heparin treatment.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Monitoring unfractionated heparin therapy
- Screening for bleeding/clotting disorders (hemophilia, von Willebrand disease, lupus anticoagulant)
- Preoperative coagulation assessment
- Investigation of unexplained bleeding or thrombosis
Typical Normal Range:
- ~25 – 35 seconds (varies by lab and reagent)
Related Tests: PT/INR, ACT, Fibrinogen, Anti-Xa Assay, Mixing Studies, Thrombin Time (TT), Coagulation Factor Assays, Bleeding Time, Platelet Count
Notes:
Prolonged aPTT suggests intrinsic pathway abnormalities or heparin effect.
Normal aPTT with prolonged PT indicates extrinsic pathway defect.
Must be interpreted with clinical history and other coagulation studies.
ASO – Antistreptolysin-O(Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Antistreptolysin-O Antibody
Alternative Names: ASO Titer, Anti-Streptolysin O, Streptolysin-O Antibody, Streptococcal Serology
Category: Serology / Infectious Disease Test
Purpose:
The ASO (antistreptolysin O) test measures ASO antibodies in blood to detect a recent group A streptococcal infection, such as Streptococcus pyogenes. It is not used to diagnose active streptococcal infections, but it helps diagnose post-streptococcal complications, such as rheumatic fever or post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis, which can occur after untreated infections.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected post-streptococcal complications (rheumatic fever, post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis)
- Evaluation of recent streptococcal pharyngitis or skin infection
- Differentiating acute rheumatic fever from other causes of arthritis or carditis
- Monitoring antibody decline after treatment
Typical Normal Range:
- Adults: <200 IU/mL
- Children: <400 IU/mL (values vary by lab)
Related Tests: Anti-DNase B, Throat Culture, Rapid Strep Test, Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR), C-Reactive Protein (CRP), Urinalysis
Notes:
Elevated ASO indicates recent streptococcal exposure but not the site of infection.
Titers peak 3–5 weeks after infection and decline over months.
Often used in combination with Anti-DNase B for higher sensitivity.
AST – Aspartate aminotransferase (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Aspartate Aminotransferase
Alternative Names: SGOT (Serum Glutamic-Oxaloacetic Transaminase), Aspartate Transaminase
Category: Liver Function / Enzyme Test
Purpose:
An AST blood test is often part of a routine blood test to assess liver health. This test can help diagnose or monitor liver problems. It can also help diagnose other health problems.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected liver disease (hepatitis, cirrhosis)
- Monitoring alcohol-related liver injury
- Evaluation of myocardial infarction (historically, less common now)
- Muscle disorders or injury
Typical Normal Range:
- 10 – 40 U/L (may vary by lab)
Related Tests: ALT (Alanine Aminotransferase) Test, Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP), GGT (Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase), Bilirubin, CK, Liver Function Panel (or Liver Panel), Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP), Albumin and Total Protein
Notes:
Elevated AST alone is not specific; AST/ALT ratio aids in differential diagnosis (e.g., alcoholic liver disease).
AT III – Antithrombin-III Activity (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Antithrombin-III Activity
Alternative Names: AT, Antithrombin Activity, AT3, Antithrombin activity, Antithrombin, functional, Heparin cofactor activity, Serine protease inhibitor
Category: Coagulation / Thrombophilia Workup
Purpose:
This test measures antithrombin III activity in the blood. Abnormal levels may indicate a risk of excessive blood clotting or bleeding.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Unexplained or recurrent venous thrombosis
- Suspected inherited thrombophilia
- Monitoring patients on heparin therapy (resistance to heparin)
- Evaluation of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
Typical Normal Range:
- 80 – 120% activity (may vary by lab)
Related Tests: Protein C, Protein S, Factor V Leiden, PT, aPTT, Antithrombin Antigen Test, Lupus anticoagulant test.
Notes:
Low AT III may be inherited or acquired (liver disease, nephrotic syndrome, heparin therapy, DIC).
Tests Starting from B
B12 – Vitamin B12 (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin)
Alternative Names: Cobalamin, Serum B12, Pernicious anemia – vitamin B12 level
Category: Vitamin / Nutritional Assessment
Purpose:
Vitamin B12 is essential for the production of healthy DNA and red blood cells, maintaining the nervous system, and producing energy. It is essential for proper cell function, nerve health, and preventing some types of anemia. Vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to serious health problems, including fatigue, neurological disorders like memory loss, and megaloblastic anemia.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of anemia (especially megaloblastic anemia)
- Suspected vitamin B12 deficiency (fatigue, neuropathy)
- Malabsorption disorders (pernicious anemia, gastric/ileal surgery)
- Monitoring patients with strict vegetarian/vegan diets or long-term PPI use
Typical Normal Range:
- 200 – 900 pg/mL (may vary by lab)
Related Tests: Folate, Methylmalonic Acid (MMA), Homocysteine, CBC, Intrinsic Factor Antibody and Parietal Cell Antibody Tests,
Notes:
Borderline results may require confirmatory testing (MMA, homocysteine). Deficiency can cause irreversible neurological damage if untreated.
BMP – Basic Metabolic Panel (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Basic Metabolic Panel
Alternative Names: Chem-7, Basic Chemistry Panel, Chemistry Screen,Chem 7 (referring to the seven components of the panel excluding calcium), Chem 8 (referring to the eight components of the panel including calcium), Electrolyte Panel, SMAC7 (Sequential Multiple Analysis with Computer – 7)
Category: General Health / Metabolic Panel
Purpose:
A basic metabolic panel (BMP) measures eight different substances in the blood. It provides important information about the body’s fluid balance, metabolism (the process by which the body produces energy from the food you eat), and kidney function.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Routine health checkups
- Monitoring kidney disease or hypertension
- Evaluation of dehydration or electrolyte imbalance
- Monitoring patients on diuretics or other chronic medications
Typical Normal Range:
- Sodium: 135–145 mmol/L
- Potassium: 3.5–5.0 mmol/L
- Chloride: 98–106 mmol/L
- CO₂ (Bicarbonate): 22–29 mmol/L
- BUN: 7–20 mg/dL
- Creatinine: 0.6–1.3 mg/dL
- Glucose: 70–100 mg/dL (fasting)
- Calcium: 8.5–10.5 mg/dL
Related Tests: CMP (Comprehensive Metabolic Panel), Electrolytes, eGFR, Liver function tests,
Notes:
CMP includes all BMP components plus liver function tests.
BNP – B-type natriuretic peptide (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: B-type Natriuretic Peptide
Alternative Names: Brain Natriuretic Peptide, Natriuretic Peptide Test, N-Terminal Pro B-Type Natriuretic Peptide (NT-proBNP)
Category: Cardiac Biomarker / Blood Test
Purpose:
B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) is a hormone released by the heart, especially in cases of stress, such as heart failure. Its function is to protect the heart by dilating blood vessels, promoting the excretion of salt and water through the kidneys, and thus reducing blood pressure and the heart’s workload.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected or worsening heart failure
- Differentiating cardiac vs. pulmonary causes of dyspnea
- Monitoring severity of heart failure
- Assessing prognosis in cardiovascular disease
Typical Normal Range:
- <100 pg/mL (values may vary by lab)
Related Tests: NT-proBNP, Troponin, Echocardiogram, Electrocardiogram (ECG), Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP) Test, Creatine Kinase (CK) and CK-MB, Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP) or Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP), Electrolytes, Electrocardiogram (EKG), Chest X-ray
Notes:
Levels may be affected by age, kidney function, and obesity.
BUN – Blood Urea Nitrogen (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Blood Urea Nitrogen
Alternative Names: Serum Urea Nitrogen, Urea Nitrogen Test, Urea
Category: Kidney Function Test / Metabolic Panel
Purpose:
The common blood test, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), reveals important information about kidney function. It measures the amount of blood urea nitrogen (BUN).
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected kidney disease or injury
- Monitoring chronic kidney disease (CKD)
- Evaluation of dehydration or fluid status
- Assessing response to dialysis or other renal treatments
Typical Normal Range:
- 7–20 mg/dL (may vary by lab)
Related Tests: Creatinine, eGFR, Electrolytes, Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP), BUN-to-Creatinine Ratio, Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP) or Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP), Glucose, Proteins, Liver Function Tests, Urinalysis, Microalbuminuria Test
Notes:
Levels may rise with dehydration, high-protein diet, or GI bleeding, not only kidney dysfunction.
Tests Starting from C
C1 – Complement C1 (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Complement Component 1
Alternative Names: C1 Esterase, Complement C1 Complex, C1q
Category: Immunology / Complement System Test
Purpose:
Complement component C1 acts as a crucial initiator complex for the classical complement pathway, recognizing and binding to antibody-antigen complexes or certain abnormal structures on pathogens and apoptotic cells.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Recurrent bacterial infections
- Hereditary angioedema (HAE) evaluation (C1 inhibitor deficiency)
- Autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus, vasculitis)
- Monitoring complement activity in immunologic disorders
Typical Normal Range:
- Assay-dependent; usually reported as functional activity (%)
Related Tests: C3, C4, CH50, C1q, C1 Esterase Inhibitor (C1-INH), Total Complement Activity (CH50 or CH100) Test, C-Reactive Protein (CRP) and Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
Notes:
Low levels may indicate genetic deficiency, autoimmune disease, or consumption during active inflammation.
C1Q – C1Q Binding Assay (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: C1q Binding Assay
Alternative Names: C1q Immune Complex Assay, Circulating Immune Complex Test, C1q Binding Immune Complexes, C1qScreen Assay
Category: Immunology / Autoimmune Test
Purpose:
A C1q binding assay measures the ability of C1q to bind to immune complexes, which is essential for the initiation of the classical complement pathway. This assay is intended to detect circulating immune complexes (CICs), assess the activity of autoimmune diseases such as lupus, and evaluate the binding of therapeutic antibodies to C1q during drug development.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Evaluation of autoimmune connective tissue diseases
- Monitoring disease activity in lupus or vasculitis
- Investigating unexplained immune-mediated symptoms
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative or within assay-specific reference range
Related Tests: ANA, Anti-dsDNA, Complement (C3, C4), CH50, Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) and C-Reactive Protein (CRP), Rheumatoid Factor (RF) and Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide (anti-CCP) Antibodies,
Notes:
Not disease-specific; positive results should be interpreted in clinical context with other autoimmune markers.
C2 – Complement C2 (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Complement Component 2
Alternative Names: C2 Complement Protein, Complement Component 2, C2 Antigen Test
Category: Immunology / Complement System Test
Purpose:
Complement component 2 (C2) acts as a crucial enzyme in the classical and lectin pathways of the complement system, which is part of the body’s immune defense against invaders such as bacteria and viruses.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Recurrent severe bacterial or viral infections
- Suspected hereditary complement deficiency
- Autoimmune conditions (e.g., systemic lupus erythematosus)
- Monitoring immune system activity in immunologic disorders
Typical Normal Range:
- Assay-dependent; reported as concentration (mg/dL) or functional activity (%)
Related Tests: C1, C3, C4, CH50, AH50, Total Complement Activity (CH50 or CH100),Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) Test, C1 Esterase Inhibitor (C1-INH) Test,
Notes:
C2 deficiency is rare but strongly associated with recurrent infections and early-onset lupus.
C3 – Complement C3 (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Complement Component 3
Alternative Names: C3 Complement Protein, Complement Component 3 Test, C3 Antigen Test
Category: Immunology / Complement System Test
Purpose:
Complement C3 is a key protein of the immune system. It helps fight foreign invaders, such as bacteria and viruses, by activating the system to destroy them. It does this by splitting into C3a and C3b, which trigger an inflammatory response, mark microbes for destruction (opsonization), and contribute to the formation of membrane attack complexes that destroy cells.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected autoimmune diseases (e.g., systemic lupus erythematosus)
- Recurrent or severe bacterial infections
- Monitoring complement activation in immune complex disorders
- Assessing renal disease (e.g., glomerulonephritis)
Typical Normal Range:
- ~90–180 mg/dL (may vary by lab)
Related Tests: C4, Total Complement Activity (CH50 or CH100), AH50, C1q, C2, C-Reactive Protein (CRP) and Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR), Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) Test, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
Notes:
Low levels may indicate complement consumption (active autoimmune disease, infections); elevated levels may reflect acute or chronic inflammation.
C4 – Complement C4 (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Complement Component 4
Alternative Names: C4 Complement Protein, Complement Component 4 Test, C4 Antigen Test
Category: Immunology / Complement System Test
Purpose:
Complement component 4 (C4) is an important blood protein that is part of the immune complement system and helps fight infections and remove dead cells from the body. Its function is to activate the classical and lectin complement pathways, leading to the formation of C3 convertase, which helps destroy pathogens such as bacteria and viruses.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Monitoring autoimmune disease activity
- Evaluation of recurrent bacterial infections
- Assessment of hereditary or acquired angioedema
Typical Normal Range:
- ~10–40 mg/dL (may vary by lab)
Related Tests: C3, CH50, AH50, C1q, C1 Esterase Inhibitor (C1-INH), Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) Test, Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) and C-Reactive Protein (CRP)
Notes:
Low C4 with normal C3 often suggests hereditary angioedema or classical pathway activation (e.g., lupus).
Ca – Calcium (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Calcium
Alternative Names: Serum Calcium, Total Calcium, Ionized Calcium Test:
Category: Electrolyte / Mineral Test
Purpose:
Calcium plays a fundamental role in the formation of strong bones and teeth, but is also essential for muscle contraction, nerve function, blood clotting, hormone secretion, and vascular regulation. It acts as a structural element of bones and as a signaling molecule throughout the body, requiring adequate dietary intake and vitamin D for proper absorption.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of bone disorders (e.g., osteoporosis, osteomalacia)
- Suspected parathyroid disease (hyperparathyroidism or hypoparathyroidism)
- Kidney disease or kidney stone risk assessment
- Monitoring critically ill patients for electrolyte imbalance
Typical Normal Range:
- Total Calcium: ~8.5–10.5 mg/dL (2.1–2.6 mmol/L); Ionized Calcium: ~4.6–5.3 mg/dL (1.16–1.32 mmol/L)
Related Tests: Ionized Calcium, Phosphate, Magnesium, Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) Test, Vitamin D, Albumin Test, Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP) or Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP), Urine Calcium Test
Notes:
About half of total calcium is bound to proteins; albumin levels should be considered when interpreting results.
CA-125 – Cancer antigen 125 (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Cancer Antigen 125
Alternative Names: Carbohydrate Antigen 125, MUC16, Cancer Antigen 125 Test, CA-125 Tumor Marker Test
Category: Tumor Marker / Oncology Test
Purpose:
The CA-125 test measures a specific protein in the blood that can indicate the presence of certain types of cancer, including ovarian cancer, and can be used to monitor treatment response and detect recurrence in diagnosed patients.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected ovarian cancer
- Monitoring treatment response in ovarian cancer
- Detecting recurrence of ovarian cancer
- Supporting evaluation of pelvic masses in women
Typical Normal Range:
- <35 U/mL (may vary by lab)
Related Tests: HE4, CEA, CA 19-9, BRCA mutation testing, Ultrasound/CT imaging, Biopsy, CT Scan (Computed Tomography), Transvaginal Ultrasound (TVS)
Notes:
Elevated levels are not specific to cancer; may also rise in benign conditions (e.g., endometriosis, menstruation, liver disease, pregnancy).
CBC – Complete Blood Count (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Complete Blood Count
Alternative Names: Full Blood Count (FBC), Hemogram, Full Haemogram (FHG), Blood Cell Count, CBC with Differential
Category: Hematology Test
Purpose:
A complete blood count (CBC) is a common blood test used to assess overall health, diagnose conditions such as anemia, infections, and blood cancers, and monitor the effects of medical treatments. It measures the number, size, and characteristics of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets to provide detailed information about overall health.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Routine health check-ups
- Suspected anemia, infection, or bleeding disorders
- Monitoring chronic diseases (e.g., kidney disease, cancer)
- Assessing response to treatments such as chemotherapy
Typical Normal Range:
- WBC: ~4,000–11,000/µL
- RBC: ~4.2–6.1 million/µL
- Hemoglobin: ~12–17 g/dL
- Hematocrit: ~36–52%
- Platelets: ~150,000–450,000/µL (ranges vary by age/sex/lab)
Related Tests: Peripheral Smear, Reticulocyte Count, Iron Studies, Coagulation Panel, Bone Marrow Aspiration and Biopsy
Notes:
Provides a broad screening but requires further testing for specific diagnosis.
CBCD – Complete Blood Count with Differential (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Complete Blood Count with Differential
Alternative Names: CBC with Differential, Full Blood Count with Differential, WBC Differential Count, Blood Cell Count with Differential
Category: Hematology Test
Purpose:
A complete blood count with differential helps diagnose and monitor a wide range of diseases by measuring red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and hemoglobin, while the differential specifies the amounts of the five different types of white blood cells.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected infections (bacterial, viral, parasitic)
- Hematologic disorders (e.g., leukemia, lymphoma)
- Monitoring immune status in chronic disease or chemotherapy
- Investigation of unexplained fever, fatigue, or cytopenias
Typical Normal Range:
- WBC: ~4,000–11,000/µL
- Neutrophils: ~40–70%
- Lymphocytes: ~20–40%
- Monocytes: ~2–8%
- Eosinophils: ~1–4%
- Basophils: ~0–1%
- RBC, Hemoglobin, Hematocrit, Platelets: same as CBC
Related Tests: Peripheral Blood Smear, Reticulocyte Count, Bone Marrow Biopsy, Iron Studies, Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) and C-Reactive Protein (CRP)
Notes:
Differential helps distinguish between infection types, allergic responses, and hematologic malignancies.
CEA – Carcinoembryonic Antigen (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Carcinoembryonic Antigen
Alternative Names: CEA Tumor Marker, CEA Blood Test, Carcinoembryonic Antigen Assay, CEA Assay, Embryonic Carcinoma Antigen
Category: Tumor Marker / Oncology Test
Purpose:
The primary purpose of the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) test is to monitor known cancer, particularly colorectal cancer, rather than diagnose it. It is a blood test that measures the level of a protein called CEA in the blood. High CEA levels can indicate the presence or recurrence of certain types of cancer, help evaluate the effectiveness of treatment, and track the progression or spread of cancer.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Monitoring colorectal cancer treatment and recurrence
- Assessing prognosis in gastrointestinal cancers
- Supporting evaluation of suspected lung, breast, or pancreatic cancers
- Follow-up in patients with known malignancies
Typical Normal Range:
- <3 ng/mL (non-smokers), <5 ng/mL (smokers) — may vary by lab
Related Tests: CA 19-9, CA 125, AFP, CA 15-3, Imaging studies (CT, MRI, PET), CBC, Colonoscopy, Liver Function Tests, Biopsy,Imaging Studies (CT, MRI, PET scans)
Notes:
Not recommended as a screening test; levels may rise in benign conditions (e.g., smoking, inflammation, liver disease).
CH50 – Complement Immunoassay, Total (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Total Hemolytic Complement (CH50)
Alternative Names: Total Complement Activity, Classical Pathway Complement Test, Total Hemolytic Complement, Total Complement Activity, CH100
Category: Immunology / Complement System Test
Purpose:
The CH50 immunoassay measures total complement activity to assess the overall function of the innate immune system. This test facilitates the diagnosis and monitoring of autoimmune diseases, such as lupus and certain kidney diseases, by detecting potential deficiencies or dysfunctions of the complement system, which is essential for fighting infections and removing dead cells.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected complement deficiency
- Evaluation of recurrent bacterial infections
- Autoimmune disease assessment (e.g., systemic lupus erythematosus)
- Monitoring disease activity in immune-mediated disorders
Typical Normal Range:
- ~30–75 U/mL (varies by lab and method)
Related Tests: AH50, C3, C4, C1q, C1 Esterase Inhibitor (C1-INH), Autoimmune Disease Markers, Inflammatory Markers, Rheumatoid Factor (RF), Anti-dsDNA Antibody Test, Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) Test
Notes:
Low CH50 may indicate complement deficiency, excessive complement consumption, or classical pathway activation.
CK – Creatine Kinase (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Creatine Kinase
Alternative Names: Creatine Phosphokinase (CPK), Total CK
Category: Enzyme Test / Muscle & Cardiac Marker
Purpose:
Creatine kinase (CK) is an essential enzyme for providing chemical energy to energy-intensive tissues, such as muscles and the brain, by facilitating the transfer of phosphate groups for ATP production. In the heart and skeletal muscle, elevated CK levels may indicate tissue damage or disease, such as a heart attack or muscle inflammation.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected myocardial infarction (less common now, replaced by troponin)
- Rhabdomyolysis or severe muscle injury
- Muscular dystrophies and neuromuscular disorders
- Monitoring statin-related myopathy or drug-induced muscle damage
Typical Normal Range:
- ~20–200 U/L (varies by age, sex, and lab)
Related Tests: Troponin, LDH, Aldolase, Myoglobin, CK Isoenzymes (CK-MB, CK-MM, CK-BB), Troponin Test,
Notes:
CK is non-specific; isoenzyme testing (CK-MB, CK-MM, CK-BB) helps localize source (cardiac, skeletal muscle, brain).
Cl – Chloride (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Chloride
Alternative Names: Serum Chloride, Blood Chloride, Chloride Blood Test, Cl Test
Category: Electrolyte Test
Purpose:
Chloride (Cl−) is essential for maintaining fluid balance, acid-base balance, and nerve and muscle function, as it acts as an electrolyte. It forms the gastric acid (hydrochloric acid) essential for digestion and helps maintain electroneutrality by counteracting positive ions such as sodium and potassium.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of dehydration or fluid imbalance
- Acid–base disorders (metabolic acidosis/alkalosis)
- Monitoring kidney disease
- Assessment in patients on IV fluids or diuretics
Typical Normal Range:
- ~98–107 mmol/L (may vary by lab)
Related Tests: Sodium, Potassium, Bicarbonate (CO₂), Anion Gap, CMP, Urine Chloride Test, Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP), Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP)
Notes:
CK is non-specific; isoenzyme testing (CK-MB, CK-MM, CK-BB) helps localize source (cardiac, skeletal muscle, brain).
CMB – CKMB Panel (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Creatine Kinase-MB Panel
Alternative Names: CK-MB, CK-MB Isoenzyme Test, CPK-MB, Cardiac Enzymes
Category: Cardiac Enzyme Test / Myocardial Injury Marker
Purpose:
The CK-MB test measures the amount of creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB), a heart-specific enzyme, in the blood to aid in the diagnosis and monitoring of myocardial infarction (heart attack). Elevated levels of CK-MB in the blood indicate heart muscle damage, while elevated CK-MB or CK-BB isoforms suggest skeletal muscle or brain damage.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected acute myocardial infarction (AMI)
- Monitoring progression or resolution of cardiac injury
- Distinguishing cardiac vs. skeletal muscle CK elevation
- Evaluating chest pain of uncertain origin
Typical Normal Range:
- <5–6 ng/mL or <3–5% of total CK (ranges vary by lab)
Related Tests: Total CK, Troponin I/T, LDH, Myoglobin, Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG), Imaging Studies
Notes:
Less specific and less sensitive than troponins; mainly used historically but sometimes still ordered alongside troponins for cardiac evaluation.
CMP – Comprehensive Metabolic Panel(Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Comprehensive Metabolic Panel
Alternative Names: CK-MB, CK-MB Isoenzyme Test, CPK-MB, Cardiac Enzymes
Category: Metabolic / Biochemical Panel
Purpose:
A comprehensive metabolic profile (CMPP) is a common blood test that provides an overview of the body’s chemical balance, metabolism, and organ function. It measures 14 different substances to assess liver and kidney function, control blood sugar, and monitor fluid and electrolyte balance.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Routine health check-ups and baseline assessments
- Monitoring chronic diseases (e.g., diabetes, hypertension, kidney disease)
- Evaluating liver and kidney function
- Investigating fluid, electrolyte, or acid–base disorders
Typical Normal Range:
- (includes 14 tests; ranges vary by lab)
- Glucose: ~70–100 mg/dL (fasting)
- Calcium: ~8.5–10.5 mg/dL
- Sodium: ~135–145 mmol/L
- Potassium: ~3.5–5.0 mmol/L
- Chloride: ~98–107 mmol/L
- CO₂ (bicarbonate): ~22–29 mmol/L
- BUN: ~7–20 mg/dL
- Creatinine: ~0.6–1.3 mg/dL
- Albumin: ~3.5–5.0 g/dL
- Total Protein: ~6.0–8.3 g/dL
- ALP: ~44–147 U/L
- ALT: ~7–56 U/L
- AST: ~10–40 U/L
- Total Bilirubin: ~0.1–1.2 mg/dL
Related Tests: BMP, LFT, eGFR, Electrolyte Panel, CBC (Complete Blood Count), Lipid Panel, Urinalysis, HbA1c, Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP)
Notes:
Provides a broad view of metabolic status; abnormal results often require correlation with clinical findings and follow-up tests.
CMV – Cytomegalovirus (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Cytomegalovirus
Alternative Names: CMV Antibody Test, CMV IgG/IgM, Human Herpesvirus 5 (HHV-5) Test, CMV (serum), Cytomegalovirus serologic test, CMV antigenemia or CMV Ag test (antigen test), CMV PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), CMV DNA test
Category: Infectious Disease / Virology
Purpose:
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a virus, not a virus with a “function” in the biological sense; rather, it has a life cycle and effects on the human body. CMV is a common and ubiquitous herpesvirus that infects people of all ages and persists in the body for life after initial exposure.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Pregnant women (screening for congenital infection risk)
- Immunocompromised patients (e.g., transplant recipients, HIV/AIDS)
- Newborns suspected of congenital CMV infection
- Patients with unexplained fever, hepatitis, or mononucleosis-like illness
Typical Normal Range:
- CMV IgM: Negative (non-reactive)
- CMV IgG: Negative (non-reactive)
Related Tests: EBV Antibodies, Toxoplasma IgG/IgM, Rubella IgG/IgM, HIV Test, CMV IgG Avidity Test, Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Test, Antigenemia Test, Viral Culture,
Notes:
CMV infection is usually asymptomatic in healthy individuals but can cause severe complications in neonates and immunosuppressed patients. IgM suggests recent/active infection; IgG indicates past exposure or immunity.
CMV Ag – CMV Antigenemia (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Cytomegalovirus Antigenemia
Alternative Names: CMV pp65 Antigen Test, CMV Antigen Detection, CMV Ag Test , CMV Antigenemia Assay, Direct Antigen Detection
Category: Infectious Disease / Virology
Purpose:
The primary purpose of the CMV antigenemia (CMV-Ag) test is to diagnose and monitor active CMV infection in immunosuppressed patients, such as people with HIV/AIDS or organ or bone marrow transplant recipients. This test detects the CMV pp65 antigen in leukocytes, providing a direct and rapid method for the early detection of CMV infection, essential for prompt initiation of antiviral treatment and prevention of disease progression.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Monitoring CMV reactivation in transplant recipients
- Diagnosing active CMV infection in immunosuppressed patients
- Guiding initiation of antiviral therapy
- Differentiating CMV disease from other opportunistic infections
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (No CMV antigen detected)
Related Tests: CMV IgG/IgM, CMV PCR (DNA test), EBV Antibody Panel, Quantitative PCR (Viral Load), CMV IgG Avidity Test
Notes:
More specific than serology for detecting active infection; commonly used for early detection and monitoring of CMV replication in high-risk groups (e.g., bone marrow or organ transplant patients).
CO – Carbon Monoxide (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Carbon Monoxide
Alternative Names: Carboxyhemoglobin Test, COHb Test, Carbon Monoxide Blood Test, Hemoglobin Derivatives Test
Category: Toxicology / Environmental Exposure
Purpose:
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a key reagent in the industrial production of methanol, acetic acid, and plastics. It serves as a raw material for these chemicals and as a reducing agent to extract metals from ores. It is also a component of fuel gas and is used in some lasers and in food processing to preserve the red color of fresh meat.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected carbon monoxide poisoning (e.g., smoke inhalation, faulty heating systems)
- Patients with headache, dizziness, confusion, or unexplained syncope
- Occupational exposure monitoring (firefighters, industrial workers)
- Evaluation of hypoxia with normal oxygen saturation readings
Typical Normal Range:
- Non-smokers: < 2% COHb
- Smokers: < 9% COHb
Related Tests: Arterial Blood Gas (ABG), Methemoglobin, Pulse CO-oximetry, Breath Analysis,
Notes:
Elevated COHb impairs oxygen delivery to tissues; levels >20% are considered toxic and often require treatment (e.g., oxygen therapy or hyperbaric oxygen).
CO2 – Carbon Dioxide (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Carbon Dioxide
Alternative Names: Bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻), Total CO₂, Serum CO₂, Carbon dioxide content or CO₂ content
Category: Electrolytes / Metabolic Panel
Purpose:
Carbon is present in carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas that traps heat near Earth. It allows the Earth to retain some of the heat it receives from the Sun, preventing it from escaping into space. But CO2 is only beneficial up to a point: beyond that, the Earth’s temperature rises too much.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Assessment of metabolic acidosis or alkalosis
- Monitoring patients with kidney disease
- Evaluation of respiratory disorders (COPD, asthma)
- Routine inclusion in Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP) or Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP)
Typical Normal Range:
- Non-smokers: < 2% COHb
- Smokers: < 9% COHb
Related Tests: Arterial Blood Gas (ABG), Electrolytes (Na⁺, K⁺, Cl⁻), Anion Gap, Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP) or Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP)
Notes:
Low CO₂ suggests metabolic acidosis; high levels may indicate metabolic alkalosis or CO₂ retention from respiratory disorders.
COHB – Carboxyhemoglobin (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Carboxyhemoglobin
Alternative Names: CO Hemoglobin, Blood Carbon Monoxide Test, CO-Oximetry
Category: Toxicology / Hematology
Purpose:
The primary purpose of carboxyhemoglobin (COHb) measurement is to diagnose and monitor carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning by quantifying the amount of CO bound to hemoglobin, which impedes the transport of oxygen in the blood.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected carbon monoxide poisoning (smoke inhalation, exhaust exposure)
- Monitoring high-risk occupations (firefighters, industrial workers, miners)
- Assessing unexplained hypoxia despite normal oxygen saturation
- Evaluating smoke inhalation injuries in burn victims
Typical Normal Range:
- Non-smokers: < 2%
- Smokers: < 9%
- Toxic: > 20% (often symptomatic and requiring treatment)
Related Tests: CO (Carbon Monoxide), Methemoglobin, Arterial Blood Gas (ABG), Pulse CO-oximetry, Cardiac and Neurological Tests, Electrolyte Panel and Basic/Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (BMP/CMP)
Notes:
Elevated COHb reduces oxygen delivery to tissues. Severe cases may require high-flow oxygen or hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
CPK – Creatine Phosphokinase (Creatine Kinase) (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Creatine Phosphokinase (also called Creatine Kinase, CK)
Alternative Names: CK, Total CK, CPK Enzyme Test, Creatine Phosphokinase
Category: Enzymes / Muscle & Cardiac Markers
Purpose:
The primary purpose of creatine phosphokinase (CPK, also known as creatine kinase) is to provide energy to tissues with high and fluctuating energy needs, such as the heart, brain, and skeletal muscle, by catalyzing the transfer of a phosphate group to creatine, thus forming phosphocreatine.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected myocardial infarction (heart attack)
- Evaluation of muscle injury, trauma, or rhabdomyolysis
- Monitoring neuromuscular diseases (e.g., muscular dystrophy, myositis)
- Assessing drug- or exercise-induced muscle damage
Typical Normal Range:
- Men: 55 – 170 U/L
- Women: 30 – 135 U/L (ranges may vary by lab)
Related Tests: CK-MB, Troponin, LDH, AST, Myoglobin, Electrolyte Panel and Kidney Function Tests (BUN and Creatinine), Aldolase
Notes:
Elevated CK is nonspecific; isoenzyme testing (CK-MB for heart, CK-MM for skeletal muscle, CK-BB for brain) helps localize the source of injury.
Cr – Creatinine (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Creatinine
Alternative Names: Serum Creatinine, Blood Creatinine, Urine Creatinine, Kidney Function Test, Renal Function Test
Category: Renal Function / Metabolic Waste Marker
Purpose:
A creatinine test measures how effectively your kidneys filter waste from your blood. Creatinine is a chemical compound produced during energy production in your muscles. Healthy kidneys filter creatinine from your blood.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Screening and monitoring chronic kidney disease (CKD)
- Assessing acute kidney injury (AKI)
- Monitoring renal function in patients on nephrotoxic drugs
- Routine inclusion in Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP) or Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP)
Typical Normal Range:
- Men: 0.7 – 1.3 mg/dL
- Women: 0.6 – 1.1 mg/dL (ranges may vary by lab)
Related Tests: Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN), Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR), Urine Creatinine, Creatinine Clearance, Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP), Urine Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio (UACR)
Notes:
Elevated creatinine suggests impaired kidney function or reduced glomerular filtration; interpretation should include eGFR for accuracy.
CRCL, CrCl – Creatinine Clearance (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Creatinine Clearance
Alternative Names: CRCL, 24-Hour Urine Creatinine Clearance, Renal Clearance Test, CCT , Serum Creatinine Clearance, Renal Function Test or Kidney Function Test
Category: Renal Function
Purpose:
The creatinine clearance test assesses kidney function by analyzing the amount of creatinine in the urine and blood. Creatinine is a waste product that the kidneys normally remove from the blood. An abnormal creatinine level can be a sign of kidney disease.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of kidney function and filtration capacity
- Monitoring progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD)
- Adjusting medication dosages cleared by the kidneys
- Assessment of renal function in transplant and dialysis patients
Typical Normal Range:
- Men: 97 – 137 mL/min
- Women: 88 – 128 mL/min (ranges may vary by lab)
Related Tests: Serum Creatinine, eGFR, BUN, Urine Creatinine, Urine Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio (UACR)
Notes:
Requires both serum and 24-hour urine creatinine measurement; less commonly used now due to widespread use of eGFR but still valuable in certain clinical settings.
CRD – Component-resolved diagnosis (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Component-Resolved Diagnosis
Alternative Names: Molecular Allergy Testing, Allergen Component Testing, Molecular-based Allergy Diagnostics, Allergen Microarray Testing
Category: Allergy / Immunology
Purpose:
Component-resolved diagnosis (CRD) aims to identify sensitization to specific allergen molecules within a source, providing an accurate diagnosis for improved clinical management, particularly in complex cases of food or respiratory allergies.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Differentiating true allergy from cross-reactivity (e.g., food–pollen syndrome)
- Assessing risk of severe allergic reactions (e.g., peanut Ara h 2 vs. Ara h 8)
- Guiding allergen immunotherapy selection
- Clarifying complex allergy profiles in polysensitized patients
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (no IgE detected against allergen components)
Related Tests: Total IgE, Specific IgE (RAST, ImmunoCAP), Skin Prick Test, Oral Food Challenge (OFC), Basophil Activation Test (BAT)
Notes:
Provides molecular-level detail about allergen sensitization; enhances precision in allergy management and prognosis compared to traditional IgE testing.
CREAT – Creatinine (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Creatinine
Alternative Names: Serum Creatinine, Blood Creatinine, CREAT, Urine Creatinine, Kidney Function Test or Renal Function Test
Category: Renal Function / Metabolic Waste Marker
Purpose:
Creatine is designed to enhance athletic performance, especially during short, intense activities, by quickly providing energy to the muscles. It helps increase strength and muscle mass, promotes muscle recovery, and may also have beneficial effects on brain function and muscle aging.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Routine kidney function assessment (part of BMP or CMP)
- Screening for chronic kidney disease (CKD)
- Monitoring acute kidney injury (AKI)
- Dose adjustment for renally cleared medications
Typical Normal Range:
- Men: 0.7 – 1.3 mg/dL
- Women: 0.6 – 1.1 mg/dL (ranges may vary by lab)
Related Tests: Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN), eGFR, Creatinine Clearance (CrCl), Urine Creatinine, Urine Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio (UACR), Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP)
Notes:
Creatinine levels must be interpreted with eGFR; affected by muscle mass, diet, and hydration status.
CRP – C-Reactive Protein (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: C-Reactive Protein
Alternative Names: hs-CRP (High-Sensitivity CRP, for cardiac risk), Serum CRP, Acute Phase Reactant
Category: Inflammatory Marker
Purpose:
The primary purpose of a CRP (C-reactive protein) test is to detect and monitor inflammation in the body, as the liver releases CRP in response to inflammation due to infection, injury, or chronic diseases such as arthritis or heart disease.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected bacterial or inflammatory infections
- Monitoring autoimmune and inflammatory diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, lupus)
- Evaluating post-surgical or post-transplant complications
- Cardiovascular risk assessment (with hs-CRP)
Typical Normal Range:
- Standard CRP: < 10 mg/L
- High-sensitivity CRP (hs-CRP):
- Low risk: < 1.0 mg/L
- Average risk: 1.0 – 3.0 mg/L
- High risk: > 3.0 mg/L
Related Tests: ESR (Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate), Procalcitonin, Fibrinogen, ANA Panel, Lipid Panel, Rheumatoid Factor (RF), Specific Autoimmune Disease Tests, Complete Blood Count (CBC),
Notes:
CRP is a nonspecific marker; elevated levels indicate inflammation but do not pinpoint the cause. hs-CRP is particularly used for cardiovascular risk stratification.
Cu – Copper (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Copper
Alternative Names: Serum Copper, Plasma Copper, Blood Copper, Urine Copper, Hepatic Copper, Liver Copper
Category: Trace Elements / Metabolic
Purpose:
Copper (Cu) is a vital biological component in humans and plants, acting as an essential cofactor for many enzymes, supporting energy production, iron metabolism, and the development of connective tissues, the nervous system, and blood vessels.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected Wilson’s disease (copper accumulation disorder)
- Evaluation of Menkes disease (copper deficiency disorder)
- Monitoring patients with unexplained liver disease or neurological symptoms
- Assessing nutritional deficiencies or malabsorption syndromes
Typical Normal Range:
- Serum Copper: 70 – 140 µg/dL (ranges vary by lab)
Related Tests: Ceruloplasmin, 24-Hour Urine Copper, Liver Function Tests (LFTs), Zinc, Genetic Testing, Slit-Lamp Eye Exam
Notes:
Levels may be decreased in Wilson’s disease, Menkes disease, and malnutrition; increased in liver disease, infections, and during pregnancy or estrogen therapy.
Tests Starting from D
D Bil – Direct Bilirubin (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Direct Bilirubin
Alternative Names: Conjugated Bilirubin, DBil
Category: Liver Function Test (LFT)
Purpose:
The D-Bil (direct bilirubin) test is used to evaluate liver health and diagnose conditions such as bile duct obstruction or liver disease, as high levels indicate that the liver is not removing bilirubin effectively.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Assessment of jaundice (to differentiate direct vs. indirect bilirubin causes)
- Evaluation of liver diseases (hepatitis, cirrhosis)
- Detecting biliary obstruction (e.g., gallstones, tumors)
- Monitoring patients with suspected hemolytic or hepatobiliary disorders
Typical Normal Range:
- 0.0 – 0.3 mg/dL (ranges may vary by lab)
Related Tests: Total Bilirubin, Indirect Bilirubin, ALT, AST, ALP, GGT, Liver Function Panel, Urine Bilirubin
Notes:
Elevated direct bilirubin usually indicates impaired excretion due to liver dysfunction or bile duct obstruction, unlike indirect bilirubin which rises in hemolysis.
DAT – Direct Antiglobulin (Coombs) Test (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Direct Antiglobulin Test
Alternative Names: Conjugated Bilirubin, DBil
Category: Hematology / Immunohematology
Purpose:
The direct antiglobulin test (DAT) is a laboratory test that detects immunoglobulins or complement on the surface of red blood cells. Its purpose is to distinguish hemolysis from an immune-mediated or non-immune-mediated etiology. As with all tests, DAT results should be analyzed in light of clinical and laboratory findings.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA)
- Investigation of hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN)
- Suspected drug-induced hemolytic anemia
- Workup of transfusion reactions
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (no antibody or complement coating RBCs)
Related Tests: Indirect Antiglobulin Test (IAT), Hemoglobin and Hematocrit, Reticulocyte Count, Peripheral Blood Smear, Complete Blood Count (CBC),
Notes:
A positive DAT indicates antibody- or complement-mediated RBC destruction; clinical correlation is essential to determine cause (autoimmune, drug-induced, transfusion-related, or maternal-fetal incompatibility).
DCAS – Direct Coombs/Antibody Screen(Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Direct Coombs / Antibody Screen
Alternative Names: Direct Antiglobulin Test with Antibody Screen, Direct AHG with Antibody Detection,
Category: Hematology / Immunohematology
Purpose:
The direct Coombs test (DCAS), or direct antiglobulin test (DAT), is designed to detect antibodies and complement proteins already bound to the surface of red blood cells (RBCs). This test is essential for diagnosing diseases such as autoimmune hemolytic anemia, which occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys a person’s RBCs.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of hemolytic transfusion reactions
- Investigation of autoimmune hemolytic anemia
- Screening for alloantibodies in patients with multiple transfusions
- Workup of hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN)
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (no RBC-bound antibodies or unexpected antibodies detected)
Related Tests: DAT (Direct Antiglobulin Test), IAT (Indirect Antiglobulin Test), Type & Screen, Crossmatch, Complete Blood Count (CBC), Reticulocyte Count, Bilirubin
Notes:
Combines the direct Coombs test (detects antibodies bound to RBCs) with an antibody screen (detects free unexpected antibodies in plasma), providing broader evaluation in transfusion and hemolysis workups.
DHEA – Dehydroepiandrosterone (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Dehydroepiandrosterone
Alternative Names: DHEA-S (Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate, the stable circulating form), Adrenal Androgen, DHEA-SO₄ or DHEA Sulfate, Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate
Category: Hormone / Endocrinology
Purpose:
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) is a hormone naturally produced by the adrenal glands. DHEA contributes to the production of other hormones, such as testosterone and estrogen. Natural DHEA levels peak in early adulthood and then gradually decline with age.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of adrenal tumors or hyperplasia
- Investigation of hirsutism and virilization in women
- Workup of amenorrhea or infertility
- Assessment of androgen deficiency or excess in both sexes
Typical Normal Range:
- Adult Men: ~280 – 640 µg/dL
- Adult Women: ~65 – 380 µg/dL
- Declines progressively with age
Related Tests: Testosterone, Androstenedione, Cortisol, LH, FSH, 17-Hydroxyprogesterone Test, Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) Test,
Notes:
DHEA is produced mainly by the adrenal cortex; elevated levels may suggest adrenal hyperplasia or tumors, while low levels can indicate adrenal insufficiency. DHEA-S is the preferred test due to its stability.
DHEAS – Dehydroepiandrosterone-Sulfate (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Dehydroepiandrosterone-Sulfate
Alternative Names: DHEA-S, Adrenal Androgen Sulfate, Dehydroepiandrosterone-Sulfate, DHEA Test,
Category: Hormone / Endocrinology
Purpose:
DHEAS (dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate) is a hormone that acts as a precursor to sex hormones such as estrogen and testosterone, supports the development of male and female characteristics, and plays a role in the immune and nervous systems.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Investigation of hirsutism, acne, or virilization in women
- Evaluation of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Workup of adrenal tumors or adrenal hyperplasia
- Assessment of androgen deficiency in men and women
Typical Normal Range:
- Adult Men: ~80 – 560 µg/dL
- Adult Women: ~35 – 430 µg/dL
- Peaks in early adulthood, declines with age
Related Tests: DHEA, Testosterone, Androstenedione, Cortisol, LH, FSH, Testosterone and Estrogen Tests, Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) Test, 17-Hydroxyprogesterone Test,
Notes:
DHEAS is almost exclusively produced by the adrenal glands and is more reliable than DHEA due to its longer half-life and stable serum levels.
Dig – Digoxin (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Digoxin
Alternative Names: Lanoxin Level, Digitalis Level, Digoxin Level, Cardiac Glycoside Assay
Category: Therapeutic Drug Monitoring / Cardiology
Purpose:
Digoxin is a cardiac glycoside. It’s used to control heart problems such as arrhythmias, including atrial fibrillation. It can also help manage the symptoms of heart failure, usually in conjunction with other medications.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Monitoring therapy in patients with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter
- Management of heart failure patients on digoxin
- Evaluating suspected digoxin toxicity (e.g., nausea, visual changes, arrhythmias)
- Assessing compliance and dose adjustment in long-term therapy
Typical Normal Range:
- Adult Men: ~80 – 560 µg/dL
- Adult Women: ~35 – 430 µg/dL
- Peaks in early adulthood, declines with age
Related Tests: Electrolytes (especially K⁺, Mg²⁺, Ca²⁺), ECG, Renal Function Tests (Creatinine, BUN), Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
Notes:
Digoxin has a narrow therapeutic index; toxicity risk increases with renal impairment, electrolyte imbalances, and drug interactions. Levels should be drawn at least 6–8 hours after the last dose for accuracy.
Tests Starting from E
EOS – Eosinophils (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Eosinophils
Alternative Names: Absolute Eosinophil Count (AEC), Eosinophil % (as part of CBC with Differential), Eos, Eosinophil Count,
Category: Hematology / White Blood Cell Differential
Purpose:
Eosinophils (EOS) are white blood cells that defend the body against parasitic infections, especially worms, and play a role in allergic reactions by helping to control inflammation and contain foreign substances.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Workup of allergies, asthma, and atopic disorders
- Suspected parasitic or helminthic infections
- Monitoring eosinophilic disorders (e.g., eosinophilic esophagitis, hypereosinophilic syndrome)
- Evaluation of certain hematologic malignancies (e.g., leukemia, lymphoma)
Typical Normal Range:
- Relative: 0 – 6% of total WBC
- Absolute: 0.0 – 0.5 × 10⁹/L (0 – 500/µL)
Related Tests: CBC with Differential, Basophils, IgE, Bone Marrow Examination, Total White Blood Cell (WBC) Count, Neutrophils (NEUT), Lymphocytes (LYMPH), Monocytes (MONO), Basophils (BASO)
Notes:
Elevated eosinophils (eosinophilia) are most often due to allergy or parasitic infection, but persistent or marked eosinophilia may indicate hematologic disease.
EPO – Erythropoietin (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Erythropoietin
Alternative Names: Erythropoietin Hormone Test, Serum EPO
Category: Hormone / Hematology
Purpose:
Erythropoietin (EPO) is a hormone produced primarily by the kidneys that stimulates the bone marrow to produce red blood cells, which are essential for transporting oxygen throughout the body. It is released in response to low tissue oxygen levels. The main purpose of EPO is to maintain a sufficient red blood cell mass to meet the body’s oxygen needs.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of unexplained anemia
- Differentiation between primary and secondary polycythemia
- Monitoring patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD)
- Workup of bone marrow disorders (e.g., aplastic anemia, myelodysplastic syndrome)
Typical Normal Range:
- 4 – 25 mIU/mL (ranges may vary by lab and altitude)
Related Tests: Hemoglobin, Hematocrit, Reticulocyte Count, Iron Studies, Kidney Function Tests, Complete Blood Count (CBC), Genetic Testing, Bone Marrow Biopsy
Notes:
EPO is produced mainly by the kidneys; low levels are common in CKD-related anemia, while high levels may indicate hypoxia, tumors, or secondary polycythemia.
ERA – Estrogen Receptor Assay (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Estrogen Receptor Assay
Alternative Names: ER Test, Estrogen Receptor Status, Hormone Receptor Status, ER/PR IHC Test
Category: Oncology / Pathology (Immunohistochemistry or Molecular Testing)
Purpose:
An estrogen receptor (ER) test determines whether a patient’s cancer cells, particularly breast cancer cells, possess estrogen receptors (ERs), proteins that bind estrogen and can promote cancer growth. This test is intended to guide treatment decisions by helping doctors determine if the cancer is hormone-sensitive and, therefore, likely to respond to hormone therapy, a type of endocrine treatment.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Breast cancer diagnosis and treatment planning
- Prognostic evaluation in breast cancer
- Selection of patients for hormone therapy (e.g., tamoxifen)
- Monitoring recurrence risk in ER-positive tumors
Typical Normal Range:
- Reported as Positive or Negative (% receptor expression, Allred score, or H-score)
Related Tests: Progesterone Receptor (PR) Assay, HER2/neu Testing, Ki-67, Oncotype DX, Breast Biopsy, Genetic Testing
Notes:
ER positivity suggests potential benefit from endocrine (hormonal) therapy; interpretation should be in conjunction with PR and HER2 status.
ESR – Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate
Alternative Names: Sed Rate, Westergren ESR, Sedimentation rate, Fåhraeus-Westergren test
Category: Hematology / Inflammation Marker
Purpose:
The purpose of an erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test is to detect and monitor systemic inflammation in the body by measuring the rate at which red blood cells settle into a test tube.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of systemic inflammation
- Suspected autoimmune disorders (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, lupus)
- Monitoring chronic infections or inflammatory diseases
- Adjunct in diagnosis of temporal arteritis or polymyalgia rheumatica
Typical Normal Range:
- Men: 0 – 15 mm/hr
- Women: 0 – 20 mm/hr
- (values increase with age)
Related Tests: C-Reactive Protein (CRP), CBC, ANA, Rheumatoid Factor, Plasma Viscosity (PV) Test, Procalcitonin (PCT) Test, Rheumatoid Factor (RF) and Anti-CCP (Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide) Antibody Test
Notes:
ESR is nonspecific and can be influenced by anemia, pregnancy, age, and other conditions; best interpreted with clinical findings and other tests.
Tests Starting from F
FBS – Fasting Blood Sugar (Glucose) (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Fasting Blood Sugar
Alternative Names: Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG), Fasting Glucose Test, Blood Sugar Test, Fasting Blood Glucose (FBG)
Category: Biochemistry / Diabetes Test
Purpose:
The primary purpose of a fasting blood glucose (FBS) test is to detect, diagnose, and manage conditions such as prediabetes, diabetes (type 1, type 2, and gestational), and other conditions that affect blood sugar levels after an overnight fast of at least eight hours.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Screening for diabetes and prediabetes
- Monitoring known diabetes patients
- Evaluation of hypoglycemia
- Assessment of metabolic health during routine check-ups
Typical Normal Range:
- Normal: < 100 mg/dL
- Prediabetes: 100 – 125 mg/dL
- Diabetes: ≥ 126 mg/dL (on more than one occasion)
Related Tests: HbA1c, Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT), Random Blood Sugar (RBS), Postprandial Glucose (PPBS)
Notes:
Requires at least 8 hours of fasting; affected by stress, illness, and medications.
Fe – Total Iron (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Total Iron
Alternative Names: Serum Iron, Iron Level, Fe, Serum, Fe (or Fe+2, Ferrous Ion),
Category: Biochemistry / Iron Studies
Purpose:
Total iron is essential for oxygen transport by hemoglobin and myoglobin, energy production, DNA synthesis, hormone production, and immune function. It is also a component of vital enzymes involved in cellular processes and contributes to brain function and neurotransmitter synthesis.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of iron deficiency anemia
- Investigation of iron overload disorders (e.g., hemochromatosis)
- Monitoring response to iron therapy
- Assessment of chronic diseases affecting iron metabolism
Typical Normal Range:
- Men: 65 – 175 µg/dL
- Women: 50 – 150 µg/dL
Related Tests: Ferritin, Total Iron-Binding Capacity (TIBC), Transferrin Saturation, Hemoglobin, CBC, UIBC
Notes:
Levels can fluctuate with diet, time of day, and recent iron intake; interpretation requires correlation with other iron studies.
FEP – Free Erythrocyte Protoporphyrin (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Free Erythrocyte Protoporphyrin
Alternative Names: Zinc Protoporphyrin (ZPP), Erythrocytic Protoporphyrin, RBC Porphyrins
Category: Hematology / Toxicology
Purpose:
The primary purpose of the free red cell protoporphyrin (FEP) test is to serve as a screening test for lead poisoning, particularly in children, and to help classify small cell red cell disorders.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Screening for lead exposure (especially in children)
- Evaluation of iron deficiency anemia
- Monitoring occupational lead toxicity
- Assessment of disorders affecting heme synthesis
Typical Normal Range:
- < 70 µg/dL RBCs (values may vary by lab)
Related Tests: Blood Lead Level, Ferritin, Serum Iron, TIBC, Hemoglobin, Zinc Protoporphyrin (ZPP) Test,
Notes:
Elevated FEP/ZPP occurs before anemia develops in lead poisoning or iron deficiency; useful as an early marker.
FFN – Fetal Fibronectin(Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Fetal Fibronectin
Alternative Names: fFN Test, Preterm Labor Test, Quick Check fFN test , Rapid fFN test
Category: Obstetrics / Prenatal Test
Purpose:
The fetal fibronectin (fFN) test measures the level of fFN, a protein that acts as a “glue” between the amniotic sac and the uterine lining, to predict the risk of preterm birth in symptomatic or high-risk pregnant women. A positive result indicates a possible risk of preterm birth in the coming days or weeks, allowing for early intervention to manage the pregnancy or prepare the baby for preterm birth.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Pregnant women with symptoms of preterm labor
- Assessment of risk for delivery within 7–14 days
- Decision-making for hospital admission or interventions in suspected preterm labor
- Monitoring high-risk pregnancies
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (no fFN detected)
Related Tests: Cervical Length Measurement (Ultrasound), NST (Non-Stress Test), Amniotic Fluid Tests, Actim Partus Test, Ferning Test, Nitrazine Test,
Notes:
A negative test has high negative predictive value, meaning preterm delivery is unlikely within 2 weeks; positive results require correlation with clinical findings.
FFQ – Fecal Fat(Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Fecal Fat Quantification (or Fecal Fat Test)
Alternative Names: Stool Fat Test, 72-Hour Fecal Fat, Quantitative Stool Fat, Qualitative Stool Fat, Stool Lipids, Total Fat, Quantitative, Quantitative Stool Fat Determination, Fat Absorption, Coefficient of Fat Absorption (CFA)
Category: Gastroenterology / Stool Test
Purpose:
A fecal fat test (FFQ) measures the amount of fat in a stool sample to determine whether the body is adequately absorbing dietary fat. It can be used to diagnose malabsorption, a condition characterized by poor digestion or absorption of food by the digestive system, often characterized by symptoms such as persistent diarrhea and fatty, foul-smelling stools.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Chronic diarrhea of unclear cause
- Suspected malabsorption syndromes (e.g., celiac disease, chronic pancreatitis)
- Evaluation of cystic fibrosis-related malabsorption
- Monitoring response to treatment in malabsorption disorders
Typical Normal Range:
- < 7 g fat/24 hours (on a 72-hour stool collection with standard fat diet)
Related Tests: Fecal Elastase, D-xylose Absorption Test, Serum Albumin, Stool Pancreatic Enzymes, Fecal Calprotectin, FIT, Ova and Parasite, CBC, CMP, Celiac Disease Antibody Tests, Vitamin and Mineral Levels, Endoscopy with Biopsy, CT scan, MRI
Notes:
Requires strict dietary preparation and timed stool collection; qualitative “sudan stain” may be used as a screening method.
Fol – Folate(Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Folate (Vitamin B9)
Alternative Names: Folic Acid, Serum Folate, RBC Folate, Vitamin B-9 test
Category: Vitamin / Nutritional Test
Purpose:
Folic acid performs many functions in the body: it promotes tissue growth and cell function. It works synergistically with vitamin B12 and vitamin C to help the body break down, utilize, and produce new proteins. It contributes to the formation of red blood cells (prevents anemia).
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of megaloblastic anemia
- Suspected malnutrition or malabsorption (e.g., celiac disease)
- Monitoring patients with increased folate needs (pregnancy, hemolytic anemia)
- Differentiating between folate and vitamin B12 deficiency
Typical Normal Range:
- Serum Folate: 2 – 20 ng/mL (varies by lab)
- RBC Folate: > 150 ng/mL
Related Tests: Vitamin B12, Homocysteine, Methylmalonic Acid, CBC,
Notes:
Folate deficiency causes megaloblastic anemia; must be differentiated from B12 deficiency, as both can present similarly but have different treatments.
FT3 – Free T3(Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Free Triiodothyronine
Alternative Names: Free T3, FT3, Thyroid function test
Category: Endocrinology / Thyroid Function Test
Purpose:
The primary purpose of the FT3 (free T3) test is to measure the biologically active thyroid hormone that regulates metabolism, energy, and organ function. It allows physicians to diagnose thyroid disorders such as hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism, evaluate the effectiveness of T3 treatment, and monitor thyroid status, often in combination with TSH and FT4 measurements for a comprehensive assessment of thyroid health.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Diagnosis and monitoring of hyperthyroidism
- Evaluation of suppressed TSH with normal FT4 (T3-toxicosis)
- Assessment of thyroid hormone replacement therapy
- Differentiation of thyroid disease subtypes
Typical Normal Range:
- 2.0 – 4.4 pg/mL (may vary by lab)
Related Tests: TSH, Free T4 (FT4), Total T3, Total T4, Thyroid Antibodies,
Notes:
More specific than total T3 as it is unaffected by binding protein levels; interpretation should be in context with TSH and FT4.
FT4 – Free Thyroxine (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Free Thyroxine
Alternative Names: Free T4, FT4, Free thyroxine test, Free thyroxine concentration, Thyroxine test by equilibrium dialysis
Category: Endocrinology / Thyroid Function Test
Purpose:
The main purpose of the free thyroxine (FT4) blood test is to measure the level of active thyroid hormone in the blood to assess thyroid function and diagnose conditions such as hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) or hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid).
Commonly Ordered For:
- Diagnosis and monitoring of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism
- Evaluation of abnormal TSH results
- Monitoring thyroid hormone replacement therapy
- Differentiating primary vs. secondary thyroid disorders
Typical Normal Range:
- 0.8 – 1.8 ng/dL (may vary by lab)
Related Tests: TSH, Free T3 (FT3), Total T4, Total T3, Thyroid Antibodies, TPOAb, TgAb, TSHR Ab or TRAb, Thyroglobulin Test, Thyroid Ultrasound
Notes:
Provides a more accurate measure of thyroid status than total T4, as it is not affected by binding protein changes.
Tests Starting from G
G2PP – 2 Hour Postprandial Glucose (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: 2-Hour Postprandial Glucose
Alternative Names: 2h PP Glucose, 2-Hour PPBS, Postprandial Glucose, Glucose, 2-hour postprandial, Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
Category: Biochemistry / Diabetes Test
Purpose:
The 2-hour postprandial glucose (2PPG) test determines how the body processes glucose after a meal and serves as a key diagnostic tool for diabetes by measuring whether blood sugar levels return to normal within two hours of eating.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Screening and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus
- Monitoring glycemic control in known diabetics
- Evaluation of post-meal hyperglycemia
- Assessment of therapy effectiveness in diabetes management
Typical Normal Range:
- Normal: < 140 mg/dL
- Prediabetes (Impaired Glucose Tolerance): 140 – 199 mg/dL
- Diabetes: ≥ 200 mg/dL
Related Tests: Fasting Blood Glucose Test (FPG), Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT), HbA1c, Random Blood Sugar (RBS)
Notes:
Requires fasting baseline glucose and a standardized meal or glucose load; often paired with FBS for comprehensive evaluation.
G-6-PD – Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase
Alternative Names: G6PD Test, G6PD Deficiency Test, RBC G6PD test, G6PD enzyme activity test, Favism
Category: Enzyme / Hematology
Purpose:
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) protects red blood cells from oxidative damage by providing NADPH, which prevents the buildup of harmful molecules called reactive oxygen species. This enzyme is essential for proper red blood cell function and is their primary source of NADPH.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of unexplained hemolytic anemia
- Suspected G6PD deficiency (especially in males from high-risk ethnic groups)
- Neonatal jaundice investigation
- Before prescribing oxidant drugs (e.g., primaquine, sulfa drugs)
Typical Normal Range:
- 5 – 14 U/g Hb (varies by method and lab)
Related Tests: CBC, Reticulocyte Count, Peripheral Smear, Bilirubin, Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Test, Haptoglobin Level,
Notes:
Low levels indicate G6PD deficiency, which predisposes to hemolysis after oxidative stress; testing during acute hemolysis may yield false-normal results due to young RBCs.
Gamma GT – Gamma Glutamyl Transferase(Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Gamma Glutamyl Transferase
Alternative Names: GGT, γ-GT, Gamma-Glutamyltranspeptidase, GTP
Category: Liver Function Test (LFT) / Enzyme
Purpose:
The primary purpose of the gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) test is to detect and aid in the diagnosis of liver and biliary tract diseases by measuring the blood concentration of the enzyme GGT. Elevated GGT levels can also help detect or monitor alcohol abuse, differentiate between liver and bone diseases, and detect other conditions such as heart, pancreas, or lung disease.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of liver disease (hepatitis, cirrhosis)
- Detection of cholestasis or bile duct obstruction
- Assessment of alcohol use or alcohol-related liver injury
- Monitoring hepatotoxic drug effects
Typical Normal Range:
- Men: 10 – 70 U/L
- Women: 6 – 42 U/L (ranges vary by lab)
Related Tests: ALT, AST, ALP, Bilirubin, LDH, Albumin and Total Protein Tests,
Notes:
Highly sensitive but not specific; elevated in many liver and biliary disorders, and also in chronic alcohol use and certain medications.
GCT – Glucose Challenge Test (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Glucose Challenge Test
Alternative Names: 50g Oral Glucose Challenge, Gestational Diabetes Screening Test, Glucose screening test, 1-hour glucose tolerance test, Oral glucose challenge test (OGCT)
Category: Obstetrics / Diabetes Screening
Purpose:
The primary purpose of the glucose challenge test (GCT) is to detect gestational diabetes, a condition that develops during pregnancy. This routine prenatal test, usually performed between weeks 24 and 28 of pregnancy, evaluates the body’s response to a sugary drink to detect an increased likelihood of gestational diabetes.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Routine screening in pregnant women (24–28 weeks gestation)
- High-risk pregnancies (family history, obesity, prior GDM)
- Early pregnancy if risk factors are present
- Monitoring women with borderline glucose tolerance
Typical Normal Range:
- 1-hour value after 50g glucose load: < 140 mg/dL (normal)
- 140–199 mg/dL: Abnormal, requires OGTT
- ≥ 200 mg/dL: Diagnostic of diabetes (without OGTT)
Related Tests: OGTT (Oral Glucose Tolerance Test), Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS), HbA1c,
Notes:
Performed without fasting; abnormal results are followed by a confirmatory OGTT.
GDS – Gestational Diabetes Screen (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Gestational Diabetes Screen
Alternative Names: Glucose Screening Test, GCT (Glucose Challenge Test), One-Hour Glucose Test, 50-gram, 1-hour Glucose Challenge Test
Category: Obstetrics / Diabetes Screening
Purpose:
Gestational diabetes screening (GDS) is a blood test performed during pregnancy to detect gestational diabetes by measuring high blood sugar levels. The goal of GDS is to detect gestational diabetes early so it can be managed with diet, exercise, or insulin, thereby preventing potential complications for both mother and baby, such as high birth weight or future type 2 diabetes.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Routine screening in pregnant women (24–28 weeks gestation)
- High-risk pregnancies (family history, obesity, prior GDM)
- Early pregnancy if risk factors are present
- Monitoring women with borderline glucose tolerance
Typical Normal Range:
- 1-hour value after 50g glucose load: < 140 mg/dL (normal)
- 140–199 mg/dL: Abnormal, requires OGTT
- ≥ 200 mg/dL: Diagnostic of diabetes (without OGTT)
Related Tests: OGTT (Oral Glucose Tolerance Test), Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS), HbA1c, Glucose Challenge Test (GDS),
Notes:
Performed without fasting; abnormal results are followed by a confirmatory OGTT.
GFR – Glomerular filtration rate (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Glomerular Filtration Rate
Alternative Names: eGFR (Estimated GFR), Creatinine Clearance (CrCl, when measured directly), Calculated GFR (cGFR)
Category: Nephrology / Kidney Function Test
Purpose:
The primary purpose of the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is to measure kidney function by indicating how quickly the kidneys filter waste and excess fluid from the blood. A GFR test can help determine the stage of chronic kidney disease (CKD), guide treatment and medication dosages, and inform decisions about interventions such as dialysis or transplantation.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of chronic kidney disease (CKD)
- Monitoring progression of renal disease
- Assessment before prescribing nephrotoxic drugs
- Kidney function check in hypertension and diabetes patients
Typical Normal Range:
- ≥ 90 mL/min/1.73 m²
- Mildly decreased: 60–89 mL/min/1.73 m²
- Moderately to severely decreased: < 60 mL/min/1.73 m² (CKD threshold)
Related Tests: Serum Creatinine, BUN, Urine Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio (ACR), Cystatin C, Creatinine, Creatinine Clearance, UACR,
Notes:
eGFR is calculated from serum creatinine (or cystatin C) using equations (e.g., CKD-EPI); values <60 for >3 months indicate CKD.
GGT – Gamma Glutamyl Transferase (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Gamma Glutamyl Transferase
Alternative Names: Gamma-Glutamyl Transpeptidase (GGTP), γ-GT, GTP
Category: Liver Function Test (LFT), Enzyme Assay
Purpose:
A gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) blood test measures the level of this enzyme, found primarily in the liver and bile ducts, to detect and monitor liver and bile duct diseases, detect alcohol use, and help differentiate liver problems from bone disorders.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected liver disease or bile duct obstruction
- Evaluation of alcohol use or abuse
- Unexplained elevated alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
- Monitoring patients on hepatotoxic drugs
Typical Normal Range:
- ~ 9–48 U/L (values may vary by lab, sex, and age)
Related Tests: ALT, AST, ALP, Bilirubin, Liver Function Tests (LFTs), Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) Screening
Notes:
Highly sensitive but not specific; often elevated with alcohol intake and certain medications.
GH – Growth Hormone (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Growth Hormone
Alternative Names: Somatotropin, hGH (human Growth Hormone), GH test, Growth hormone stimulation test, Growth hormone suppression test
Category: Endocrine/Hormone Test
Purpose:
Growth hormone influences our height and contributes to the development of our bones and muscles. Its natural levels fluctuate throughout the day, apparently influenced by physical activity. For example, they increase with exercise. Growth hormone levels increase during childhood and peak during puberty.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of growth disorders in children (short stature, gigantism)
- Suspected acromegaly in adults
- Assessment of pituitary gland function
- Monitoring treatment of GH deficiency or excess
Typical Normal Range:
- Men: < 5 ng/mL
- Women: < 10 ng/mL
- Children: Variable depending on age and pubertal stage
Related Tests: IGF-1, GH Stimulation Test, GH Suppression Test, Prolactin, IGFBP-3
Notes:
Levels fluctuate throughout the day; dynamic stimulation or suppression tests often required for accurate diagnosis.
Glu – Glucose (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Glucose
Alternative Names: Blood Sugar, Blood Glucose, Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS), Random Blood Sugar (RBS), Fasting plasma glucose (FPG), Fasting blood glucose (FBG), Casual plasma glucose test, Glucose tolerance test (GTT), Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), Glucose challenge test (GCT), Hemoglobin A1C (HbA1c), Glycohemoglobin, Glycated hemoglobin
Category: Metabolic Test
Purpose:
Glucose (GLU) is the body’s primary source of energy. Its main function is to provide the fuel needed for cellular activity, particularly brain activity. In medicine, glucose supplements are used to rapidly raise dangerously low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia) and to provide nutritional support to people who are unable to eat.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Screening and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus
- Monitoring glucose control in diabetic patients
- Evaluation of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia
- Routine health checkups
Typical Normal Range:
- Fasting: 70–99 mg/dL
- Random: < 140 mg/dL
Related Tests: HbA1c, Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT), Insulin, C-Peptide, Fasting Blood Glucose Test, Random Blood Glucose Test, Urine Glucose Test,
Notes:
Levels may vary with diet, stress, illness, and medications; fasting sample preferred for diagnostic accuracy.
GPR – Gram-Positive Rods (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Gram-Positive Rods
Alternative Names: Gram-Positive Bacilli, GPR on Microscopy, Georadar, Ground probing radar, Subsurface radar, Surface-penetrating radar
Category: Microbiology / Bacteriology
Purpose:
The primary goal of identifying Gram-positive bacilli (GPBs) is to facilitate the diagnosis and treatment of bacterial infections, as well as to understand their role in various ecosystems and biotechnological processes. GPBs are classified based on their ability to retain the crystal violet dye in Gram staining, which indicates a thick peptidoglycan cell wall.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Investigation of bloodstream infections (e.g., Listeria, Bacillus, Clostridium)
- Evaluation of wound, abscess, or soft tissue infections
- Diagnosis of gastrointestinal infections (Clostridium difficile)
- Differentiation of bacterial morphology during Gram stain
Typical Normal Range:
- Fasting: 70–99 mg/dL
- Random: < 140 mg/dL
Related Tests: Gram Stain, Bacterial Culture & Sensitivity, PCR for specific pathogens, Electromagnetic (EM) Locating, Seismic Reflection/Refraction, Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT), Ultrasonic Testing (UT), Magnetic Surveying
Notes:
GPRs may represent contaminants (e.g., Corynebacterium) or serious pathogens; clinical correlation essential.
Tests Starting from H
H&H – Hemoglobin and Hematocrit (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Hemoglobin and Hematocrit
Alternative Names: Hb & Hct, Hemoglobin/Hematocrit Panel, Packed Cell Volume (PCV)
Category: Hematology / Blood Test
Purpose:
The hemoglobin (Hgb) and hematocrit (Hct) test, or H&H, evaluates the amount of hemoglobin, an oxygen-carrying protein, and the percentage of red blood cells in the blood to assess overall health, diagnose conditions such as anemia, and monitor the effectiveness of treatments.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Screening and diagnosis of anemia
- Monitoring blood loss or response to transfusion
- Evaluation of dehydration or overhydration
- Assessment of polycythemia or chronic hypoxia
Typical Normal Range:
- Hemoglobin: Men 13.5–17.5 g/dL; Women 12.0–15.5 g/dL
- Hematocrit: Men 41–53%; Women 36–46%
Related Tests: CBC, RBC Count, MCV, MCH, Iron Studies, Reticulocyte Count, White Blood Cell (WBC) Count, Platelet Count, Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW)
Notes:
Hematocrit is generally about three times the hemoglobin value; results must be interpreted with hydration status in mind.
Hapto – Haptoglobin (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Hp, Serum Haptoglobin
Alternative Names: Hp, Serum Haptoglobin, Haptoglobin, blood test, Hemoglobin-binding protein
Category: Hematology / Protein Test
Purpose:
The main function of haptoglobin is to bind to free hemoglobin, a protein released by red blood cells during their destruction, to prevent kidney and tissue damage. It acts as an antioxidant, neutralizes the harmful effects of free iron, and acts as an acute-phase reactant, increasing its concentration during inflammation to limit damage and regulate the immune response.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected hemolytic anemia
- Differentiating intravascular vs extravascular hemolysis
- Monitoring hemolytic disease progression or treatment
- Evaluation of unexplained anemia or jaundice
Typical Normal Range:
- 30–200 mg/dL (values may vary by lab)
Related Tests: LDH, Indirect Bilirubin, Reticulocyte Count, Direct Antiglobulin Test (Coombs), CBC, Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Test, Bilirubin Tes, Blood Smear, Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT)
Notes:
Low levels suggest intravascular hemolysis; haptoglobin is an acute-phase reactant and may be elevated in inflammation or infection.
HAV – Hepatitis A virus (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Hepatitis A Virus
Alternative Names: Hep A, Anti-HAV Test, Viral Hepatitis A Antibody, HAV Immunity Determination, HAV Vaccination Status, Hep A Vaccination Status, HAV-Ab IgM, HAV-Ab IgG, HAV-Ab Total
Category: Infectious Disease / Serology
Purpose:
The hepatitis A virus (HAV) replicates and spreads by infecting human liver cells (hepatocytes) and causing liver inflammation through the immune system. To do so, HAV enters the body through the fecal-oral route, often through contaminated food or water, causing symptoms such as fever, nausea, and jaundice.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of acute hepatitis symptoms (jaundice, fatigue, abdominal pain)
- Determining cause of elevated liver enzymes
- Assessing immunity after vaccination
- Screening in outbreak investigations
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (non-reactive) for HAV IgM and IgG in unexposed individuals
Related Tests: HAV IgM, HAV IgG, Hepatitis B Panel, Hepatitis C Antibody, Liver Function Tests, Total Hepatitis A Antibody Test, Nucleic Acid Amplification Testing (NAAT), Hepatitis Virus Panel
Notes:
HAV IgM → indicates recent/acute infection.
HAV IgG → indicates past infection or immunity from vaccination.
Transmission is fecal–oral; infection is self-limiting and does not cause chronic disease.
HbA1c – Hemoglobin A1c (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Hemoglobin A1c
Alternative Names: Glycated Hemoglobin, A1c, Glycohemoglobin, HbA1c,
Category: Diabetes / Metabolic Test
Purpose:
The HbA1c (hemoglobin A1c) test is used to diagnose diabetes and monitor blood sugar levels in people with or at risk for it. It measures average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months by determining the percentage of hemoglobin bound to glucose in red blood cells.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Diagnosis of diabetes mellitus
- Monitoring long-term glycemic control in diabetic patients
- Assessing effectiveness of therapy (insulin/oral agents)
- Evaluating risk of diabetes-related complications
Typical Normal Range:
- Normal: < 5.7%
- Prediabetes: 5.7–6.4%
- Diabetes: ≥ 6.5%
Related Tests: Fasting Glucose, OGTT, Random Plasma Glucose Test, Fructosamine, Estimated Average Glucose (eAG), OGTT, Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG) Test,
Notes:
Not affected by short-term glucose changes; may be unreliable in hemoglobinopathies, anemia, or conditions affecting red cell lifespan.
HBeAb – Hepatitis Be Virus Antibody (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Hepatitis B e Antibody
Alternative Names: Anti-HBe, Antibody to Hepatitis B e-Antigen, Hep B e Antibody, Hepatitis B Virus e-Antibody
Category: Infectious Disease / Hepatitis B Serology
Purpose:
The HBeAb test detects antibodies against the hepatitis B virus “e” antigen (HBeAg), indicating decreased viral replication and a lower risk of transmission. A positive HBeAb test result generally indicates that the immune system has responded to the infection, often marking a transition to a less active or even inactive phase of chronic hepatitis B, or a favorable outcome from antiviral treatment.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Monitoring chronic Hepatitis B infection
- Assessing response to antiviral therapy
- Determining infectivity in HBV carriers
- Evaluating transition from active to inactive HBV infection
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (non-reactive) in unexposed/uninfected individuals
Related Tests: HBsAg, Anti-HBs or HBsAb, HBcAb (IgM/IgG), Hepatitis B e-Antigen (HBeAg), HBV DNA, Hepatitis B Viral DNA (HBV DNA) or Viral Load Test, Hepatitis B Core Antibody (Anti-HBc or HBcAb)
Notes:
Presence of HBeAb usually indicates reduced viral replication and lower infectivity; interpretation must be combined with HBsAg and HBV DNA results.
HBeAg – Hepatitis Be Virus Antigen (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Hepatitis B e Antigen
Alternative Names: HBV e Antigen, Hepatitis B Envelope Antigen Test
Category: Infectious Disease / Viral Hepatitis Serology
Purpose:
The HBe antigen, or hepatitis B e antigen, is a viral protein released into the blood during active hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, indicating high viral replication and infectivity. Its presence is an indicator of active infection, helping to determine whether the virus is actively replicating in the liver and can be transmitted to other people.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Diagnosis and staging of Hepatitis B infection
- Determining infectivity and risk of transmission
- Monitoring response to antiviral therapy
- Assessing vertical (mother-to-child) transmission risk in pregnancy
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (non-reactive) in uninfected individuals
Related Tests: HBsAg, HBsAb, HBcAb (IgM/IgG), HBeAb, HBV DNA, Anti-HBs (Hepatitis B surface antibody) Test, Anti-HBc (Hepatitis B core antibody) Test, Anti-HBe (Hepatitis B e-antibody) Test, Liver Function Tests (e.g., ALT and AST), Hepatitis B Core-Related Antigen (HBcrAg)
Notes:
Persistent HBeAg positivity indicates ongoing viral replication; seroconversion to HBeAb usually suggests lower infectivity and better prognosis.
HBsAb – Hepatitis B Surface Antibody (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
Alternative Names: Anti-HBs, Hepatitis B Surface Antibody, Quantitative, Hepatitis B Titer
Category: Infectious Disease / Viral Hepatitis Serology
Purpose:
The primary purpose of the hepatitis B surface antibody (HBsAb) test is to determine a person’s immunity to the hepatitis B virus (HBV). A positive HBsAb result indicates that the person is protected against the virus, either because they have successfully received the hepatitis B vaccine or because they have recovered from a previous infection.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Checking immunity after HBV vaccination
- Determining recovery from past HBV infection
- Pre-employment or healthcare worker screening
- Assessing need for HBV immunization
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (non-reactive) in susceptible individuals; protective immunity ≥ 10 mIU/mL
Related Tests: HBsAg, HBcAb (IgM/IgG), HBeAg, HBeAb, HBV DNA, Anti-HBc (Hepatitis B core antibody) Test
Notes:
Presence of HBsAb alone indicates immunity; interpretation depends on other HBV markers for complete status.
HBsAg – Hepatitis B Surface Antigen (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Hepatitis B Surface Antigen
Alternative Names: Australia Antigen, HBV Surface Antigen, Hep B Antigen, Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Screen
Category: Infectious Disease / Viral Hepatitis Serology
Purpose:
The HBsAg (hepatitis B surface antigen) test detects the presence of this antigen in the blood, indicating an active hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, whether acute or chronic. A positive HBsAg result means a person is contagious and can transmit the virus to others.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Screening for Hepatitis B infection
- Diagnosis of acute or chronic HBV infection
- Prenatal screening to prevent perinatal transmission
- Blood donor screening
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (non-reactive) in uninfected individuals
Related Tests: HBsAb, HBcAb (IgM/IgG), HBeAg, HBeAb, HBV DNA, Anti-HBc (Hepatitis B Core Antibody)
Notes:
First detectable marker in acute HBV infection.
Persistence > 6 months indicates chronic infection.
Interpretation should be combined with other serologic markers
HBV – Hepatitis B virus (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Hepatitis B Virus
Alternative Names: Hep B, HBV Infection, HBsAg test, IgM Anti-HBc
Category: Infectious Disease / Viral Hepatitis
Purpose:
The goal of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) is to replicate and spread to new host cells to ensure its survival and spread. To do so, it invades liver cells (hepatocytes), hijacks their cellular machinery to create new viral components and particles, and then leaves these cells to infect others.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Transmission is via blood, sexual contact, or perinatal route.
- Can cause acute or chronic infection, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Complete interpretation requires a panel of serologic markers and/or viral DNA quantification.
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (no detectable HBV markers or DNA)
Related Tests: HBsAg, HBsAb, HBcAb (IgM/IgG), HBeAg, HBeAb, HBV DNA PCR, Hepatitis B Panel, Hepatitis B e-Antibody, HBcrAg, Liver Function Tests (LFTs), Liver Biopsy
Notes:
Transmission is via blood, sexual contact, or perinatal route.
Can cause acute or chronic infection, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Complete interpretation requires a panel of serologic markers and/or viral DNA quantification.
hCG – Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Human Chorionic Gonadotropin
Alternative Names: Beta-hCG, Pregnancy Hormone
Category: Endocrinology / Reproductive Hormone Test
Purpose:
The purpose of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is to support and maintain early pregnancy by stimulating progesterone production and preparing the uterus for implantation, and to act as a fertility drug to stimulate ovulation in women and increase sperm production in men.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Confirming pregnancy (serum or urine test)
- Monitoring early pregnancy progression and viability
- Diagnosing ectopic pregnancy or miscarriage
- Tumor marker for germ cell tumors and certain trophoblastic diseases
Typical Normal Range:
- Non-pregnant women & men: < 5 mIU/mL
- Pregnancy: Rises rapidly in early gestation (doubling ~ every 48–72 hrs)
Related Tests: Progesterone, LH, FSH, Ultrasound, AFP (in tumor evaluation), Urine Pregnancy Test,
Notes:
Qualitative tests report positive/negative; quantitative tests give exact levels.
Abnormal patterns may indicate ectopic pregnancy, trophoblastic disease, or malignancy.
hCG (urine) – Urine Pregnancy Test (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (Urine Test)
Alternative Names: Urine hCG, Urine Pregnancy Test, Home Pregnancy Test, Beta-hCG – Urine, Qualitative hCG Test (Urine)
Category: Endocrinology / Reproductive Test
Purpose:
A urine sample test looks for the presence of the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), produced in the placenta after a fertilized egg implants in the uterus. This test detects a significant amount by identifying the presence of hCG, a hormone present only in pregnant women.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Early confirmation of pregnancy
- Evaluation of missed or irregular menstrual periods
- Assessment of pregnancy status before procedures or medications
- Screening in emergency or outpatient settings
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (no detectable hCG in non-pregnant individuals)
Related Tests: Serum hCG (quantitative), Progesterone, Ultrasound
Notes:
Detects pregnancy usually within ~10–14 days after conception.
Sensitivity varies by assay; false negatives may occur if done too early.
False positives possible with trophoblastic disease or certain cancers.
HCT – Hematocrit (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Hematocrit
Alternative Names: Packed Cell Volume (PCV), Crit, Hemoglobin and Hematocrit
Category: Hematology / Complete Blood Count (CBC) Component
Purpose:
The main purpose of a hematocrit (HCT) test is to measure the percentage of red blood cells in your blood, which provides a key indicator of your overall health and blood-related problems, such as anemia (too few red blood cells) or polycythemia (too many red blood cells).
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of anemia
- Monitoring blood loss or transfusion needs
- Assessment of polycythemia or chronic hypoxia
- Evaluating dehydration or overhydration
Typical Normal Range:
- Men: 41–53%
- Women: 36–46%
Related Tests: Hemoglobin, RBC Count, MCV, MCH, Reticulocyte Count, Iron Studies
Notes:
Hematocrit is typically about three times the hemoglobin value; results may be affected by hydration status.
HCV – Hepatitis C virus (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Hepatitis C Virus
Alternative Names: Hepatitis C, Anti-HCV (antibody test), HCV RNA,
Category: Infectious Disease / Viral Hepatitis
Purpose:
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) has no beneficial function; rather, it is a pathogen that causes liver inflammation, which can lead to acute or chronic liver disease. Its primary function is its parasitic replication cycle, where it infects and replicates within liver cells, triggering the body’s immune response.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Screening individuals at risk (IV drug use, transfusion history, hemodialysis)
- Evaluation of abnormal liver function tests
- Confirming diagnosis of suspected Hepatitis C infection
- Monitoring response to antiviral therapy
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (non-reactive for HCV antibodies or RNA)
Related Tests: HCV Antibody, HCV RNA PCR, HCV Genotyping, LFTs, HBV and HAV panels, Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B tests
Notes:
Anti-HCV antibody indicates exposure (past or present).
HCV RNA PCR confirms active infection.
Chronic infection can lead to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
HDL – High Density Lipoprotein (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: High Density Lipoprotein
Alternative Names: Good Cholesterol,” HDL-C, High-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels
Category: Lipid Profile / Cardiac Risk Assessment
Purpose:
High-density lipoproteins (HDL) act as “good cholesterol” by collecting excess cholesterol from cells and blood vessel walls and transporting it to the liver for disposal. This “reverse cholesterol transport” helps prevent cholesterol buildup in the arteries, thereby reducing the risk of atherosclerosis, heart attack, and stroke.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of cardiovascular risk
- Monitoring patients with dyslipidemia
- Assessment in metabolic syndrome or obesity
- Follow-up of lipid-lowering therapy
- Routine health screening
Typical Normal Range:
- Men: >40 mg/dL
- Women: >50 mg/dL
Related Tests: LDL, Total Cholesterol, Triglycerides, VLDL, Lipid Profile, HDL Cholesterol
Notes:
Higher HDL levels are generally protective against heart disease; very low HDL increases cardiovascular risk.
HFP – Hepatic Function Panel (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Hepatic Function Panel
Alternative Names: Liver Function Tests (LFTs), Liver Panel, Liver Profile, Basic Liver Profile
Category: Biochemistry / Liver Profile
Purpose:
A liver function panel (HFP), or liver function test, is a blood test used to check for liver damage, infections, diseases, and medication side effects by measuring the levels of proteins, enzymes, and bilirubin in the blood.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Assessment of liver disease (hepatitis, cirrhosis, fatty liver)
- Monitoring hepatotoxic drug therapy
- Evaluation of jaundice
- Screening in patients with alcohol use disorder
- Routine check in chronic conditions (e.g., diabetes, obesity)
Typical Normal Range:
- ALT: 7–56 U/L
- AST: 10–40 U/L
- ALP: 44–147 U/L
- Total Bilirubin: 0.1–1.2 mg/dL
- Albumin: 3.5–5.0 g/dL
Related Tests: Prothrombin Time (PT/INR), GGT, Viral Hepatitis Panel, Abdominal Ultrasound, Liver Enzymes, ALT, AST, ALP, Total Protein,
Notes:
Interpretation requires evaluating patterns (e.g., hepatocellular vs. cholestatic injury). Individual parameters within the panel guide clinical correlation.
HGB – Hemoglobin (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Hemoglobin
Alternative Names: Hb, Hgb, Hemoglobin concentration
Category: Hematology / Complete Blood Count (CBC)
Purpose:
Hemoglobin, or HbA, is the protein in red blood cells responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to the body’s tissues and returning carbon dioxide, a waste product, to the lungs for exhalation. It is essential for cellular respiration, which allows cells to grow, reproduce, and produce energy.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of anemia or polycythemia
- Monitoring blood loss or chronic disease
- Preoperative screening
- Assessment in nutritional deficiencies (iron, B12, folate)
Typical Normal Range:
- Men: 13.5–17.5 g/dL
- Women: 12.0–15.5 g/dL
- Children: 11.0–13.5 g/dL
- Newborns: 14.0–24.0 g/dL
Related Tests: Hematocrit (HCT), RBC Count, MCV, MCH, Iron Studies, Reticulocyte Count, Hemoglobin Electrophoresis, Vitamin B12 and Folate Levels
Notes:
Low HGB indicates anemia; high levels may suggest dehydration, chronic hypoxia, or polycythemia.
HGH – Human Growth Hormone (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Human Growth Hormone
Alternative Names: GH, Somatotropin, HGH
Category: Endocrinology / Hormone Testing
Purpose:
The pituitary gland is a structure in the brain that produces various specialized hormones, including growth hormone (also known as human growth hormone or HGH). This hormone influences our height and contributes to the development of our bones and muscles.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of short stature or growth delay in children
- Diagnosis of growth hormone deficiency or excess
- Assessment of acromegaly or gigantism in adults
- Monitoring response to GH therapy
Typical Normal Range:
- Adults: <10 ng/mL
- Children: variable; levels fluctuate with age and puberty
Related Tests: IGF-1 (Insulin-like Growth Factor 1), GH Stimulation Test, GH Suppression Test, Prolactin, Pituitary Function Tests, HGH Stimulation Test,
Notes:
GH secretion is pulsatile; random levels are often unreliable. Stimulation or suppression tests are preferred for accurate diagnosis.
HIV – Human Immunodeficiency Virus (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Human Immunodeficiency Virus
Alternative Names: HIV Test, HIV Screening, HIV Antibody/Antigen Test, Fourth-generation HIV test, EIA/ELISA, Western blot
Category: Infectious Disease / Serology & Molecular Testing
Purpose:
Abstract. The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system, specifically the CD4 cells (T lymphocytes), which helps it fight infections. If left untreated, HIV can weaken the immune system or lead to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).
Commonly Ordered For:
- Routine screening in high-risk individuals
- Diagnosis of suspected HIV infection
- Monitoring disease progression and treatment response
- Prenatal screening to prevent mother-to-child transmission
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (no HIV detected)
Related Tests: CD4 Count, HIV RNA (Viral Load), Western Blot (confirmatory), Complete Blood Count, Hepatitis Panel,
Notes:
HIV testing is usually performed as a 4th-generation antigen/antibody combination assay. Positive results require confirmatory testing. Early detection and treatment with antiretroviral therapy (ART) greatly improve outcomes.
HPV – Human Papilloma Virus (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Human Papillomavirus
Alternative Names: HPV DNA Test, HPV Screening, Primary HPV Testing,
Category: Infectious Disease / Molecular Testing
Purpose:
The HPV vaccine protects against genital warts and most cervical cancers. It also protects against HPV-caused vaginal, vulvar, penile, and anal cancers. It also protects against HPV-caused mouth, throat, and head and neck cancers.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Cervical cancer screening (often with Pap smear co-testing)
- Follow-up of abnormal Pap smear results
- Monitoring women at increased risk of cervical neoplasia
- Detection of high-risk HPV in men and women with anal or genital lesions
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (no high-risk HPV DNA detected)
Related Tests: Pap Smear (Cytology), Colposcopy, Cervical Biopsy, STI Panel, Primary HPV Testing, HPV/Pap Co-test
Notes:
Persistent infection with high-risk HPV types (especially 16 and 18) is strongly linked to cervical and other anogenital cancers. Vaccination significantly reduces infection risk.
HSV – Herpes Simplex Virus (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Herpes Simplex Virus
Alternative Names: HSV Test, HSV-1/HSV-2 Antibody Test, HSV PCR, Herpes Serology, Herpes Simplex Virus Culture, Herpes Simplex Virus Culture, Tzanck Smear, HSV NAAT Testing, Serum herpes simplex antibodies, DFA Test
Category: Infectious Disease / Virology
Purpose:
HSV testing can determine if you have a herpes infection. However, your healthcare provider may perform the HSV test in different ways, depending on whether you have lesions or blisters. If you have lesions or blisters, your healthcare provider will take a sample of fluid from the lesion with a swab.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Diagnosis of genital or oral herpes lesions
- Differentiation between HSV-1 and HSV-2 infections
- Evaluation of recurrent ulcers or blisters
- Screening in pregnancy to prevent neonatal herpes transmission
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (no HSV detected)
Related Tests: VZV (Varicella-Zoster Virus), Syphilis Serology, HIV, STI Panel, Gonorrhea Test, HPV Testing, Chlamydia Testing
Notes:
PCR is the most sensitive test for active infection. Serology distinguishes prior exposure but cannot always confirm timing of infection. HSV remains latent and may reactivate.
Tests Starting from I
iCa – Ionized Calcium (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Ionized Calcium
Alternative Names: Free Calcium, Unbound Calcium, Ionized Calcium, Serum, Ca Ionized, Serum
Category: Electrolyte / Mineral Test
Purpose:
Ionized calcium (iCa), or free calcium, is the active form of calcium in the blood, essential for many bodily functions, such as nerve signaling, muscle contraction, heart function, and blood clotting. It is measured through a specific blood test, which a doctor may order to assess a patient’s active calcium level, especially in cases of serious illness, surgery, kidney problems, or parathyroid disorders.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of parathyroid function
- Monitoring critically ill patients (ICU, sepsis, trauma)
- Assessment of calcium metabolism disorders
- Monitoring after major surgery or blood transfusion
Typical Normal Range:
- 1.12 – 1.32 mmol/L (may vary by lab)
Related Tests: Total Calcium, Serum Albumin, Parathyroid Hormone (PTH), Phosphate, Magnesium, BMP, CMP, Urine Calcium Test
Notes:
Ionized calcium is more accurate than total calcium in patients with abnormal albumin, acid–base disorders, or critical illness.
IFE – Immunofixation Electrophoresis (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Immunofixation Electrophoresis
Alternative Names: Serum Immunofixation, IFE Test, Immunofixation, Urine Immunofixation, Immunoelectrophoresis
Category: Protein Electrophoresis / Immunology Test
Purpose:
The immunofixation blood test uses a process called electrophoresis to separate proteins into subgroups. These subgroups are defined by their size, shape, and electrical charge. Measuring the amount of proteins in each subgroup can help detect various health problems.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected multiple myeloma
- Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS)
- Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia
- Unexplained anemia, bone pain, or renal dysfunction
Typical Normal Range:
- No monoclonal (M) protein detected
Related Tests: Serum Protein Electrophoresis (SPEP), Urine Protein Electrophoresis (UPEP), Free Light Chains Assay, Quantitative Immunoglobulins,
Notes:
More sensitive than SPEP; used to confirm and type monoclonal proteins detected on electrophoresis.
IgA – Immunoglobulin A (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: IgA – Immunoglobulin A
Alternative Names: Serum IgA, IgA Antibody Test, Immunoglobulins (IgA, IgG, IgM), IgA Lab Test, Quantitative Immunoglobulins
Category: Immunology / Serology Test
Purpose:
The IgA (immunoglobulin A) blood test measures the level of IgA in the blood. This test helps doctors diagnose immune problems, such as frequent infections. You may need to stop certain medications or refrain from eating or drinking before the blood test.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Recurrent respiratory or gastrointestinal infections
- Suspected IgA deficiency
- Evaluation of celiac disease (with IgA-tTG)
- Monitoring plasma cell disorders (e.g., multiple myeloma)
Typical Normal Range:
- 70 – 400 mg/dL (may vary by lab, age-dependent)
Related Tests: IgG, IgM, Serum Protein Electrophoresis, Immunofixation Electrophoresis, IgA-tTG (tissue transglutaminase IgA), Celiac Disease Tests, CRP, ESR, Kidney Function Tests
Notes:
IgA deficiency is the most common primary immunodeficiency; elevated levels may indicate chronic infections, liver disease, or plasma cell dyscrasias.
IgE – Immunoglobulin E (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Immunoglobulin E
Alternative Names: Total IgE, Serum IgE, RAST, Specific IgE Test, Quantitative IgE Test, Allergy Blood Test
Category: Immunology / Allergy Test
Purpose:
Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is an antibody produced by the immune system to recognize and eliminate harmful substances such as parasites. During allergic reactions, IgE mistakenly identifies harmless substances such as pollen or certain foods as threats.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Allergic rhinitis, asthma, or eczema
- Suspected food or environmental allergies
- Parasitic infections
- Evaluation of hyper-IgE syndrome or other immunodeficiencies
Typical Normal Range:
- < 100 IU/mL (age-dependent, varies by lab)
Related Tests: Allergen-Specific IgE (RAST/ImmunoCAP), IgG, IgA, IgM, Eosinophil Count, Basophil Activation Test (BAT),
Notes:
Elevated IgE is nonspecific—interpretation requires clinical correlation and sometimes allergen-specific testing.
IGF – Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I
Alternative Names: Somatomedin C, IGF-1, SMC, Insulin Growth Factor
Category: Endocrinology / Hormone Test
Purpose:
IGF-1 is a hormone, a chemical messenger present in the blood that controls the actions of certain cells or organs. IGF-1 regulates the effects of growth hormone (GH) in the body. Together, IGF-1 and GH promote normal bone and tissue growth.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of growth disorders in children (short stature, gigantism)
- Suspected acromegaly in adults
- Monitoring growth hormone therapy
- Investigation of pituitary function
Typical Normal Range:
- Varies by age and sex (generally 100 – 300 ng/mL in adults)
Related Tests: Growth Hormone (GH), IGFBP-3, Pituitary Hormone Panel, MRI of Pituitary (if indicated), X-rays
Notes:
Preferred over direct GH measurement due to less fluctuation; interpretation must consider age, sex, and pubertal status.
IgG – Immunoglobulin G (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Immunoglobulin G
Alternative Names: Serum IgG, IgG Antibody Test, Immunoglobulins Quantitative, Total Immunoglobulins
Category: Immunology / Serology Test
Purpose:
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) provides long-term protection against pathogens by identifying and neutralizing bacteria and viruses and is the only antibody that crosses the placenta, providing crucial protection to fetuses and newborns.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Assessment of recurrent or chronic infections
- Evaluation of immune deficiency or hypogammaglobulinemia
- Monitoring plasma cell disorders (e.g., multiple myeloma, MGUS)
- Autoimmune disease workup
Typical Normal Range:
- 700 – 1600 mg/dL (varies by lab, age-dependent)
Related Tests: IgA, IgM, IgE, Serum Protein Electrophoresis (SPEP), Immunofixation Electrophoresis (IFE), Complete Blood Count (CBC), CSF Immunoglobulin G Index
Notes:
IgG is the most abundant immunoglobulin; elevated in chronic infections and autoimmune disease, decreased in immune deficiencies or nephrotic syndrome.
IgM – Immunoglobulin M(Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Immunoglobulin M
Alternative Names: Serum IgM, IgM Antibody Test, Quantitative Immunoglobulins, Total Immunoglobulins, Immunoglobulin Blood Test (IgA, IgG, IgM)
Category: Immunology / Serology Test
Purpose:
The primary function of IgM is to provide an initial, short-term defense against new infections, being the first antibody produced by the immune system. A large, pentameric antibody (with five units), it effectively neutralizes pathogens by agglutinating bacteria, activating the complement cascade for their destruction,
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of recurrent or severe infections
- Detection of recent/acute infections (first antibody to appear)
- Assessment of suspected primary immunodeficiency
- Monitoring plasma cell or lymphoproliferative disorders
Typical Normal Range:
- 40 – 230 mg/dL (varies by lab, age-dependent)
Related Tests: IgG, IgA, IgE, Serum Protein Electrophoresis (SPEP), Immunofixation Electrophoresis (IFE), C-Reactive Protein (CRP), Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
Notes:
Elevated in acute infections, autoimmune disease, and some lymphoid malignancies; decreased in immunodeficiency or protein loss disorders.
INR – International Normalized Ratio(Click here for Detail)
Full Form: International Normalized Ratio
Alternative Names: Prothrombin Time INR, PT-INR, Protime or Pro time
Category: Coagulation Test / Hematology
Purpose:
The primary purpose of the international normalized ratio (INR) is to standardize prothrombin time (PT) measurements for monitoring oral anticoagulant therapy, such as warfarin, and ensure that patients’ blood clotting times remain within a therapeutic range.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Monitoring patients on warfarin therapy
- Evaluation of bleeding or clotting disorders
- Pre-operative coagulation screening
- Assessment of liver function (since clotting factors are liver-produced)
Typical Normal Range:
- 0.8 – 1.2 (therapeutic range: 2.0 – 3.0 for most indications; 2.5 – 3.5 for mechanical heart valves)
Related Tests: Prothrombin Time (PT), Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (aPTT), Fibrinogen, D-dimer, Liver Function Tests, Thrombin Time (TT), Platelet Count,
Notes:
INR standardizes PT results across labs; interpretation must consider clinical context and anticoagulant therapy goals.
Tests Starting from J
Jo-1 – Jo-1 Antibody (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Jo-1 Antibody (Histidyl-tRNA Synthetase Antibody)
Alternative Names: Anti-Jo-1, Antisynthetase Antibody, Myositis-specific antibody, Anti-tRNA Synthetase, Histidyl-tRNA Synthetase
Category: Autoantibody / Immunology Test
Purpose:
The Jo-1 antibody is an autoantibody that activates the enzyme histidyl-tRNA synthetase, which plays a crucial role in the diagnosis of inflammatory muscle diseases (myositis) and an apparent condition of antisynthetic syndrome.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected polymyositis or dermatomyositis
- Evaluation of interstitial lung disease with myositis features
- Workup of unexplained muscle weakness or elevated muscle enzymes (CK, aldolase)
- Autoimmune connective tissue disease screening
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (no detectable Jo-1 antibodies)
Related Tests: ANA, ENA Panel, Anti-Mi-2, Anti-SRP, CK (Creatine Kinase), Aldolase, MSA Panel, MRI, EMG, ESR, CRP
Notes:
Jo-1 is the most common myositis-specific antibody; presence often indicates higher risk of interstitial lung disease.
Tests Starting from K
KB – Kleihauer-Betke (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Kleihauer-Betke Test
Alternative Names: Fetal Hemoglobin Stain, Acid Elution Test, Kleihauer test, Kleihauer-Betke stain
Category: Hematology / Obstetric Test
Purpose:
The purpose of the Kleihauer-Betke (KB) test is to detect and quantify fetal red blood cells in the mother’s blood to assess the extent of fetomaternal hemorrhage (FMH) following trauma or complications such as placental abruption, ensuring that Rh-negative mothers receive the correct dose of Rh immunoglobulin (RhIG) to prevent future problems in pregnancy.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Estimation of fetomaternal hemorrhage after trauma or delivery
- Determining appropriate Rh immune globulin (RhIG) dose in Rh-negative mothers
- Suspected placental abruption
- Intrauterine fetal death with unclear cause
Typical Normal Range:
- No (or minimal) fetal cells detected in maternal blood
Related Tests: Flow Cytometry for Fetal Hemoglobin, Rh Antibody Screen, Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT), Hemoglobin Electrophoresis,
Notes:
Semi-quantitative test; less precise than flow cytometry but widely used for RhIG dosing.
K – Potassium (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Potassium
Alternative Names: Serum Potassium, K⁺, Hypokalemia or Hyperkalemia Test
Category: Electrolyte / Chemistry Test
Purpose:
Potassium (K) is an essential electrolyte for maintaining fluid balance, facilitating nerve transmission, and muscle contractions, especially in the heart. It promotes the entry of nutrients into cells and the elimination of waste, counteracts the effects of sodium on blood pressure, and contributes to the proper functioning of the heart, kidneys, and nerves.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of kidney disease or electrolyte imbalance
- Monitoring patients on diuretics or IV fluids
- Assessment of arrhythmias or cardiac symptoms
- Evaluation of acid–base disturbances
Typical Normal Range:
- 3.5 – 5.0 mmol/L (varies slightly by lab)
Related Tests: Sodium (Na), Chloride (Cl), Bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻), Creatinine, BUN, Magnesium,
Notes:
Both hypokalemia and hyperkalemia can cause life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias; prompt interpretation and management required.
Tests Starting from L
Lact(o) – Lactoferrin (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Lactoferrin
Alternative Names: Fecal Lactoferrin, Stool Lactoferrin Test, Fecal WBC (White Blood Cell) Non-microscopic, IBD-Scan
Category: Gastroenterology / Inflammatory Marker
Purpose:
Lactoferrin plays a key role in iron binding and transport, contributing to its absorption by infants and limiting its availability to bacteria. It also has broad-spectrum immune functions, with antimicrobial (against bacteria, viruses, and fungi), antiviral, and anti-inflammatory properties.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Differentiating inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) from irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- Monitoring disease activity in ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease
- Evaluation of unexplained chronic diarrhea
- Follow-up of treatment response in IBD
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (no lactoferrin detected in stool)
Related Tests: Fecal Calprotectin, CRP, ESR, Stool Culture, Colonoscopy, Ova and Parasite Exam, Stool Culture and C. difficile Toxin Testing, FOBT, FIT
Notes:
Elevated in intestinal inflammation (IBD, infections); not elevated in non-inflammatory conditions like IBS.
LD – Lactate Dehydrogenase (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Lactate Dehydrogenase
Alternative Names: LDH, Lactic Acid Dehydrogenase, LD test, Lactic dehydrogenase test
Category: Enzyme / General Biochemistry Test
Purpose:
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) is an enzyme that helps cells produce energy through cellular respiration. It is found in almost all body tissues, including muscles, liver, kidneys, and red blood cells.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of hemolysis or hematologic disorders
- Monitoring cancers (e.g., lymphoma, leukemia, germ cell tumors)
- Assessment of liver or muscle injury
- Evaluation of suspected myocardial or pulmonary infarction (historical use, less common now)
Typical Normal Range:
140 – 280 U/L (varies by lab and method)
Related Tests: AST, ALT, CK, Haptoglobin, Bilirubin, Uric Acid, Troponin, Creatine Kinase (CK) and Creatine Kinase-MB (CK-MB), ALP, CBC, C-Reactive Protein (CRP) and Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
Notes:
Nonspecific; elevated in many conditions involving tissue breakdown. Isoenzyme testing may help identify tissue source.
LDH – Lactate Dehydrogenase (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Lactate Dehydrogenase
Alternative Names: LD, Lactic Acid Dehydrogenase, Lactic dehydrogenase test, LDH isoenzymes test, LD fractionation
Category: Enzyme / General Biochemistry Test
Purpose:
LDH is present in many tissues and organs, including muscles, liver, heart, pancreas, kidneys, brain, and blood cells. The LDH test is primarily used to identify the location and severity of tissue damage. It is also sometimes used to monitor the progression of certain diseases.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Hemolytic anemia evaluation
- Cancer monitoring (lymphoma, leukemia, germ cell tumors)
- Assessment of liver, lung, heart, or muscle injury
- Supportive marker in suspected tissue ischemia or infarction
Typical Normal Range:
140 – 280 U/L (method- and lab-dependent)
Related Tests: AST, ALT, CK, Haptoglobin, Bilirubin, Uric Acid, LDH Isoenzymes, CBC, Pleural Fluid , CSF, Aldolase, Troponin (cTN)
Notes:
LDH is highly nonspecific; isoenzyme analysis can help identify organ source of elevation.
LDL – Low-Density Lipoprotein (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol
Alternative Names: “Bad Cholesterol,” LDL-C, Lipid panel, Coronary risk panel, Fasting lipid panel
Category: Lipid Profile / Cardiology Test
Purpose:
Due to their structure, fats cannot circulate independently in the blood. Therefore, lipoproteins transport fats to various cells in the body. LDL particles contain a large amount of cholesterol and a smaller amount of protein. They are often referred to as “bad cholesterol.”
Commonly Ordered For:
- Optimal: < 100 mg/dL
- Near optimal: 100 – 129 mg/dL
- Borderline high: 130 – 159 mg/dL
- High: 160 – 189 mg/dL
- Very high: ≥ 190 mg/dL
Typical Normal Range:
140 – 280 U/L (method- and lab-dependent)
Related Tests: Total Cholesterol, HDL, Triglycerides, VLDL, Apolipoprotein B, Lipoprotein (a)
Notes:
LDL is the primary therapeutic target in dyslipidemia management; lowering LDL reduces cardiovascular risk.
LFT – Liver Function Tests (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Liver Function Tests
Alternative Names: Hepatic Panel, Liver Panel, Liver Chemistries, Liver Blood Tests
Category: Biochemistry / Organ Function Test
Purpose:
Liver function tests (LFTs) are blood tests that measure substances produced by the liver to aid in the diagnosis, monitoring, and evaluation of liver health, injury, and disease. Their purpose is to detect liver disease, determine the severity of liver damage, monitor its progression, and detect potential medication side effects.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Assessment of jaundice or unexplained fatigue
- Monitoring chronic liver diseases (hepatitis, cirrhosis, fatty liver)
- Evaluating drug- or alcohol-related hepatotoxicity
- Pre-operative or routine health checkups
Typical Normal Range:
ALT: 7 – 56 U/L
AST: 10 – 40 U/L
ALP: 44 – 147 U/L
Total Bilirubin: 0.1 – 1.2 mg/dL
Albumin: 3.5 – 5.0 g/dL
Total Protein: 6.3 – 7.9 g/dL
Related Tests: GGT, Prothrombin Time (PT/INR), Hepatitis Panel, Ultrasound Liver, Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP), Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST), Alanine Transaminase (ALT)
Notes:
LFT is a panel of tests; abnormal results require interpretation with clinical findings and imaging/serology.
LH – Luteinizing Hormone (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Luteinizing Hormone
Alternative Names: Interstitial Cell Stimulating Hormone (ICSH), Lutropin
Category: Endocrinology / Reproductive Hormone Test
Purpose:
Luteinizing hormone (LH) regulates reproductive processes by stimulating the production of steroid hormones and the release of eggs (ovulation) in women and testosterone in men.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of infertility (male and female)
- Assessment of menstrual irregularities or anovulation
- Suspected polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Evaluation of delayed or precocious puberty
Typical Normal Range:
Men: 1.5 – 9.0 IU/L
Women (follicular): 1.9 – 12.5 IU/L
Women (mid-cycle peak): 8.7 – 76.3 IU/L
Women (luteal): 0.5 – 16.9 IU/L
Postmenopausal women: 15.9 – 54.0 IU/L
Related Tests: FSH, Estradiol, Progesterone, Testosterone, Prolactin, Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG)
Notes:
LH surges mid-cycle to trigger ovulation; interpretation requires correlation with cycle phase or gonadal status.
Li+ or Li – Lithium (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Lithium
Alternative Names: Serum Lithium, Lithium Level, Li⁺ Test, Lithium blood test,
Category: Therapeutic Drug Monitoring / Psychiatry
Purpose:
“Li+” refers to a lithium ion, the positively charged form of the lithium atom (Li), essential for the lithium-ion batteries that power laptops, phones, and electric cars. “Li” on its own, or “lithium,” refers to the neutral metallic element itself.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Monitoring patients on lithium therapy for bipolar disorder
- Evaluating suspected lithium toxicity
- Assessing adherence to therapy
- Adjusting lithium dosage in renal impairment or drug interactions
Typical Normal Range:
- Therapeutic (maintenance): 0.6 – 1.2 mmol/L
- Toxic: > 1.5 mmol/L
Related Tests: Renal Function Tests (Creatinine, BUN), Electrolytes, Thyroid Function Tests, Calcium, CBC, Electrolyte tests
Notes:
Lithium has a narrow therapeutic index; levels should be checked regularly, especially after dose changes, illness, or dehydration.
LMW Heparin – Low Molecular Weight Heparin (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Low Molecular Weight Heparin
Alternative Names: LMWH, Fractionated Heparin, Anti-Xa Assay, Low Molecular Weight Heparin Activity, Heparin Anti-Xa, Plasma
Category: Anticoagulant / Hematology (Therapeutic Monitoring)
Purpose:
Low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) is an anticoagulant used to prevent and treat blood clots, primarily deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). Its purpose is to prevent the growth of existing clots, prevent the formation of new clots, and manage conditions with a high risk of thrombosis.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Monitoring anticoagulation in renal impairment
- High-risk patients (pregnancy, obesity, pediatrics)
- Assessment of suspected over- or under-anticoagulation
- Adjusting therapeutic dosing in special populations
Typical Normal Range:
- Prophylaxis: 0.2 – 0.5 IU/mL
- Therapeutic (twice daily dosing): 0.5 – 1.0 IU/mL
- Therapeutic (once daily dosing): 1.0 – 2.0 IU/mL
Related Tests: aPTT, PT/INR, Platelet Count, Creatinine, Unfractionated Heparin Assay, Fibrinogen and other coagulation factor tests
Notes:
Unlike unfractionated heparin, LMWH usually does not require routine monitoring; anti-Xa testing is reserved for special cases.
Tests Starting from M
MCH – Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin
Alternative Names: Average Hemoglobin Content, Mean Cell Hemoglobin
Category: Hematology (CBC Parameter)
Purpose:
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) measures the average amount of hemoglobin per red blood cell. This value, found on a complete blood count (CBC), provides information about the health of red blood cells.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of anemia
- Investigation of fatigue, pallor, or weakness
- Monitoring response to anemia treatment
- Differentiating between microcytic, normocytic, and macrocytic anemias
Typical Normal Range:
- 27–33 pg/cell (may vary by lab)
Related Tests: MCV, MCHC, Hemoglobin, Hematocrit, RBC count, RDW (Red Cell Distribution Width)
Notes:
Abnormal values are usually interpreted alongside other CBC indices for accurate diagnosis.
MCHC – Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration
Alternative Names: Average Hemoglobin Concentration, Mean Cell Hemoglobin Concentration, complete blood count (CBC)
Category: Hematology (CBC Parameter)
Purpose:
The MCHC test determines the average hemoglobin concentration in red blood cells to assess red blood cell health and diagnose anemia by indicating whether red blood cells carry an adequate amount of hemoglobin; high or low results suggest various conditions, such as iron deficiency or autoimmune hemolytic anemia.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of anemia
- Investigation of pale or abnormally colored red blood cells
- Monitoring therapy in anemia or hematologic disorders
- Distinguishing between hypochromic and normochromic cells
Typical Normal Range:
- 32–36 g/dL (may vary by lab)
Related Tests: MCH, MCV, Hemoglobin, Hematocrit, RDW, Red Blood Cell
Notes:
Low MCHC indicates hypochromia (e.g., iron deficiency anemia); high values may suggest hereditary spherocytosis or autoimmune hemolytic anemia.
MCV – Mean Corpuscular Volume (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Mean Corpuscular Volume
Alternative Names: Average Red Blood Cell Volume, Mean Cell Volume,
Category: Hematology (CBC Parameter)
Purpose:
The main purpose of the MCV (mean corpuscular volume) test is to measure the average size of red blood cells (RBCs), which facilitates the diagnosis and classification of different types of anemia and other conditions. An abnormal MCV (too small or too large) may indicate underlying problems such as iron deficiency, lead poisoning, vitamin deficiencies (B12 or folate), liver disease, or kidney failure.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of anemia
- Investigation of pale or abnormally colored red blood cells
- Monitoring therapy in anemia or hematologic disorders
- Distinguishing between hypochromic and normochromic cell
Typical Normal Range:
- Range: 80–100 fL (may vary by lab)
Related Tests: MCH, MCHC, Hemoglobin, Hematocrit, RDW,
Notes:
Low MCV → microcytic anemia (e.g., iron deficiency, thalassemia)
High MCV → macrocytic anemia (e.g., B12 or folate deficiency, liver disease)
MetHb/MetHgb – Methemoglobin (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Methemoglobin
Alternative Names: MetHgb, Ferric Hemoglobin, Co-oximetry, Methemoglobin and Sulfhemoglobin, Blood,
Category: Hematology / Blood Gas & Co-oximetry
Purpose:
Methemoglobin (MetHb) has no specific function. It is a dysfunctional form of hemoglobin that cannot transport oxygen to the body’s tissues because the iron in its heme oxidizes from ferrous (Fe₂+) to ferric (Fe₃+). Physiological levels below 1–2% are normal, but higher levels, known as methemoglobinemia, cause a decrease in oxygen delivery, resulting in symptoms such as cyanosis, fatigue, and headaches.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of cyanosis unresponsive to oxygen therapy
- Suspected methemoglobinemia (drug- or chemical-induced)
- Monitoring exposure to oxidizing agents (e.g., nitrates, benzocaine, dapsone)
- Assessment of congenital hemoglobinopathies
Typical Normal Range:
- <1–2% of total hemoglobin
Related Tests: Carboxyhemoglobin, Oxyhemoglobin saturation, Arterial Blood Gas (ABG), Co-oximetry, Pulse Oximetry (SpO2), Arterial Blood Gas Analysis (SaO2), Methemoglobin Reductase, Hemoglobin Electrophoresis, Sulfhemoglobin Test, Methylene Blue Test
Notes:
Elevated levels impair oxygen delivery; severe cases may cause hypoxia and require treatment (e.g., methylene blue).High MCV → macrocytic anemia (e.g., B12 or folate deficiency, liver disease)
Mg, Mag – Magnesiumn (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Magnesium
Alternative Names: Serum Magnesium, Plasma Magnesium, Mg test, Mag test
Category: Clinical Chemistry / Electrolytes
Purpose:
Magnesium is a cofactor in over 300 enzyme systems that regulate various biochemical reactions in the body, including protein synthesis, muscle and nerve function, glycemic control, and blood pressure regulation [1-3]. Magnesium is required for energy production, oxidative phosphorylation, and glycolysis.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of muscle weakness, cramps, or seizures
- Monitoring patients with kidney disease
- Assessment in malnutrition, alcoholism, or malabsorption
- Monitoring therapy with diuretics or digitalis
- Evaluation of arrhythmias or unexplained electrolyte disturbances
Typical Normal Range:
- 1.7–2.4 mg/dL (0.7–1.0 mmol/L; may vary by lab)
Related Tests: Calcium, Phosphate, Potassium, Creatinine, Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) Test, CMP, Magnesium in Urine Test, RBC
Notes:
Both hypo- and hypermagnesemia can cause serious neuromuscular and cardiac effects; levels often interpreted with other electrolytes.
MIC – Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
Alternative Names: Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (AST), Minimal Inhibitory Concentration,
Category: Microbiology / Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
Purpose:
The primary objective of the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) test is to determine the lowest concentration of an antimicrobial agent (such as an antibiotic) required to stop the visible growth of a specific microorganism, such as a bacterium.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Identifying effective antibiotic therapy in bacterial infections
- Detecting antimicrobial resistance patterns
- Guiding treatment in severe or resistant infections (e.g., sepsis, pneumonia)
- Monitoring hospital-acquired and multidrug-resistant organisms
Typical Normal Range:
- Reported as organism- and drug-specific values (µg/mL)
Related Tests: Disk Diffusion (Kirby-Bauer), E-test, Broth Dilution, PCR for resistance genes, MBC, MFC,
Notes:
MIC values must be interpreted using clinical breakpoints (CLSI/EUCAST); results depend on organism, antibiotic, and patient context.
MMA – Methylmalonic Acid (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Methylmalonic Acid
Alternative Names: MMA Test, Serum/Plasma Methylmalonate, Urinary Methylmalonic Acid,
Category: Clinical Chemistry / Metabolic & Nutritional Tests
Purpose:
Methylmalonic acid (MMA) plays a vital role as a diagnostic indicator of vitamin B12 deficiency and certain metabolic disorders. Elevated levels of MMA indicate that the body’s enzymes and cells are not properly utilizing vitamin B12, which can lead to nerve damage and anemia.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of suspected vitamin B12 deficiency
- Differentiating B12 deficiency from folate deficiency
- Investigation of unexplained anemia or neuropathy
- Monitoring patients with pernicious anemia or malabsorption syndromes
Typical Normal Range:
- Serum/Plasma: 0.08–0.56 µmol/L (may vary by lab)
- Urine: <3.6 mmol/mol creatinine (varies by method)
Related Tests: Vitamin B12, Homocysteine, Folate, Complete Blood Count (CBC),
Notes:
Elevated MMA is an early and sensitive marker of B12 deficiency; levels may also rise in renal impairment, so kidney function should be considered.
Mn – Manganese (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Manganese
Alternative Names: Serum Manganese, Plasma Manganese, Whole Blood Manganese, Manganese, Urine, Manganese (Mn) Test
Category: Clinical Chemistry / Trace Elements
Purpose:
Manganese (Mn) is an essential nutrient for human health. It acts as a catalyst for enzymes involved in lipid and carbohydrate metabolism, bone and connective tissue formation, and blood clotting. It is also essential for bone health, the nervous system, the immune system, and reproduction.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Assessment of suspected manganese toxicity (e.g., welders, miners, battery workers)
- Evaluation of parenteral nutrition patients for trace element balance
- Investigation of neurological symptoms resembling Parkinsonism
- Monitoring patients with chronic liver disease (risk of manganese accumulation)
Typical Normal Range:
- Whole Blood: 4–15 µg/L (varies by lab)
- Serum/Plasma: <1.5 µg/L (less reliable than whole blood)
Related Tests: Zinc, Copper, Iron, Lead, Liver Function Tests,
Notes:
Elevated levels may cause neurotoxicity (“manganism”); deficiency is rare but may contribute to bone and metabolic disorders. Whole blood is the preferred specimen for accuracy.
Mono – Mononucleosis (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Mononucleosis Test
Alternative Names: Monospot Test, Heterophile Antibody Test, Heterophile agglutination test, Paul-Bunnell test
Category: Serology / Infectious Disease TestingClinical Chemistry / Trace Elements
Purpose:
Mononucleosis, or mononucleosis, is the term used to refer to a disease caused by a virus, most commonly the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), which infects and replicates in the human body, generally affecting lymphocytes and causing symptoms such as fever, sore throat, and extreme fatigue.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of fever, sore throat, and lymphadenopathy
- Suspected infectious mononucleosis in adolescents and young adults
- Differentiating mononucleosis from other viral pharyngitis
- Supporting diagnosis of EBV-related illness
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (no heterophile antibodies detected)
Related Tests: EBV-specific antibodies (VCA IgM, VCA IgG, EBNA), CMV antibodies, CBC (with atypical lymphocytes), Throat Culture, Liver Function Tests
Notes:
The Monospot test may be falsely negative early in illness or in young children; EBV-specific antibody testing is more definitive.
Mono – Mononucleosis (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Mononucleosis Test
Alternative Names: Monospot Test, Heterophile Antibody Test, Heterophile agglutination test, Paul-Bunnell test
Category: Serology / Infectious Disease TestingClinical Chemistry / Trace Elements
Purpose:
Mononucleosis, or mononucleosis, is the term used to refer to a disease caused by a virus, most commonly the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), which infects and replicates in the human body, generally affecting lymphocytes and causing symptoms such as fever, sore throat, and extreme fatigue.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of fever, sore throat, and lymphadenopathy
- Suspected infectious mononucleosis in adolescents and young adults
- Differentiating mononucleosis from other viral pharyngitis
- Supporting diagnosis of EBV-related illness
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (no heterophile antibodies detected)
Related Tests: EBV-specific antibodies (VCA IgM, VCA IgG, EBNA), CMV antibodies, CBC (with atypical lymphocytes), Throat Culture, Liver Function Tests
Notes:
The Monospot test may be falsely negative early in illness or in young children; EBV-specific antibody testing is more definitive.
Tests Starting from N
NA – Sodium (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Sodium
Alternative Names: Serum Sodium, Plasma Sodium, Na⁺,
Category: Clinical Chemistry / Electrolytes
Purpose:
The main functions of sodium in the human body are to maintain fluid and electrolyte balance, regulate blood pressure and volume, and contribute to the proper functioning of nerves and muscles. It is an essential electrolyte for cellular processes, such as nutrient absorption and the functioning of cell membranes.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of dehydration or overhydration
- Investigation of confusion, seizures, or altered mental status
- Monitoring patients with kidney disease, heart failure, or liver cirrhosis
- Assessing electrolyte balance in patients on IV fluids or diuretics
Typical Normal Range:
- 135–145 mmol/L (may vary by lab)
Related Tests: Potassium, Chloride, Bicarbonate (CO₂), Osmolality, Creatinine, Urine Sodium Test,
Notes:
Low sodium (hyponatremia) may cause neurological symptoms.
High sodium (hypernatremia) often indicates water loss or sodium excess.
Interpretation should consider fluid status and overall electrolyte balance.
NEOTY – Neonate Type and DAT (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Neonate Blood Type and Direct Antiglobulin Test
Alternative Names: Neonatal Blood Grouping and Direct Coombs Test, Direct Antiglobulin Test, Direct Coombs, Blood, Polyspecific Coombs
Category: Transfusion Medicine / Immunohematology
Purpose:
The purpose of the NEOTY test – Newborn Blood Type Test and Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT) is to diagnose hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN), a condition in which maternal antibodies cross the placenta and attach to the baby’s red blood cells, causing their destruction.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN)
- Infants with jaundice or anemia soon after birth
- Assessment when maternal blood group incompatibility is suspected (e.g., Rh or ABO incompatibility)
- Guiding transfusion and treatment decisions in neonates
Typical Normal Range:
Blood Type: Reported as ABO and Rh group
DAT: Negative (no antibody coating of red cells)
Related Tests: Maternal antibody screen, Indirect Antiglobulin Test (IAT), Bilirubin, Hemoglobin/Hematocrit, Complete Blood Count (CBC), Blood Type and Screen,
Notes:
Positive DAT indicates antibody-mediated hemolysis; clinical correlation with bilirubin and hemoglobin levels is essential for management.
NEOXM – Neonate Type and XM (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Neonate Blood Type and Crossmatch
Alternative Names: Neonatal Blood Grouping and Crossmatching, Neonate Transfusion Profile, Newborn Type and Screen, Newborn Crossmatch and Transfusion
Category: Transfusion Medicine / Immunohematology
Purpose:
Determines the newborn’s ABO and Rh blood type and performs a crossmatch to ensure compatibility for transfusion.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Newborns requiring blood transfusion (e.g., anemia, hemorrhage)
- Evaluation in suspected hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN)
- Infants with significant jaundice or hemolysis needing exchange transfusion
- Pre-transfusion safety testing in neonates
Typical Normal Range:
Blood Type: Reported as ABO and Rh group
Crossmatch: Compatible
Related Tests: Neonate Type and DAT (NEOTY), Maternal antibody screen, Indirect Antiglobulin Test (IAT), Hemoglobin/Hematocrit, Bilirubin,
Notes:
Ensures safe transfusion in neonates; maternal antibodies must be considered when selecting compatible blood.
NH3 – Ammonia(Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Newborn Blood Type and Rh Factor
Alternative Names: Neonatal Blood Grouping, Cord Blood ABO/Rh Typing,
Category: Transfusion Medicine / Immunohematology
Purpose:
The term “NTR” likely refers to a blood test to determine a newborn’s blood type and Rh factor. This serves to identify Rh factor incompatibility with the mother, which can cause hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN) or jaundice.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Routine testing of newborns at delivery
- Infants born to Rh-negative mothers
- Evaluation of risk for hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN)
- Guiding transfusion needs in neonates
Typical Normal Range:
- Reported as ABO group (A, B, AB, O) and Rh factor (positive or negative)
Related Tests: Neonate Type and DAT (NEOTY), Maternal Antibody Screen, Indirect Antiglobulin Test (IAT), Bilirubin, Hemoglobin/Hematocrit,
Notes:
Essential for early detection of maternal-fetal blood group incompatibility; usually performed on cord blood at birth.
Tests Starting from O
17-OHP > 17-Hydroxyprogesterone (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: 17-Hydroxyprogesterone
Alternative Names: 17-OHP, OHP, 17-OH Progesterone, 17OHP, 17-OH Progesterone, 17-Alpha-Hydroxyprogesterone, OH-Progesterone, 17-alpha hydroxyprogesterone, Progesterone – 17-OH, 17-Hydroxyprogesterone, 17-Hydroxyprogesterone (Neonatal Screen)
Category: Endocrinology / Hormone Test
Purpose:
This test measures the amount of 17-hydroxyprogesterone (17-OHP) in a sample of your blood. 17-OHP is a substance produced by the adrenal glands. These glands are two small organs located above each kidney. They produce different types of hormones necessary for maintaining life and health. Hormones are chemical messengers circulating in the blood that control the actions of certain cells or organs.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Newborn screening for CAH
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Infertility evaluation
- Signs of excess androgens
Typical Normal Range:
- Newborn: < 630 ng/dL
- Adult Men: < 200 ng/dL
- Adult Women (follicular phase): < 80 ng/dL
Related Tests: Cortisol, ACTH Stimulation Test, DHEA-S
Notes:
Usually performed in the morning; levels can vary with menstrual cycle phase and stress.
3-ANCA > Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies (c-ANCA / p-ANCA) (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies
Alternative Names: c-ANCA, p-ANCA, PR3-ANCA (Proteinase 3), MPO-ANCA (Myeloperoxidase), ANCA Test, ANCA Screen, c-ANCA/p-ANCA Test, ANCA Antibody Test, ANCAs, Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody Test, Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies Test, ANCA Blood Test, Vasculitis ANCA Test, Autoimmune Vasculitis Test
Category: Immunology / Autoimmune Test
Purpose:
An ANCA test can determine whether you have one or both pANCA and cANCA antibodies. ANCA or MPO and PR3 tests are ordered if you have signs and symptoms suggestive of systemic autoimmune vasculitis.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA)
- Microscopic polyangiitis (MPA)
- Autoimmune vasculitis symptoms (sinusitis, lung/kidney involvement)
Typical Normal Range:
Negative (no detectable ANCA)
Negative: Less than 2 IU/mL.
Equivocal: 2-3 IU/mL (may require further testing).
Positive: Greater than 3 IU/mL.
Related Tests: ANA, ESR, CRP, Renal Function Tests
Notes:
Pattern differentiation (c-ANCA vs p-ANCA) can guide diagnosis; positive results require correlation with clinical findings.
Tests Starting from P
PAP – Papanicolaou (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Papanicolaou Test
Alternative Names: Pap Smear, Cervical Cytology, Pap Test, Vaginal smear technique
Category: Cytology / Cancer Screening
Purpose:
The Pap smear (Pap test) is used to detect and diagnose cervical cancer and precancerous lesions by microscopic examination of cells collected from the cervix. This routine screening procedure can detect abnormalities early, before they become cancerous or spread, thus optimizing the effectiveness of treatment.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Routine cervical cancer screening in women
- Evaluation of abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge
- Follow-up of previously abnormal Pap or HPV results
- Monitoring after treatment for cervical dysplasia or cancer
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative for intraepithelial lesion or malignancy (NILM)
Related Tests: HPV DNA Test, Colposcopy, Cervical Biopsy, Endocervical Curettage (ECC), Cone Biopsy, LEEP
Notes:
Recommended as part of routine gynecological care; interpretation follows Bethesda System categories (NILM, ASC-US, LSIL, HSIL, etc.). Often combined with HPV testing for enhanced screening.
PAP – Prostatic Acid Phosphatase (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Prostatic Acid Phosphatase
Alternative Names: Acid Phosphatase (Prostatic), Serum Acid Phosphatase, Prostatic Specific Acid Phosphatase (PSAP)
Category: Clinical Chemistry / Tumor Markers (historical use)
Purpose:
Prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP) is an enzyme primarily used in pathology to identify the origin of metastatic cancer cells (e.g., whether they originate in the prostate), differentiate certain tumor types, and, historically, to detect prostate cancer.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Historical use in staging and monitoring prostate cancer
- Rarely for evaluation of prostatic carcinoma with metastasis
- Research or specialized diagnostic settings
- Occasionally in forensic medicine (e.g., semen detection)
Typical Normal Range:
<3.5 ng/mL (varies by lab and method)
Related Tests: PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen), Alkaline Phosphatase, LDH, Complete Blood Count (CBC), Prostate Biopsy, Digital Rectal Exam (DRE),
Notes:
Largely obsolete in routine prostate cancer evaluation; PSA is the preferred marker. PAP may still have niche use in certain clinical or forensic contexts.
Pb – Lead (Click here for Detail)
Full Form:Lead
Alternative Names: Blood Lead Level, BLL, Lead Testing, Serum lead level
Category: Clinical Chemistry / Toxicology
Purpose:
The purpose of lead (Pb) comes from its unique properties, including its high density, malleability and corrosion resistance, making it essential for applications such as lead-acid batteries, radiation shielding and specialty alloys and solders, although its use has declined due to its toxicity.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Screening children at risk of lead poisoning (e.g., environmental exposure, old housing/paint)
- Evaluation of developmental delay, learning problems, or behavioral changes
- Occupational exposure monitoring (battery, smelting, construction, painting industries)
- Investigation of abdominal pain, anemia, or neuropathy of unclear cause
Typical Normal Range:
Children: <3.5 µg/dL (CDC reference value; action required if ≥3.5 µg/dL)
Adults: <5 µg/dL (OSHA/CDC guidelines; varies by occupational standards)
Related Tests: Zinc Protoporphyrin (ZPP), Iron Studies, CBC, Heavy Metal Panel (Mercury, Arsenic, Cadmium), Abdominal X-ray, X-ray fluorescence (XRF)
Notes:
Lead toxicity affects neurological, hematologic, and renal systems; no safe level is established, especially in children. Whole blood (not serum/plasma) is required for accurate measurement.
PBG – Porphobilinogen (Click here for Detail)
Full Form:Porphobilinogen
Alternative Names: Urinary Porphobilinogen Test, PBG in Urine, Porphyria – urine, PBG,
Category: Clinical Chemistry / Metabolic Disorders
Purpose:
Porphobilinogen (PBG) is a precursor of the heme biosynthetic pathway and is primarily used as a diagnostic marker for acute porphyrias, such as acute intermittent porphyria (AIP), by measuring its levels in urine and blood.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of suspected acute intermittent porphyria (AIP)
- Investigation of severe unexplained abdominal pain, neuropathy, or psychiatric symptoms
- Workup of photosensitivity or unexplained neurological crises
- Monitoring treatment and attacks in known porphyria patients
Typical Normal Range:
- <2 mg/L (varies by lab and method)
Related Tests: Urinary δ-Aminolevulinic Acid (ALA), Total Porphyrins, Plasma/Urine Porphyrin Fractionation, Genetic Testing for Porphyrias, Enzyme testing,
Notes:
Elevated urinary PBG during acute attacks is diagnostic of acute hepatic porphyrias; sample should be protected from light to avoid degradation.
PCP – Phencyclidine (Click here for Detail)
Full Form:Phencyclidine
Alternative Names: Angel Dust Test, PCP Drug Screen, Killer Weed test, Rocket Fuel test, Super Weed test
Category: Toxicology / Drug Screening
Purpose:
Detects phencyclidine, a dissociative hallucinogen, in biological samples to assess recent or chronic use.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of suspected drug intoxication (agitation, hallucinations, violent behavior)
- Emergency toxicology screening in altered mental status
- Workplace or legal drug testing programs
- Monitoring patients with a history of substance abuse
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (no PCP detected)
Related Tests: Urine Drug Screen Panel (THC, Cocaine, Amphetamines, Opiates, Benzodiazepines), Confirmatory GC-MS/LC-MS,
Notes:
Immunoassay screening may yield false positives (e.g., with dextromethorphan, diphenhydramine, tramadol); confirmatory testing is required.
PEP – Protein Electrophoresis (Click here for Detail)
Full Form:Protein Electrophoresis
Alternative Names: Serum Protein Electrophoresis (SPEP), Urine Protein Electrophoresis (UPEP), Protein ELP, Paraprotein Detection, Gel Electrophoresis or Capillary Electrophoresis
Category: Clinical Chemistry / Protein Studies
Purpose:
Serum protein electrophoresis (SPEP) is a laboratory test that separates proteins in a blood sample to identify and measure different types of proteins, helping to diagnose and monitor conditions such as multiple myeloma, autoimmune diseases, liver or kidney disease, and nutritional deficiencies.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of suspected multiple myeloma or related plasma cell disorders
- Investigation of unexplained hyperproteinemia or hypoproteinemia
- Workup of monoclonal gammopathy (M-protein, paraprotein)
- Assessment of chronic inflammation, autoimmune disease, or liver disease
Typical Normal Range:
- Albumin: ~55–65%
- Alpha-1 globulin: ~2–5%
- Alpha-2 globulin: ~6–12%
- Beta globulin: ~8–14%
- Gamma globulin: ~12–22%
- (values may vary by lab)
Related Tests: Immunofixation Electrophoresis (IFE), Serum Free Light Chains, Total Protein, Immunoglobulins (IgG, IgA, IgM), Total Protein and Albumin Tests, Urine Immunofixation Electrophoresis (UIFE)
Notes:
Monoclonal spikes (M-spikes) suggest plasma cell dyscrasia; urine testing (UPEP) is often paired with SPEP for complete evaluation.
PHOS – Phosphorus(Click here for Detail)
Full Form:Phosphorus
Alternative Names: Inorganic Phosphate, Serum Phosphate,
Category: Clinical Chemistry / Electrolytes & Minerals
Purpose:
Phosphorus (P or Phos) is an essential mineral that performs multiple vital functions in the human body, including the formation of bones, teeth and cell membranes, the supply of DNA and RNA, and a key role in energy production through ATP, enzyme activation, and the regulation of gene transcription.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of bone and mineral disorders
- Monitoring patients with chronic kidney disease or dialysis
- Assessment of malnutrition, malabsorption, or refeeding syndrome
- Workup of unexplained muscle weakness, confusion, or seizures
Typical Normal Range:
- 2.5–4.5 mg/dL (0.81–1.45 mmol/L; may vary by lab)
Related Tests: Magnesium, Parathyroid Hormone (PTH), Vitamin D, Creatinine, Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) Test, Calcium Test
Notes:
Hypophosphatemia may cause muscle weakness, respiratory failure, or hemolysis.
Hyperphosphatemia is common in renal failure and secondary hyperparathyroidism.
Interpretation should consider calcium–phosphate balance and kidney function.
PKU – Phenylketonuria(Click here for Detail)
Full Form:Phenylketonuria Screening Test
Alternative Names: Newborn PKU Test, Phenylalanine Test, Guthrie Test (historical)
Category: Newborn Screening / Metabolic Disorders
Purpose:
The goal of understanding phenylketonuria (PKU) is to enable early diagnosis and treatment to prevent serious health consequences, including brain damage and intellectual disability, caused by the buildup of the amino acid phenylalanine in the body.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Routine newborn screening (state-mandated in many countries)
- Evaluation of suspected inborn error of metabolism
- Infants with developmental delay, seizures, or microcephaly of unclear cause
- Monitoring dietary management in known PKU patients
Typical Normal Range:
- <2 mg/dL phenylalanine in blood (varies by method and lab)
Related Tests: Tandem Mass Spectrometry Newborn Screen, Amino Acid Profile, Tyrosine, Genetic Testing for PAH mutations,
Notes:
Early detection and strict dietary management (low-phenylalanine diet) prevent intellectual disability and neurological damage; lifelong monitoring is often required.
PLT or PLT Ct – Platelet Count(Click here for Detail)
Full Form:Phenylketonuria Screening Test
Alternative Names: Newborn PKU Test, Phenylalanine Test, Guthrie Test (historical), Phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) deficiency
Category: Newborn Screening / Metabolic Disorders
Purpose:
The goal of understanding phenylketonuria (PKU) is to enable early diagnosis and treatment to prevent serious health consequences, including brain damage and intellectual disability, caused by the buildup of the amino acid phenylalanine in the body.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Routine newborn screening (state-mandated in many countries)
- Evaluation of suspected inborn error of metabolism
- Infants with developmental delay, seizures, or microcephaly of unclear cause
- Monitoring dietary management in known PKU patients
Typical Normal Range:
- <2 mg/dL phenylalanine in blood (varies by method and lab)
Related Tests: Tandem Mass Spectrometry Newborn Screen, Amino Acid Profile, Tyrosine, Genetic Testing for PAH mutations, Additional blood and urine tests,
Notes:
Early detection and strict dietary management (low-phenylalanine diet) prevent intellectual disability and neurological damage; lifelong monitoring is often required.
PO4 – Phosphorus(Click here for Detail)
Full Form:Phosphorus
Alternative Names: Inorganic Phosphate, Serum Phosphate, PHOS, HPO4-2, PO4-3
Category: Clinical Chemistry / Electrolytes & Minerals
Purpose:
PO4, or phosphate, is essential for life, as it is a key component of cell membranes, DNA and RNA, and is crucial for energy transfer within cells (ATP) and the formation and maintenance of bones and teeth.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Monitoring patients with kidney disease or dialysis
- Evaluation of bone and mineral disorders
- Assessment of malnutrition, malabsorption, or refeeding syndrome
- Workup of muscle weakness, seizures, or altered mental status
Typical Normal Range:
- 2.5–4.5 mg/dL (0.81–1.45 mmol/L; varies by lab)
Related Tests: Calcium, Magnesium, Parathyroid Hormone (PTH), Vitamin D, Creatinine, Kidney Function Tests
Notes:
Hypophosphatemia may cause hemolysis, muscle weakness, or respiratory failure.
Hyperphosphatemia is most often due to renal failure or hypoparathyroidism.
Always interpret in relation to calcium and kidney function.
PRL – Prolactin(Click here for Detail)
Full Form:Prolactin
Alternative Names:Serum Prolactin, Lactogenic Hormone, Prolactin level test
Category: Endocrinology / Hormone Testing
Purpose:
Prolactin is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland that primarily stimulates breast development and milk production (lactation) in women after childbirth. It also plays a role in various other bodily processes, although its specific functions in men are less understood.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Investigation of galactorrhea (unexpected breast milk production)
- Evaluation of amenorrhea or infertility
- Assessment of pituitary adenomas (prolactinomas)
- Workup of erectile dysfunction or decreased libido in men
Typical Normal Range:
- Women: <25 ng/mL
- Men: <20 ng/mL
Related Tests: LH, FSH, Estradiol, Testosterone, TSH, MRI of pituitary (if abnormal)
Notes:
Elevated prolactin (hyperprolactinemia) may result from pituitary tumors, hypothyroidism, pregnancy, or certain medications; low levels are rarely clinically significant.
PRU – Platelet Reactivity Units(Click here for Detail)
Full Form:Platelet Reactivity Units
Alternative Names:VerifyNow P2Y12 Assay, P2Y12 Reaction Units, VerifyNow P2Y12 Assay, Clopidogrel (Plavix) Platelet Function Test, Thienopyridine Platelet Function Test
Category: Hematology / Coagulation & Platelet Function
Purpose:
The purpose of platelet reactivity units (PRUs) is to measure the effectiveness of P2Y12 receptor blocking drugs, such as clopidogrel and prasugrel, by quantifying the degree of platelet P2Y12 receptor blockade they produce.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Monitoring response to P2Y12 inhibitor therapy in patients with coronary stents
- Evaluation of high on-treatment platelet reactivity (risk of thrombosis)
- Assessment of low platelet reactivity (risk of bleeding)
- Guiding personalized antiplatelet therapy in cardiovascular disease
Typical Normal Range:
- PRU <180: Low platelet reactivity (↑ bleeding risk) PRU 180–240: Optimal therapeutic range PRU >240: High platelet reactivity (↓ drug effect, ↑ thrombosis risk)
- (ranges may vary by institution)
Related Tests: Platelet Function Assay (PFA-100), Light Transmission Aggregometry (LTA), Aspirin Reaction Units (ARU), CBC with Platelets, MEA, VASP, Platelet Function Analyzer, Thromboelastography (TEG), Thromboelastometry (ROTEM)
Notes:
Elevated prolactin (hyperprolactinemia) may result from pituitary tumors, hypothyroidism, pregnancy, or certain medications; low levels are rarely clinically significant.
PSA – Prostate Specific Antigen(Click here for Detail)
Full Form:Prostate-Specific Antigen
Alternative Names:Serum PSA, Total PSA, Free PSA (fPSA),
Category: Tumor Marker / Urology
Purpose:
The primary purpose of PSA (prostate-specific antigen) testing is to serve as a blood test to detect prostate cancer and monitor its progression. It can also detect benign conditions such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or prostatitis. Healthcare professionals measure PSA levels because prostate cancer cells can release higher amounts of this protein into the blood than normal prostate cells.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Screening men for prostate cancer (age- and risk-based)
- Evaluation of urinary symptoms (e.g., frequency, weak stream, nocturia)
- Monitoring treatment response in prostate cancer patients
- Surveillance for recurrence after prostate cancer therapy
Typical Normal Range:
- <4.0 ng/mL (general cutoff for adults)
- Age-adjusted reference ranges often applied (lower in younger men, higher in older men)
Related Tests: Free PSA (%fPSA), Prostate Health Index (PHI), Digital Rectal Exam (DRE), PAP (Prostatic Acid Phosphatase), Imaging (MRI, Ultrasound),
Notes:
Elevated PSA may occur with prostate cancer, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostatitis, or recent instrumentation. Interpretation should consider age, risk factors, and clinical context.
PT – Prothrombin Time(Click here for Detail)
Full Form:Prothrombin Time
Alternative Names:Pro-time, Prothrombin assay, Clotting time (extrinsic pathway),
Category: Coagulation test
Purpose:
The primary purpose of prothrombin time (PT) is to measure the clotting time of blood plasma, which helps diagnose bleeding disorders, monitor the use of anticoagulants such as warfarin, evaluate liver function, and monitor vitamin K levels. This test measures both extrinsic and common clotting pathways and is often expressed as an international normalized ratio (INR) for standardized comparison.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Monitoring warfarin (Coumadin) therapy
- Investigating unexplained bleeding or bruising
- Assessing liver function and clotting factor synthesis
- Screening before surgery for bleeding risk
Typical Normal Range:
- 11–13.5 seconds (varies by lab); INR 0.8–1.1 in healthy individuals
Related Tests: INR (International Normalized Ratio), aPTT (Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time), Fibrinogen, Platelet Count, Coagulation Factor Tests, Fibrinogen Test, Platelet Count
Notes:
Always interpreted with INR when monitoring anticoagulant therapy.
PTH – Parathyroid Hormone(Click here for Detail)
Full Form:Parathyroid Hormone
Alternative Names:Parathormone, Parathyrin, Intact PTH (iPTH), PTH assay, Parathyrin
Category: Endocrine/Hormone test
Purpose:
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) primarily maintains blood calcium levels by stimulating calcium release from bones, increasing calcium absorption in the intestines through active vitamin D, and preventing its excretion by the kidneys.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Diagnosing hyperparathyroidism or hypoparathyroidism
- Evaluating unexplained high or low calcium levels
- Monitoring chronic kidney disease (CKD) and secondary hyperparathyroidism
- Assessing bone disorders related to calcium imbalance
Typical Normal Range:
- 10–65 pg/mL (varies by lab and assay)
Related Tests:Serum Calcium, Phosphate, Vitamin D, Alkaline Phosphatase, Magnesium Test,
Notes:
Blood sample should be collected fasting; interpretation requires correlation with calcium and vitamin D levels.
PTT – Partial Thromboplastin Time(Click here for Detail)
Full Form:Partial Thromboplastin Time
Alternative Names:aPTT (Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time), APTT test, Intrinsic Pathway Coagulation Factor
Category: Coagulation test
Purpose:
A PTT test measures the time it takes for blood to clot by evaluating the intrinsic pathway of the coagulation cascade. Its purpose is to assess the body’s ability to form clots, detect clotting disorders (such as hemophilia), detect clotting factor deficiencies, and monitor heparin therapy.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Monitoring unfractionated heparin therapy
- Investigating prolonged bleeding or clotting disorders
- Diagnosing hemophilia and other factor deficiencies
- Pre-surgical coagulation screening (in select cases)
Typical Normal Range:
- 25–35 seconds (varies by lab)
Related Tests: PT (Prothrombin Time), INR, Fibrinogen, Thrombin Time (TT), Coagulation Factor Tests, Platelet Tests, D-Dimer Test
Notes:
Sensitive to deficiencies of clotting factors VIII, IX, XI, XII; affected by anticoagulant therapy and liver disease.
Tests Starting from Q
QIG – Quantitative Immunoglobulins (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Quantitative Immunoglobulins
Alternative Names: Immunoglobulin levels, IgG/IgA/IgM quantitation, Serum immunoglobulins, Gamma-Globulins, Quantitative, Quantitative Nephelometry Test
Category: Immunology/Serology test
Purpose:
Quantitative immunoglobulin (QIG) tests measure the levels of IgG, IgA, and IgM antibodies in the blood to diagnose immune system disorders, including deficiencies (such as recurrent infections), autoimmune diseases (such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis), certain types of cancer (such as lymphoma or multiple myeloma), and chronic inflammatory diseases.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluating recurrent or chronic infections (suspected immune deficiency)
- Diagnosing autoimmune diseases
- Monitoring multiple myeloma or other plasma cell disorders
- Assessing response to immunosuppressive therapy
Typical Normal Range:
- IgG: 700–1600 mg/dL
- IgA: 70–400 mg/dL
- IgM: 40–230 mg/dL
Related Tests: Serum Protein Electrophoresis (SPEP), Immunofixation, Free Light Chains, IgE level, Immunoglobulin Subclass Tests
Notes:
Interpretation must consider age, clinical history, and possible secondary causes of altered immunoglobulin levels (e.g., liver disease, medications).
Tests Starting from R
RBC – Red Blood Cell (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Red Blood Cell Count
Alternative Names: Erythrocyte count, RBCs, Red count
Category: Hematology (Complete Blood Count – CBC)
Purpose:
Red blood cells (RBCs), or erythrocytes, are primarily responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to the body’s tissues and transporting carbon dioxide, a waste product, back to the lungs for exhalation.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluating anemia or polycythemia
- Monitoring chronic diseases affecting blood production
- Assessing blood loss or bone marrow function
- Routine health checkup (as part of CBC)
Typical Normal Range:
- Men: 4.7–6.1 million/µL
- Women: 4.2–5.4 million/µL
- Children: 4.1–5.5 million/µL
- Newborns: 4.8–7.1 million/µL
Related Tests: Hemoglobin (Hb), Hematocrit (Hct), MCV, MCH, Reticulocyte Count, White blood cell (WBC) count, Platelet count, RBC indices, MCHC, RDW
Notes:
Interpretation should consider hydration status, altitude, and overall CBC results.
RET – Reticulocyte Count (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Reticulocyte Count
Alternative Names: Retic count, Immature red blood cell count, Reticulocyte percent, Reticulocyte index (RI), CRC, Reticulocyte production index (RPI)
Category: Hematology
Purpose:
The reticulocyte count measures immature red blood cells to assess bone marrow function and production. A high count indicates that the bone marrow is compensating for the loss of red blood cells, such as in anemia due to hemorrhage or destruction, while a low count suggests that the bone marrow is not producing enough red blood cells.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluating bone marrow response to anemia
- Monitoring recovery after bone marrow suppression or chemotherapy
- Assessing effectiveness of anemia treatment (e.g., iron, B12, folate therapy)
- Investigating causes of abnormal red blood cell production
Typical Normal Range:
- Adults: 0.5–1.5% of RBCs (absolute: 25,000–75,000/µL)
- Newborns: up to 4–6%
Related Tests: RBC Count, Hemoglobin, Hematocrit, Peripheral Blood Smear, Iron Studies, Complete Blood Count (CBC), Hemoglobin (Hb) and Hematocrit (Hct),
Notes:
Often expressed as corrected reticulocyte count or reticulocyte production index (RPI) to adjust for anemia severity.
RF – Rheumatoid Factor (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Rheumatoid Factor
Alternative Names: RF test, Rheumatoid arthritis factor,
Category: Immunology/Autoimmune test
Purpose:
The purpose of a rheumatoid factor (RF) test is to detect autoantibodies in the blood that may indicate an autoimmune disease, primarily rheumatoid arthritis (RA), but also Sjögren’s syndrome, lupus, and juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
- Differentiating types of arthritis and joint pain
- Investigating systemic autoimmune diseases (e.g., Sjögren’s syndrome)
- Monitoring disease activity in RA (with other markers)
Typical Normal Range:
- <14 IU/mL (reference ranges vary by lab)
Related Tests: Anti-CCP (Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide), ANA (Antinuclear Antibody), ESR, CRP, Complete Blood Count (CBC)
Notes:
Not specific for RA—can be elevated in infections, other autoimmune disorders, and some healthy individuals.
RFP – Renal Function Panel (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Renal Function Panel
Alternative Names: Kidney function tests, Renal profile
Category: Chemistry / Metabolic panel
Purpose:
Kidney function tests measure kidney function. Most of these tests check how efficiently the kidneys eliminate waste. A kidney test may include a blood test, a 24-hour urine sample, or both. Results are usually available the same day or within a few days.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Assessing suspected kidney disease or injury
- Monitoring patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD)
- Evaluating electrolyte or acid–base disturbances
- Monitoring effects of medications affecting kidneys
Typical Normal Range:
- Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN): 7–20 mg/dL
- Creatinine: 0.6–1.3 mg/dL
- Sodium: 135–145 mmol/L
- Potassium: 3.5–5.0 mmol/L
- Chloride: 98–106 mmol/L
- CO₂ (bicarbonate): 22–29 mmol/L
- Calcium: 8.5–10.5 mg/dL
- Phosphorus: 2.5–4.5 mg/dL
- Albumin: 3.5–5.0 g/dL
Related Tests: eGFR (Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate), Urinalysis, Electrolyte Panel, CMP (Comprehensive Metabolic Panel),
Notes:
Interpretation should consider hydration status, medications, and clinical history; eGFR is crucial for staging CKD.
RhIG (Eval) – RhIG Evaluation (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Rh Immune Globulin Evaluation
Alternative Names: RhIG screen, Rh prophylaxis evaluation, Anti-D immune globulin workup, RhoGam Work-up, Postpartum RhIG Evaluation, Rh Immune Eligibility (RHIE)
Category: Transfusion medicine / Prenatal immunohematology
Purpose:
Rh(D) immunoglobulin (RhIG) is a medication used for the management and treatment of Rh-negative pregnancies and inflammatory thrombocytopenic purpura. It belongs to the immunoglobulin class.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Pregnant Rh-negative women (antenatal and postpartum assessment)
- After potential fetomaternal hemorrhage (e.g., trauma, procedures)
- Following miscarriage, abortion, or ectopic pregnancy in Rh-negative women
- Prior to administering RhIG prophylaxis
Typical Normal Range:
- Not applicable (evaluation test, not a quantitative result)
Related Tests: ABO & Rh Typing, Antibody Screen (Indirect Coombs test), Kleihauer-Betke test, Fetomaternal Hemorrhage (FMH) quantification,
Notes:
Ensures appropriate RhIG dosing; critical for preventing hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn (HDFN).
RPR – Rapid Plasma Reagin (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Rapid Plasma Reagin
Alternative Names: Syphilis serology (non-treponemal), RPR test, Automated Reagin Test (ART)
Category: Serology / Infectious disease test
Purpose:
RPR (rapid plasma reagin) is a screening test for syphilis. It measures substances (proteins) called antibodies present in the blood of people who may have the disease.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Screening for syphilis infection
- Confirming suspected syphilis in symptomatic patients
- Monitoring treatment response in syphilis
- Routine prenatal and blood donor screening
Typical Normal Range:
- Non-reactive
Related Tests: VDRL (Venereal Disease Research Laboratory test), FTA-ABS (Fluorescent Treponemal Antibody Absorption), TP-PA (Treponema pallidum Particle Agglutination), Toluidine Red Unheated Serum Test (TRUST), Enzyme Immunoassays (EIA) and Chemiluminescence Immunoassays (CIA)
Notes:
Non-treponemal test—false positives may occur (e.g., in pregnancy, autoimmune disease, viral infections); positive results require confirmation with treponemal tests.
RSV – Respiratory Syncytial Virus (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Respiratory Syncytial Virus
Alternative Names: RSV test, RSV antigen test, RSV PCR, Bronchiolitis – RSV test
Category: Infectious disease / Virology
Purpose:
RSV is not a virus with a “purpose” in the biological sense, but rather a common and highly contagious respiratory virus that causes respiratory tract infections in people of all ages.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Infants and children with bronchiolitis or pneumonia
- Elderly or immunocompromised patients with respiratory symptoms
- Hospitalized patients with acute lower respiratory tract infections
- Outbreak monitoring in neonatal and pediatric units
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (No RSV detected)
Related Tests: Influenza testing, COVID-19 PCR/antigen, Adenovirus panel, Respiratory viral panel (multiplex PCR), Rapid Antigen Test (RAT),
Notes:
Can be performed via antigen detection, PCR, or viral culture; PCR is most sensitive. Clinical correlation with symptoms is essential.
Tests Starting from S
Scl-70 – Scleroderma Antibody (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Anti–Scl-70 Antibody (Anti–Topoisomerase I Antibody)
Alternative Names: Anti–Topoisomerase I, Scleroderma antibody,
Category: Immunology / Autoimmune serology
Purpose:
The Scl-70 antibody (or anti-Scl-70/anti-topoisomerase I) test is intended to help diagnose systemic sclerosis (SSc), particularly the diffuse form, and to assess its severity and potential organ involvement, particularly pulmonary fibrosis and restrictive lung disease.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected systemic sclerosis (scleroderma)
- Evaluating patients with skin thickening, Raynaud’s phenomenon, or interstitial lung disease
- Differentiating between limited and diffuse forms of systemic sclerosis
- Supporting autoimmune connective tissue disease diagnosis
Typical Normal Range:
- Newborn: < 630 ng/dL
- Adult Men: < 200 ng/dL
- Adult Women (follicular phase): < 80 ng/dL
Related Tests: ANA (Antinuclear Antibody), Anti-centromere antibody, Anti-RNA polymerase III, ENA panel, Anti-fibrillarin,
Notes:
A positive result supports diagnosis of diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis; interpretation requires correlation with clinical findings.
SHBG – Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin
Alternative Names: Testosterone-binding globulin, Androgen-binding protein, Sex Steroid-Binding Globulin (SSBG), Androgen-Binding Protein (ABP) (when produced in the testes)
Category: Endocrinology / Hormone-binding protein
Purpose:
Sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) is a protein produced by the liver that binds and transports sex hormones such as testosterone and estrogen into the bloodstream, regulating their availability and preventing them from being activated in the body.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluating androgen disorders (low testosterone, hirsutism, infertility)
- Suspected polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Assessing abnormal estrogen or androgen levels
- Liver disease, thyroid dysfunction, or metabolic syndrome workup
Typical Normal Range:
- Men: 10–57 nmol/L
- Women: 18–144 nmol/L
Related Tests: Total Testosterone, Free Testosterone (calculated), Estradiol, LH/FSH, Free Androgen Index (FAI), Prolactin
Notes:
SHBG is influenced by age, sex hormones, liver function, thyroid status, obesity, and insulin resistance; free androgen index may be calculated using SHBG.
SIFE – Serum Immunofixation Electrophoresis (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Serum Immunofixation Electrophoresis
Alternative Names: Immunofixation (IFE), Immunofixation electrophoresis (serum), IFE, Serum, Protein Electrophoresis by Immunofixation
Category: Immunology / Protein studies
Purpose:
Serum immunofixation electrophoresis (SIFE) is used to identify and characterize abnormal proteins, most commonly monoclonal gammopathies, which may indicate serious conditions such as multiple myeloma, lymphoma, kidney disease, and certain autoimmune diseases.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected multiple myeloma or related plasma cell disorders
- Evaluating unexplained high total protein or abnormal serum protein electrophoresis (SPEP)
- Monitoring progression or remission in monoclonal gammopathies
- Differentiating monoclonal vs. polyclonal immunoglobulin elevations
Typical Normal Range:
- No monoclonal protein detected (normal polyclonal pattern)
Related Tests: SPEP (Serum Protein Electrophoresis), UPEP (Urine Protein Electrophoresis), Free Light Chains, Quantitative Immunoglobulins, Urine Immunofixation Electrophoresis (UIFE),
Notes:
More sensitive than SPEP for detecting small monoclonal proteins; essential in diagnosing and monitoring plasma cell dyscrasias.
Siro – Sirolimus (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Sirolimus (drug level test)
Alternative Names: Rapamycin level, Rapamune level, Sirolimus Level
Category: Therapeutic Drug Monitoring (TDM) / Immunosuppressant assay
Purpose:
Sirolimus is used in combination with other medications to prevent kidney transplant rejection. It belongs to a group of medications called immunosuppressants. When a patient receives an organ transplant, the body’s white blood cells attempt to eliminate (reject) the transplanted organ.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Monitoring kidney, liver, or heart transplant patients on sirolimus
- Preventing transplant rejection while minimizing toxicity
- Adjusting immunosuppressant dosage
- Evaluating suspected drug toxicity or subtherapeutic levels
Typical Normal Range:
- 3–20 ng/mL (therapeutic range varies by transplant type and clinical protocol)
Related Tests: Tacrolimus level, Cyclosporine level, Everolimus level, CBC, Liver & Renal Function Tests, Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN),
Notes:
Blood should be collected as a trough level (just before next dose); metabolism influenced by CYP3A4 and drug interactions.
SPEP – Serum Protein Electrophoresis (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Serum Protein Electrophoresis
Alternative Names: Protein electrophoresis, Serum protein fractionation,
Category: Immunology / Protein studies
Purpose:
The primary purpose of a serum protein electrophoresis (SPEP) test is to separate and measure different proteins in the blood, which aids in the diagnosis and monitoring of diseases such as multiple myeloma, other plasma cell disorders, chronic inflammation, liver disease, kidney disease, and certain autoimmune or neurological diseases.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected multiple myeloma or monoclonal gammopathy
- Evaluating unexplained hyperproteinemia or hypoproteinemia
- Investigating chronic inflammation or autoimmune disorders
- Assessing liver disease or nephrotic syndrome
Typical Normal Range:
- Albumin: 55–65%
- α1-globulins: 2–4%
- α2-globulins: 6–12%
- β-globulins: 8–14%
- γ-globulins: 12–22%
Related Tests: SIFE (Serum Immunofixation Electrophoresis), UPEP (Urine Protein Electrophoresis), Quantitative Immunoglobulins, Free Light Chains, Total Protein Test, Serum Free Light Chain (sFLC) test
Notes:
Detects monoclonal (M-protein) or polyclonal gammopathies; abnormal results usually require confirmation with immunofixation.
SSA – Sjögren’s Syndrome A Antibody (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Sjögren’s Syndrome A Antibody (Anti-Ro antibody)
Alternative Names: Anti-Ro antibody, Anti-SSA antibody, Ro/SSA antibody
Category: Immunology / Autoimmune serology
Purpose:
The anti-SSA antibody (Sjögren’s syndrome A) is used to aid in the diagnosis of Sjögren’s syndrome (SS) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), although it is not exclusive to these conditions. Its presence in a patient with symptoms of connective tissue disease strongly suggests a diagnosis of SS or SLE and may indicate an increased risk of certain systemic manifestations and potential complications, such as congenital heart block during pregnancy.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected Sjögren’s syndrome (dry eyes, dry mouth)
- Evaluation of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Investigating neonatal lupus or congenital heart block risk
- Workup of unexplained autoimmune symptoms
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (<20 U/mL or as defined by lab)
Related Tests: SSB (Anti-La antibody), ANA (Antinuclear Antibody), ENA panel, dsDNA antibody, Immunoglobulin Levels, Complete Blood Count (CBC), Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) and C-Reactive Protein (CRP) Tests, Rheumatoid Factor (RF) Test
Notes:
Often positive in Sjögren’s syndrome and SLE; may cross the placenta, posing risk for neonatal lupus and congenital heart block.
SSB – Sjögren’s Syndrome B Antibody (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Sjögren’s Syndrome B Antibody (Anti-La antibody)
Alternative Names: Anti-La antibody, Anti-SSB antibody, Autoantibodies to SS-B/La
Category: Immunology / Autoimmune serology
Purpose:
The primary purpose of detecting anti-SSB (La) antibodies is to help diagnose Sjögren’s syndrome and certain other autoimmune connective tissue diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected Sjögren’s syndrome (with dry eyes, dry mouth, parotid swelling)
- Differentiating connective tissue diseases (often with SSA/Anti-Ro)
- Evaluating systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients
- Assessing risk of neonatal lupus when present in pregnant women
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (<20 U/mL or as defined by lab)
Related Tests: SSA (Anti-Ro antibody), ANA, ENA panel, dsDNA antibody, Rheumatoid Factor (RF) Test, Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR), C-reactive protein (CRP)
Notes:
Often found with SSA (Anti-Ro); presence of both antibodies increases specificity for Sjögren’s syndrome.
SSDNA – Single Stranded DNA (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Single-Stranded DNA Antibody
Alternative Names: Anti-ssDNA antibody, ssDNA Ab,
Category: Immunology / Autoimmune serology
Purpose:
Single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) is a fundamental intermediary in essential biological processes such as DNA replication, transcription, recombination, and repair, where it serves as a template for enzymes to synthesize new DNA or regulate gene expression.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Differentiating autoimmune connective tissue disorders
- Evaluating unexplained positive ANA results
- Monitoring autoimmune disease activity (in some cases)
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (<20 U/mL or as defined by lab)
Related Tests: dsDNA antibody (Anti-double stranded DNA), ANA, ENA panel, Histone antibody
Notes:
Less specific than dsDNA antibody for lupus; may be positive in other autoimmune or inflammatory conditions.
Tests Starting from T
T Bil – Total Bilirubin (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Total Bilirubin
Alternative Names: Serum bilirubin, TBil, Total serum bilirubin, Neonatal Bilirubin, Jaundice Bilirubin Blood Test
Category: Clinical Chemistry / Liver function test
Purpose:
A total bilirubin (T Bil) test measures bilirubin, a waste product from the breakdown of red blood cells, to help diagnose liver and gallbladder diseases, monitor liver function, and evaluate jaundice.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected liver disease (hepatitis, cirrhosis)
- Evaluating jaundice in adults and newborns
- Assessing hemolytic anemia
- Monitoring liver function in patients on hepatotoxic drugs
Typical Normal Range:
- 0.3–1.2 mg/dL (varies slightly by lab)
Related Tests: Direct (Conjugated) Bilirubin, Indirect (Unconjugated) Bilirubin, ALT, AST, ALP, GGT, Complete Blood Count (CBC)
Notes:
Elevated levels may reflect hepatocellular disease, cholestasis, or increased hemolysis; interpretation requires fractionated bilirubin.
T3 – Triiodothyronine (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Triiodothyronine
Alternative Names: Total T3, Serum T3, Triiodothyronine test, T3 radioimmunoassay, Total triiodothyronine (TT3), Free triiodothyronine (FT3)
Category: Endocrinology / Thyroid function test
Purpose:
T3 (triiodothyronine) is a potent thyroid hormone that regulates metabolism, body temperature, heart rate, muscle function, and brain development. It plays a vital role in growth and development, bone health, and controlling the body’s energy use.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected hyperthyroidism (e.g., Graves’ disease)
- Evaluating unexplained weight loss, palpitations, or goiter
- Monitoring thyroid replacement or suppressive therapy
- Clarifying abnormal TSH or T4 results
Typical Normal Range:
- 80–200 ng/dL (may vary by lab)
Related Tests: Free T3, Free T4, Total T4, TSH, Thyroid Antibodies, Thyroid Ultrasound,
Notes:
More sensitive for hyperthyroidism than hypothyroidism; Free T3 measurement may provide more accuracy in certain cases.
T4 – Thyroxine (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Thyroxine
Alternative Names: Total T4, Serum T4, Free T4 index (FTI), Free thyroxine test, Thyroxine screen
Category: Endocrinology / Thyroid function test
Purpose:
T4, or thyroxine, is the main hormone produced by the thyroid gland, which regulates the body’s energy use (metabolic rate), growth, and nearly all other bodily functions, including heart rate, digestion, brain development, and bone health.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism
- Clarifying abnormal TSH results
- Monitoring thyroid hormone replacement therapy
- Evaluating pituitary or hypothalamic causes of thyroid dysfunction
Typical Normal Range:
- 4.5–11.2 µg/dL (varies by lab)
Related Tests: Free T4, T3 (Total & Free), TSH, Thyroid Antibodies, Thyroglobulin Test
Notes:
Total T4 levels are influenced by thyroid-binding proteins; Free T4 provides a more accurate reflection of thyroid hormone status.
Tacro – Tacrolimus (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Tacrolimus
Alternative Names: FK506, Prograf level, Tacro, Tacrolimus Level, Tacrolimus, Whole Blood, Tacrolimus, Immunoassay, Tacrolimus, Blood
Category: Immunosuppressant drug monitoring
Purpose:
Tacrolimus is used in combination with other kidney medications to prevent rejection of a transplanted organ (e.g., liver, heart, or lung). This medication may be combined with steroids, azathioprine, basiliximab, or mycophenolate mofetil. Tacrolimus belongs to a group of immunosuppressant medications.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Monitoring organ transplant recipients (kidney, liver, heart, lung)
- Evaluating suspected tacrolimus toxicity
- Assessing drug compliance in transplant patients
- Guiding dose adjustment during therapy
Typical Normal Range:
- Trough level: 5–20 ng/mL (varies with organ type and time post-transplant)
Related Tests: Cyclosporine level, Sirolimus level, Everolimus level, Liver function tests, Kidney function tests, Electrolyte tests, Tests for signs of infection, Biopsy of the transplanted organ
Notes:
Requires trough (pre-dose) blood sample; levels influenced by drug interactions and liver function.
TBG – Thyroxine Binding Globulin (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Thyroxine Binding Globulin
Alternative Names: Thyroxine-Binding Protein, TBG Serum Test, TBG level,
Category: Endocrinology / Thyroid Function Test
Purpose:
Thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG) primarily transports thyroid hormones (T4 and T3) in the blood. As the primary carrier protein, it binds a large proportion of circulating T4 and facilitates the delivery of these hormones to the body’s target tissues.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of abnormal thyroid function tests
- Investigation of inherited or acquired TBG deficiency/excess
- Assessment of altered thyroid hormone transport in liver disease or pregnancy
- Monitoring patients on drugs affecting thyroid-binding proteins (e.g., estrogen, steroids)
Typical Normal Range:
- 13–39 mg/L (values may vary by lab and method)
Related Tests: Total T4, Free T4(FT4), Total T3, TSH, Free T3 (FT3), T3 Resin Uptake (T3RU)
Notes:
Abnormal TBG does not indicate thyroid disease itself; interpretation should be made in conjunction with thyroid hormone levels.
TG – Triglycerides (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Triglycerides
Alternative Names: Serum Triglycerides, Lipid Panel – TG, Fasting Lipoprotein Panel, Coronary Risk Panel
Category: Lipid Profile / Cardiology
Purpose:
Triglycerides (TG) are a type of fat found in the blood that the body uses for energy, storing unused calories for later use. They come from the foods you eat (including fats, sugars, and alcohol) and the calories your body produces.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of cardiovascular disease risk
- Screening for hyperlipidemia or metabolic syndrome
- Monitoring lipid-lowering therapy
- Assessing risk of pancreatitis in severe hypertriglyceridemia
Typical Normal Range:
- Normal: <150 mg/dL (<1.7 mmol/L)
- Borderline High: 150–199 mg/dL (1.7–2.2 mmol/L)
- High: 200–499 mg/dL (2.3–5.6 mmol/L)
- Very High: ≥500 mg/dL (≥5.7 mmol/L)
Related Tests: Total Cholesterol, LDL-C, HDL-C, VLDL-C, Apolipoproteins, Fasting Glucose, Triglycerides, Lipoprotein (a) or Lp(a)
Notes:
Fasting sample (8–12 hours) is usually recommended; elevated levels may be secondary to diabetes, obesity, alcohol use, or certain medications.
Theo – Theophylline (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Theophylline
Alternative Names: Theo-Dur level, Aminophylline level, Blood theophylline level, Serum theophylline concentrations
Category: Drug Monitoring / Respiratory Medicine
Purpose:
Theophylline is used to prevent and treat wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness caused by asthma, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and other lung diseases. It relaxes and opens the airways, making breathing easier.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Monitoring patients on theophylline therapy for asthma or COPD
- Evaluating suspected theophylline toxicity
- Guiding dose adjustments, especially in children and elderly
- Assessing effects of drug interactions or altered metabolism (e.g., liver disease, smoking)
Typical Normal Range:
- Therapeutic trough level: 10–20 µg/mL
Related Tests: Liver function tests, Kidney function tests, Arterial blood gases, Other bronchodilator levels, Blood sugar and electrolyte tests
Notes:
Blood levels should be measured at steady-state (usually 4–8 hours after dose, depending on formulation); narrow therapeutic index with risk of seizures, arrhythmias, and toxicity.
TIBC – Total Iron Binding Capacity (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Total Iron Binding Capacity
Alternative Names: Transferrin Iron Binding Capacity, Serum Iron Binding Capacity, Iron Binding Capacity (IBC), Siderophilin (an older term for transferrin)
Category: Iron Studies / Hematology
Purpose:
The primary purpose of a total iron binding capacity (TIBC) test is to measure the blood’s ability to transport iron, which indirectly assesses transferrin in the body. It can diagnose iron metabolism disorders, such as iron deficiency anemia or iron overload, by indicating whether iron stores are low (high TIBC) or high (low TIBC).
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of suspected iron deficiency anemia
- Differentiating anemia of chronic disease from iron deficiency
- Monitoring iron status in chronic illness or malnutrition
- Assessing possible iron overload (e.g., hemochromatosis)
Typical Normal Range:
- 240–450 µg/dL (45–80 µmol/L)
Related Tests: Serum Iron, Transferrin, Transferrin Saturation, Ferritin, Unsaturated Iron-Binding Capacity (UIBC), Complete Blood Count (CBC)
Notes:
TIBC is an indirect measure of transferrin; usually interpreted together with iron and ferritin levels for accurate assessment.
TORCH – TOxoplasmosis, Rubella Cytomegalovirus, Herpes simplex (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: TORCH Panel (Toxoplasmosis, Rubella, Cytomegalovirus, Herpes Simplex)
Alternative Names: TORCH Screen, TORCH Profile, Congenital Infection Panel
Category: Infectious Disease / Prenatal & Neonatal Screening
Purpose:
The TORCH test is a group of blood tests designed to detect infections (toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus, and herpes simplex virus) that can be transmitted from a mother to her fetus or newborn and potentially cause serious health problems, including birth defects, developmental delays, and other serious complications.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Pregnant women during prenatal screening
- Evaluation of infants with congenital anomalies or developmental delay
- Investigation of suspected intrauterine or perinatal infections
- Assessment of women with history of miscarriage or stillbirth
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative (no detectable IgM antibodies; IgG indicates past infection or immunity)
Related Tests: Individual IgM/IgG tests for Toxoplasmosis, Rubella, CMV, HSV; Parvovirus B19; Syphilis serology, T – Toxoplasmosis
Notes:
TORCH is a screening panel; positive results require confirmatory testing. Interpretation differs for IgM (acute/recent infection) and IgG (past exposure or immunity).
TP – Total Protein (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Total Protein
Alternative Names: Serum Total Protein, TP Test, Total Protein with A/G Ratio
Category: Biochemistry / Liver & Kidney Function Tests
Purpose:
A total protein (TP) test measures the amount of protein in the blood to help diagnose and monitor conditions affecting the liver, kidneys, and immune system, as well as to assess nutritional status.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of liver disease (cirrhosis, hepatitis)
- Assessment of kidney disease (nephrotic syndrome, protein loss)
- Monitoring nutritional status or malabsorption disorders
- Workup of immune disorders, chronic inflammation, or malignancies (e.g., multiple myeloma)
Typical Normal Range:
- 6.0–8.3 g/dL (60–83 g/L)
Related Tests: Albumin, Globulin, Albumin/Globulin (A/G) Ratio, Serum Protein Electrophoresis, CMP, Urine Protein to Creatinine Ratio (UPCR)
Notes:
Abnormal levels require further evaluation to distinguish between albumin and globulin changes; hydration status can influence results.
TREP – Treponemal Antibodies (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Treponemal Antibodies Test
Alternative Names: Syphilis Antibody Test, Treponema pallidum Antibody (TP-Ab), TPHA, FTA-ABS, EIA: Enzyme Immunoassay (for T. pallidum antibodies), CIA: Chemiluminescence Immunoassay
Category: Infectious Disease / Serology
Purpose:
Treponemal antibody tests (such as TP-PA and EIA) detect specific antibodies produced by the body in response to the bacterium Treponema pallidum, which causes syphilis. These tests are primarily used as confirmatory tests for syphilis, often following a positive result from a less specific screening test.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Screening for syphilis in blood donors, prenatal care, or high-risk groups
- Confirmatory testing after a positive non-treponemal test (e.g., VDRL, RPR)
- Evaluation of patients with symptoms suggestive of syphilis
- Monitoring previously treated patients for evidence of persistent infection
Typical Normal Range:
- Nonreactive (Negative)
Related Tests: VDRL, RPR, TPHA, FTA-ABS, HIV Test, Hepatitis B & C Serology, PCR
Notes:
Treponemal tests usually remain positive for life, even after successful treatment; non-treponemal tests are used to monitor treatment response.
Trep Ab – Treponemal Antibodies (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Treponemal Antibodies
Alternative Names: Treponema pallidum Antibody (TP-Ab), Syphilis Antibody Test, TPHA, FTA-ABS, CIA, EIA, TP-PA
Category: Infectious Disease / Serology
Purpose:
Treponemal antibody (Trep Ab) tests are used to diagnose syphilis by detecting antibodies produced specifically in response to the bacterium Treponema pallidum, the cause of syphilis.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Screening for syphilis in prenatal testing, blood donors, or high-risk individuals
- Confirmation of reactive non-treponemal tests (VDRL, RPR)
- Evaluation of patients with symptoms suggestive of syphilis
- Workup of unexplained neurological, dermatological, or systemic findings
Typical Normal Range:
- Nonreactive (Negative)
Related Tests: VDRL, RPR, TPHA, FTA-ABS, HIV Antibody Test, Hepatitis B & C Serology,
Notes:
Treponemal antibody tests usually remain positive for life, even after successful treatment; non-treponemal tests are required to assess disease activity and treatment response.
TRH – Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone
Alternative Names: Thyroliberin, Protirelin, TRH stimulation test
Category: Endocrinology / Hormone Stimulation Test
Purpose:
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) primarily stimulates the anterior pituitary gland to release thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which in turn regulates the production and secretion of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Assessment of secondary (pituitary) vs. tertiary (hypothalamic) hypothyroidism
- Evaluation of unexplained thyroid function abnormalities
- Research or specialized endocrine investigations
- Historical use in suspected pituitary or hypothalamic disorders
Typical Normal Range:
- Baseline plasma TRH is usually undetectable; for TRH stimulation test:
- TSH rise of ≥2–5 mIU/L above baseline within 20–30 minutes is expected
Related Tests: TSH, Free T4, Free T3, TRH Stimulation Test, Pituitary Hormone Panel, Thyroid Ultrasound, Thyroid Uptake and Scan, Thyroid Antibody Tests
Notes:
Rarely performed in routine clinical practice; mainly used in specialized endocrinology settings. Synthetic TRH (protirelin) may be administered intravenously for stimulation testing.
Trig – Triglycerides (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Triglycerides
Alternative Names: TG, Serum Triglycerides, Lipid Panel – Triglycerides, fasting lipoprotein panel,
Category: Lipid Profile / Cardiology
Purpose:
Triglycerides are the main type of body fat and are primarily used to store excess energy from food. They provide fuel for cells and are stored in fat cells for use between meals or during times of energy need. While essential for health, high triglyceride levels are a risk factor for conditions such as heart disease, stroke, and metabolic syndrome.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Screening for dyslipidemia and cardiovascular risk
- Evaluation of metabolic syndrome or diabetes mellitus
- Monitoring response to lipid-lowering therapy
- Assessment of hypertriglyceridemia-related pancreatitis risk
Typical Normal Range:
- Normal: <150 mg/dL (<1.7 mmol/L)
- Borderline High: 150–199 mg/dL (1.7–2.2 mmol/L)
- High: 200–499 mg/dL (2.3–5.6 mmol/L)
- Very High: ≥500 mg/dL (≥5.7 mmol/L)
Related Tests: Total Cholesterol, LDL-C, HDL-C, VLDL-C, Apolipoproteins, Fasting Glucose, Triglycerides,
Notes:
Fasting (8–12 hours) sample is preferred; elevated levels may result from obesity, diabetes, alcohol use, or certain medications.
TSH – Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Thyroid Stimulating Hormone
Alternative Names: Thyrotropin, hTSH, Thyrotropic hormone
Category: Endocrinology / Thyroid Function Test
Purpose:
TSH tells the thyroid how much thyroid hormone to produce. If thyroid hormone levels in the blood are too low, the pituitary gland produces more TSH to stimulate the thyroid to work harder. If levels are too high, the pituitary gland produces little or no TSH.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Screening for hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism
- Monitoring thyroid hormone replacement therapy
- Adjusting dose in patients on levothyroxine
- Evaluating pituitary or hypothalamic function
Typical Normal Range:
- 0.4 – 4.0 mIU/L (may vary slightly by lab and method)
Related Tests: Free T4, Free T3, Total T4, Total T3, Anti-TPO Antibodies, TRH Test, Thyroid Antibody Tests, Thyroglobulin (Tg) Test, Thyroid Imaging Tests
Notes:
Most sensitive single test for thyroid function; interpretation should be made along with Free T4/T3 levels, especially in pituitary disease or during therapy monitoring.
TSI – Thyroid Stimulating Immunoglobulin (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Thyroid Stimulating Immunoglobulin
Alternative Names: Thyroid Stimulating Antibody (TSAb), TSH Receptor Antibody (TSHR-Ab – stimulating type), Long-acting thyroid stimulator (LATS), TSIG, Thyretain
Category: Endocrinology / Autoimmune Thyroid Tests
Purpose:
The TSI assessments evaluate college readiness in reading, writing, and mathematics. The results are used for college placement. Applicants take a placement test with 20 to 25 questions per section.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Diagnosis of Graves’ disease
- Differentiating Graves’ disease from other causes of hyperthyroidism
- Predicting risk of neonatal thyrotoxicosis in infants of affected mothers
- Monitoring disease activity or relapse after treatment
Typical Normal Range:
- Negative or ≤1.3 TSI index (reference ranges vary by laboratory and method)
Related Tests: TSH, Free T4, Free T3, Anti-TPO Antibodies, Anti-Tg Antibodies, TRAb (TSH receptor antibody panel), Thyroid Peroxidase Antibody (TPOAb) Test, Thyroglobulin Antibody (TgAb) Test
Notes:
A positive TSI strongly supports Graves’ disease; levels may remain elevated even after clinical remission.
TT – Thrombin Time (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Thrombin Time
Alternative Names: Thrombin Clotting Time (TCT), Fibrin Time, Fibrinogen Screen
Category: Hematology / Coagulation Test
Purpose:
The thrombin time (TT) assesses blood coagulation by measuring the time it takes for fibrinogen to convert to fibrin after the addition of thrombin, a clotting enzyme, to plasma. Its purpose is to detect abnormalities in the final phase of the coagulation cascade, such as low fibrinogen levels, fibrinogen dysfunction, or the presence of inhibitors such as heparin.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of suspected fibrinogen abnormalities (quantitative or qualitative)
- Investigation of prolonged clotting times (aPTT, PT)
- Monitoring effects of thrombin-inhibiting drugs (e.g., heparin, dabigatran)
- Workup of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) or liver disease
Typical Normal Range:
- 14–21 seconds (varies slightly by lab)
Related Tests: PT (Prothrombin Time), aPTT (Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time), Fibrinogen, Reptilase Time, D-Dimer,
Notes:
Prolonged TT may result from low or abnormal fibrinogen, heparin contamination, or direct thrombin inhibitors; Reptilase Time helps differentiate heparin effect from fibrinogen defects.
Tests Starting from U
UIFE – Urine Immunofixation Electrophoresis(Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Urine Immunofixation Electrophoresis
Alternative Names: Urinary IFE, Immunofixation of Urine, Urine Protein Immunofixation, Bence-Jones proteins,
Category: Hematology / Protein Electrophoresis
Purpose:
UIFE (urinary immunofixation electrophoresis) is a laboratory test that identifies and measures abnormal proteins in a urine sample, most commonly monoclonal proteins (M proteins) associated with plasma cell disorders such as multiple myeloma, Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia, and amyloidosis.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Diagnosis of multiple myeloma or related plasma cell dyscrasias
- Detection of Bence-Jones proteinuria (free light chains in urine)
- Evaluation of unexplained proteinuria
- Monitoring treatment response in plasma cell disorders
Typical Normal Range:
- No monoclonal protein detected (Negative)
Related Tests: Cortisol, ACTH Stimulation Test, DHEA-S
Notes:
More sensitive than urine protein electrophoresis alone; often performed alongside SPEP/IFE for comprehensive evaluation of monoclonal gammopathies.
UPE, UPEP, Ur Prot Elect – Urine Protein Electrophoresis (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Urine Protein Electrophoresis
Alternative Names: UPE, UPEP, Urinary Protein Electrophoresis, Urine electrophoresis, Bence Jones protein
Category: Hematology / Protein Electrophoresis
Purpose:
The purpose of a urine protein electrophoresis (UPEP) test is to detect, identify, and measure specific proteins in urine to help diagnose conditions such as multiple myeloma, amyloidosis, and kidney problems by looking for abnormalities in the types and amounts of proteins present.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Screening for monoclonal proteins in suspected multiple myeloma or related disorders
- Detection of Bence-Jones proteins (free light chains)
- Evaluation of persistent or unexplained proteinuria
- Monitoring disease progression or treatment response in plasma cell disorders
Typical Normal Range:
- Normal urine shows only small amounts of albumin; no monoclonal protein bands detected
Related Tests: Serum Protein Electrophoresis (SPEP), Urine Immunofixation (UIFE), Serum Immunofixation (SIFE), Serum Free Light Chains, UACR,
Notes:
Less sensitive than urine immunofixation; a 24-hour urine collection is often recommended for accurate quantification of protein excretion.
Tests Starting from V
VCA – Viral Capsid Antigen (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Viral Capsid Antigen
Alternative Names: EBV VCA, Epstein-Barr Virus Capsid Antigen, VCA IgM, VCA IgG, EBV Capsid Antibody IgM/IgG
Category: Serology / Infectious Disease
Purpose:
The purpose of viral capsid antigen (VCA) is to serve as a diagnostic marker for Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infections, allowing physicians to determine whether a patient has an acute, past, or recurrent Epstein-Barr virus infection by detecting antibodies to it.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of infectious mononucleosis symptoms (fever, sore throat, lymphadenopathy)
- Differentiating acute vs. past EBV infection
- Unexplained lymphadenopathy or hepatosplenomegaly
- Screening in immunocompromised patients with suspected EBV reactivation
Typical Normal Range:
- VCA IgM: Negative (absence suggests no acute infection)
- VCA IgG: Negative (absence suggests no prior exposure)
Related Tests: EBV Nuclear Antigen (EBNA), Early Antigen (EA), Monospot Test, CMV Antibodies, EBV DNA PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), Epstein-Barr Nuclear Antigen (EBNA) Test,
Notes:
Presence of VCA IgM = acute/recent EBV infection.
Presence of VCA IgG with EBNA IgG = past infection.
Interpretation requires correlation with other EBV serologies.
VDRL – Venereal Disease Reference Lab (Syphilis Test, CSF) (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Venereal Disease Research Laboratory Test
Alternative Names: Syphilis Test (CSF/Serum), Nontreponemal Syphilis Test, VDRL, CSF, Neurosyphilis test
Category: Serology / Infectious Disease
Purpose:
The VDRL test is designed to detect syphilis by detecting antibodies produced by the body in response to the causative bacteria. Used with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF-VDRL), it is specifically designed to aid in the diagnosis of neurosyphilis, a type of syphilis that affects the brain and spinal cord. The test analyzes a blood or CSF sample to look for these antibodies; a positive result indicates possible exposure to the bacteria.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Initial screening for syphilis
- Confirmation of neurosyphilis (CSF testing)
- Monitoring treatment response in syphilis patients
- Investigation of unexplained neurological symptoms with syphilis risk
Typical Normal Range:
- Nonreactive (Negative)
Related Tests: RPR (Rapid Plasma Reagin), FTA-ABS (Fluorescent Treponemal Antibody Absorption), TPHA (Treponema pallidum Hemagglutination Assay), Treponema Pallidum Particle Agglutination Assay (TP-PA),
Notes:
VDRL is a nontreponemal test; false positives may occur (e.g., autoimmune disease, infections, pregnancy).
A reactive VDRL must be confirmed with a treponemal-specific test.
CSF VDRL is more specific for neurosyphilis but less sensitive.
Vit A – Vitamin A (Retinol) (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Vitamin A (Retinol)
Alternative Names: Retinol Test, Serum Vitamin A, Retinol Test, Serum Retinol
Category: Nutritional / Biochemistry
Purpose:
Vitamin A (retinol) is essential for good vision, especially in low light, and for maintaining the structure of the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. It supports cell division, immune system function, and a healthy pregnancy and breastfeeding. Vitamin A contributes to retinal pigment production and cell health, thus preventing corneal damage.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected vitamin A deficiency (night blindness, xerophthalmia)
- Malabsorption syndromes (e.g., celiac disease, cystic fibrosis)
- Chronic liver disease assessment
- Monitoring supplementation or suspected vitamin A toxicity
Typical Normal Range:
- 20–60 µg/dL (0.70–2.09 µmol/L) *values may vary by lab
Related Tests: Vitamin D, Vitamin E, Vitamin K, Liver Function Tests (LFTs), Retinol-Binding Protein (RBP), Carotenoid Testing,
Notes:
Fasting sample is recommended for accurate measurement.
Deficiency can cause vision and immune problems.
Excess vitamin A may lead to toxicity (headache, liver damage, teratogenicity).
Vit B1 – Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Vitamin B1 – Thiamine
Alternative Names: Thiamine Test, Thiamin Pyrophosphate (TPP) Level, Thiamine diphosphate (TDP), Whole blood thiamine, Erythrocyte thiamine pyrophosphate
Category: Nutritional / Biochemistry
Purpose:
Thiamine, also known as vitamin B1, is one of the B vitamins. It helps convert food into energy and maintain a healthy nervous system. The body cannot produce thiamine on its own. However, you can usually get enough of it through food.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected thiamine deficiency (e.g., beriberi, Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome)
- Chronic alcoholism
- Malabsorption syndromes or prolonged parenteral nutrition
- Unexplained neuropathy, confusion, or heart failure
Typical Normal Range:
- 2.5–7.5 µg/dL (varies by lab and method)
Related Tests: Vitamin B6, Vitamin B12, Folate, RBC Transketolase Activity,
Notes:
Whole blood or plasma is tested; fasting sample preferred.
Deficiency commonly linked to alcoholism, poor diet, or chronic illness.
Early detection is important, as neurological damage may be irreversible if untreated.
Vit B12 – Vitamin B12 (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin)
Alternative Names: Cobalamin Test, Serum B12,
Category: Nutritional / Hematology
Purpose:
Vitamin B12 plays an essential role in the formation of red blood cells, DNA production and repair, and proper brain and nervous system function. Its deficiency can cause symptoms such as fatigue, nerve problems such as tingling or memory impairment, and a type of anemia characterized by an abnormally large volume of red blood cells.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Evaluation of macrocytic anemia (megaloblastic anemia)
- Neurological symptoms (numbness, tingling, memory issues)
- Suspected malabsorption (pernicious anemia, gastric surgery, Crohn’s disease)
- Monitoring in strict vegetarians/vegans or elderly patients
Typical Normal Range:
- 200–900 pg/mL (148–665 pmol/L; varies by lab)
Related Tests: Folate, Homocysteine, Methylmalonic Acid (MMA), Complete Blood Count (CBC),
Notes:
Low levels may indicate dietary deficiency, pernicious anemia, or malabsorption.
Elevated MMA and homocysteine help confirm deficiency.
Early treatment prevents irreversible neurological damage.
Vit B2 – Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
Alternative Names: Riboflavin Test, Erythrocyte Glutathione Reductase Activity (Functional Test), Vitamin B2, Quantitative,
Category: Nutritional / Biochemistry
Purpose:
Vitamin B2, or riboflavin, is essential for converting food into energy, metabolizing fats, proteins, and carbohydrates, and for the proper functioning of cells, skin, mucous membranes, and red blood cells. It acts as a coenzyme, promoting various metabolic reactions and antioxidant functions in the body.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected riboflavin deficiency (ariboflavinosis)
- Symptoms like cheilitis, glossitis, angular stomatitis
- Malnutrition or chronic alcoholism
- Patients on long-term dialysis or malabsorption syndromes
Typical Normal Range:
- 5–50 µg/L (varies by lab and method)
Related Tests: Vitamin B1, Vitamin B6, Vitamin B12, Folate, Vitamin B3, Folate (Folic Acid/Vitamin B9), Tests for Anemia
Notes:
Riboflavin deficiency often coexists with other B-complex deficiencies.
Functional enzyme activity tests (e.g., RBC glutathione reductase) are more sensitive than direct serum measurement.
Water-soluble; deficiency develops quickly if intake is low.
Vit B6 – Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine)
Alternative Names: Pyridoxal-5′-Phosphate (PLP) Test, Pyridoxine Test, PLP Test , Vitamin B6 Profile, P-5-P Test
Category: Nutritional / Biochemistry
Purpose:
Pyridoxine primarily treats vitamin B6 deficiency and helps relieve nausea and vomiting during pregnancy. It exists in various forms, including pyridoxine, pyridoxal, and pyridoxamine, which are converted into the active coenzyme, pyridoxal 5-phosphate (PLP or P5P), in the body.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Unexplained peripheral neuropathy or seizures
- Evaluation of microcytic anemia (sideroblastic anemia)
- Chronic alcoholism or malnutrition
- Monitoring patients on isoniazid, hydralazine, or penicillamine therapy (drugs that interfere with B6 metabolism)
Typical Normal Range:
- 5–50 µg/L (20–202 nmol/L; varies by lab)
Related Tests: Vitamin B1, Vitamin B2, Vitamin B12, Folate, Homocysteine, Tryptophan Load Test, Urinary Cystathionine, Complete Blood Count (CBC),
Notes:
Plasma PLP is the most reliable indicator of B6 status.
Deficiency can cause neurological and hematological issues.
Excessive supplementation may also cause neuropathy.
Vit C – Vitamin C (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid)
Alternative Names: Ascorbic Acid Test, Plasma Vitamin C, Plasma test, Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid)
Category: Nutritional / Biochemistry
Purpose:
Vitamin C’s functions include acting as an antioxidant to protect cells, supporting the body’s collagen production for tissue repair and wound healing, maintaining immune function, and promoting iron absorption.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected scurvy (bleeding gums, poor wound healing, fatigue)
- Malnutrition or restrictive diets
- Chronic alcoholism or malabsorption syndromes
- Monitoring supplementation in high-dose therapy
Typical Normal Range:
- 0.4–2.0 mg/dL (23–114 µmol/L; varies by lab)
Related Tests: Vitamin A, Vitamin E, Vitamin D, Zinc, Complete Blood Count (CBC),
Notes:
Plasma/serum levels reflect recent intake rather than long-term stores.
Deficiency leads to connective tissue weakness and impaired immunity.
Instability of vitamin C requires proper sample handling (light-protected, immediate processing).
Vit D – 25-Hydroxy Vitamin D (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: 25-Hydroxy Vitamin D (Calcidiol)
Alternative Names: 25(OH)D, Calcidiol, Vitamin D Test, 25-hydroxycholecalciferol test
Category: Nutritional / Endocrinology
Purpose:
25-Hydroxyvitamin D, or calcidiol, is a form of vitamin D stored in the body. Its function is to indicate overall vitamin D status, helping to ensure adequate levels for bone health and calcium absorption. Measuring its concentration through a blood test is the most accurate way to determine vitamin D excess or deficiency.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Suspected vitamin D deficiency (fatigue, bone pain, muscle weakness)
- Osteoporosis or osteomalacia evaluation
- Chronic kidney disease and parathyroid disorders
- Monitoring vitamin D supplementation or toxicity
Typical Normal Range:
- Deficient: <20 ng/mL (<50 nmol/L)
- Insufficient: 20–29 ng/mL (50–74 nmol/L)
- Sufficient: 30–100 ng/mL (75–250 nmol/L)
- Possible Toxicity: >150 ng/mL (>375 nmol/L)
Related Tests: Calcium, Phosphorus, Parathyroid Hormone (PTH), Alkaline Phosphatase,
Notes:
25(OH)D is preferred for status assessment; 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D is not routinely measured.
Deficiency is common worldwide, especially in elderly, malnourished, or low sun exposure populations.
Over-supplementation may lead to hypercalcemia and kidney damage
VLDL – Very Low Density Lipoprotein (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Very Low Density Lipoprotein
Alternative Names: VLDL Cholesterol, VLDL-C, Very Low-Density Lipoprotein Test
Category: Lipid Profile / Cardiology
Purpose:
Very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL) serve as a vehicle for the liver to transport triglycerides and cholesterol to the body’s peripheral tissues. Once synthesized by the liver, VLDL transports fatty acids to muscle and fat cells for energy production and storage.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Routine lipid profile for cardiovascular risk assessment
- Hyperlipidemia or dyslipidemia evaluation
- Monitoring response to lipid-lowering therapy
- Patients with obesity, diabetes, or metabolic syndrome
Typical Normal Range:
- 2–30 mg/dL (varies by lab)
Related Tests: Total Cholesterol, LDL, HDL, Triglycerides, Apolipoprotein B,
Notes:
VLDL is usually calculated as Triglycerides ÷ 5 (when TG <400 mg/dL).
Elevated VLDL is associated with atherosclerosis and pancreatitis risk.
Interpretation should be done along with LDL, HDL, and triglycerides.
VMA – Vanillylmandelic Acid (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Vanillylmandelic Acid
Alternative Names: Urinary VMA Test, Catecholamine Metabolite Test,
Category: Biochemistry / Endocrinology
Purpose:
Very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL) serve as a vehicle for the liver to transport triglycerides and cholesterol to the body’s peripheral tissues. Once synthesized by the liver, VLDL transports fatty acids to muscle and fat cells for energy production and storage.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Routine lipid profile for cardiovascular risk assessment
- Hyperlipidemia or dyslipidemia evaluation
- Monitoring response to lipid-lowering therapy
- Patients with obesity, diabetes, or metabolic syndrome
Typical Normal Range:
- <7 mg/24 hours (adults; varies by age and lab)
Related Tests: Plasma Free Metanephrines, Urinary Metanephrines, Catecholamines, HVA (Homovanillic Acid),
Notes:
24-hour urine collection is required for accurate results.
Certain foods (vanilla, caffeine, bananas, chocolate) and drugs may interfere with test accuracy.
Often used along with metanephrine assays for higher sensitivity.
VZG – Varicella zoster IgG (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Varicella Zoster Virus Immunoglobulin G
Alternative Names: VZV IgG, Chickenpox/Herpes Zoster IgG Antibody Test, Varicella-Zoster Antibody, IgG, Serum, VZV IgG Serology
Category: Serology / Infectious Disease
Purpose:
A varicella-zoster IgG (VZG) test determines whether a person has antibodies to the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), which causes chicken pox and shingles, indicating prior infection or immunity due to vaccination.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Determining immunity to varicella (chickenpox)
- Pre-vaccination or post-vaccination antibody testing
- Screening in healthcare workers, pregnant women, or immunocompromised patients
- Confirmation of past exposure or infection history
Typical Normal Range:
- Positive = Immune; Negative = Non-immune (cut-off values vary by lab)
Related Tests: Varicella Zoster IgM, Herpes Simplex Virus IgG/IgM, Measles IgG, VZV DNA testing (PCR),
Notes:
A positive IgG indicates past infection or successful vaccination.
IgM is tested for acute or recent infection, while IgG indicates long-term immunity.
Recommended before pregnancy or immunosuppressive therapy to confirm immune status.
Tests Starting from W
WBC – White Blood Cell Count (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: White Blood Cell Count
Alternative Names: Leukocyte Count, Total WBC,
Category: Hematology / Complete Blood Count (CBC)
Purpose:
The white blood cell (WBC) count measures the number of white blood cells in the blood. It is used to diagnose and monitor conditions such as infections, inflammation, allergic reactions, autoimmune diseases, and some types of cancer. A high or low WBC count indicates that the immune system is reacting to or fighting an underlying problem.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Investigation of suspected infection (bacterial, viral, fungal, parasitic)
- Monitoring immune status in immunocompromised patients
- Evaluation of hematologic conditions (e.g., leukemia, bone marrow disorders)
- Monitoring response to chemotherapy or immunosuppressive therapy
Typical Normal Range:
- 4,000 – 11,000 /µL (4.0 – 11.0 × 10⁹/L)
Related Tests: Differential Leukocyte Count, Neutrophil Count, Lymphocyte Count, Hemoglobin, Platelet Count, Complete Blood Count (CBC), Bone Marrow Aspiration and Biopsy
Notes:
Interpretation requires differential count; levels may vary with age, pregnancy, medications, stress, and infections.
Tests Starting from X
Xa – Heparin Anti-Xa(Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Heparin Anti-Factor Xa Assay
Alternative Names: Anti-Xa Activity, LMWH Monitoring, Unfractionated Heparin Activity Test, Anti-Factor Xa
Category: Hematology / Coagulation Test
Purpose:
Its primary purpose is to monitor low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) therapy, particularly in patients with certain conditions such as renal failure or obesity, and to monitor unfractionated heparin (UFH) therapy in specific situations, for example when the aPTT test is unreliable due to factors such as lupus anticoagulant or heparin resistance.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Monitoring unfractionated heparin (UFH) therapy when aPTT is unreliable
- Monitoring low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) in special populations (renal impairment, obesity, pregnancy)
- Adjusting therapeutic heparin dosing
- Evaluation of suspected heparin resistance or overdose
Typical Normal Range:
- Prophylactic LMWH: 0.2 – 0.5 IU/mL
- Therapeutic LMWH: 0.5 – 1.0 IU/mL (twice-daily dosing) or 1.0 – 2.0 IU/mL (once-daily dosing)
- UFH therapeutic: 0.3 – 0.7 IU/mL
Related Tests: aPTT, PT/INR, Platelet Count, Thrombin Time, ACT, Prothrombin Time (PT), International Normalized Ratio (INR), Tests for Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs)
Notes:
Timing of sample collection is critical—generally 4 hours post-dose for LMWH; steady-state levels needed for accurate interpretation.
XM – X = Cross, M=Match Crossmatch (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Crossmatch (X = Cross, M = Match)
Alternative Names: electronic crossmatch
Category: Transfusion Medicine / Immunohematology
Purpose:
A blood compatibility test (BCT) is a blood compatibility test performed before a transfusion to ensure that the recipient’s blood plasma does not contain antibodies that can react with the donor’s red blood cells, potentially causing a dangerous hemolytic reaction. In solid organ transplantation, this test detects antibodies against donor-specific human leukocyte antigens (HLAs). A positive result (BCT) indicates a high risk of graft rejection and is a contraindication to transplantation.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Pre-transfusion testing in patients requiring blood transfusion
- Evaluation of transfusion reactions
- Preparation for surgery with anticipated blood loss
- Workup of patients with known or suspected alloantibodies
Typical Normal Range:
- Compatible (no agglutination or hemolysis observed)
Related Tests: ABO & Rh Typing, Antibody Screen, Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT), Indirect Antiglobulin Test (IAT), Type and Screen (T&S)
Notes:
Can be immediate-spin, electronic, or antiglobulin crossmatch depending on clinical need; essential step in transfusion safety.
Tests Starting from Y
Tests Starting from Z
Zn – Zinc (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Zinc
Alternative Names: Serum Zinc, Plasma Zinc, Zn Level, Zinc, Blood
Category: Clinical Chemistry / Trace Elements
Purpose:
Zinc is thought to support essential biological functions in humans, including strengthening the immune system, facilitating DNA synthesis and protein production, promoting growth and development from childhood through adolescence, and aiding in wound healing and maintaining the senses of taste and smell.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Assessment of suspected zinc deficiency (e.g., poor wound healing, growth delay, impaired immunity)
- Evaluation of malabsorption syndromes or chronic diarrhea
- Monitoring patients on parenteral nutrition or zinc supplementation
- Investigation of suspected zinc toxicity from supplements or occupational exposure
Typical Normal Range:
- Serum/Plasma Zinc: 60 – 120 µg/dL (9 – 18 µmol/L)
Related Tests: Copper, Ceruloplasmin, Magnesium, Iron Studies, Zinc Protoporphyrin (ZPP), Urinary Zinc Excretion, Hair or Nail Analysis
Notes:
Fasting sample preferred; hemolysis can falsely elevate results. Zinc levels may be influenced by infection, stress, and time of day.
ZPP – Zinc Protoporphyrin (Click here for Detail)
Full Form: Hematology / Iron & Porphyrin Studies
Alternative Names: Erythrocyte Protoporphyrin, ZPP/Heme Ratio, FEP (Free Erythrocyte Protoporphyrin), Protoporphyrin, Zinc
Category: Hematology / Iron & Porphyrin Studies
Purpose:
The purpose of a Zinc Protoporphyrin (ZPP) test is to help diagnose iron deficiency and lead poisoning. Elevated ZPP levels indicate either insufficient iron for red blood cell development or chronic exposure to lead, which interferes with the red blood cell synthesis pathway.
Commonly Ordered For:
- Screening for iron deficiency anemia
- Screening for lead poisoning, especially in children and workers with occupational exposure
- Monitoring treatment response in iron deficiency or lead toxicity
- Evaluating unexplained microcytic anemia
Typical Normal Range:
- Adults: <40 µg/dL RBC (varies by lab)
- ZPP/Heme ratio: <70 µmol/mol heme
Related Tests: Serum Ferritin, Serum Iron, TIBC, Transferrin Saturation, Blood Lead Level, Hemoglobin Test, Porphyrin Tests,
Notes:
ZPP rises in both iron deficiency and lead exposure; confirmatory tests are needed for diagnosis. Best used as a screening rather than definitive test.



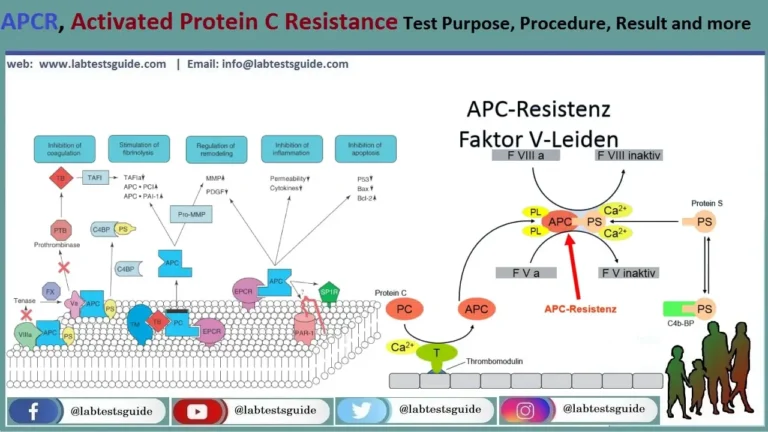
First time on this site. This is just what i was looking for. As a Patient i had no idea what i was looking mat. Thank you for help and keep the info for people like me.
It would also be helpful if you would include normal ranges for each item in listing.
Thanks for Suggestion. Please Check Lab Tests Normal Values