Fetal death, also known as stillbirth, refers to the loss of a pregnancy after 20 weeks of gestation before the baby is born. This tragic event can occur for various reasons, and it is a distressing experience for expectant parents. Fetal death can be caused by a wide range of factors

Definition of Fetal Death.
Fetal death, also known as stillbirth, is the term used to describe the loss of a pregnancy after 20 weeks of gestation or when the fetus reaches a weight of 500 grams (approximately 1.1 pounds) or more before birth. It is a heartbreaking event in which a baby, who has been developing in the womb, dies prior to delivery. Fetal death is distinct from a miscarriage, which typically refers to the loss of a pregnancy before the 20th week of gestation or when the fetus weighs less than 500 grams.
Understanding Fetal Development:
Here are key aspects to understand about fetal development.
Stages of Fetal Development:
Fetal development is typically divided into three main stages:
- Embryonic Stage: This stage covers the first eight weeks of pregnancy. It begins with fertilization when sperm meets egg and leads to the formation of the embryo. During this period, critical organs and structures begin to form.
- Fetal Stage: This stage follows the embryonic stage and lasts from the ninth week until birth. During this time, the embryo is referred to as a fetus. The fetus continues to grow and develop, with the focus shifting to refining existing structures and systems.
- Trimesters: Pregnancy is often divided into three trimesters, each lasting roughly three months. These trimesters help track the different stages of fetal development and maternal changes throughout pregnancy.
- Gestational Age and Viability: Gestational age refers to how far along a pregnancy is, typically measured in weeks or months. Viability refers to the point at which the fetus has a chance of surviving outside the womb with medical assistance. This point is usually around 24 weeks, but it can vary depending on various factors.
Fetal Vital Organs and Systems:
During fetal development, all major organ systems form and continue to mature. Some key developments include.
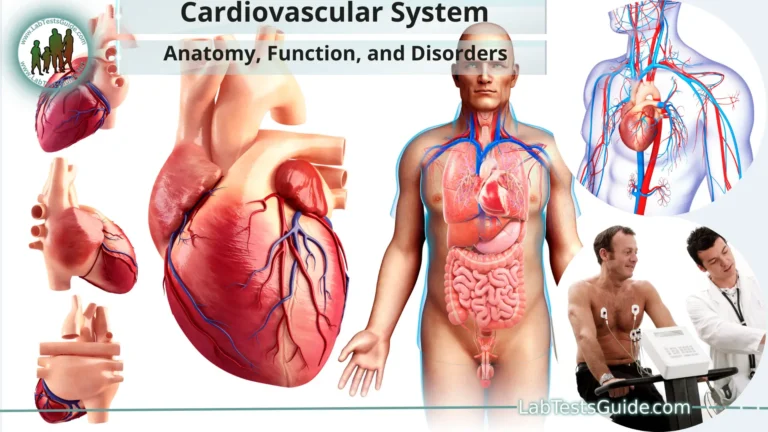
- Cardiovascular System: The heart forms early and gradually becomes more efficient at pumping blood.
- Nervous System: The brain and spinal cord develop, and the fetus begins to exhibit basic reflexes.
- Respiratory System: Lungs start to develop, but they are not fully functional until late in pregnancy.
- Digestive System: Organs like the stomach and intestines develop and become capable of digesting nutrients.
- Skeletal System: Bones begin to ossify and harden, and the skeleton takes shape.
- Reproductive System: The sex of the fetus is determined early, and reproductive organs continue to differentiate.
- Amniotic Fluid: The fetus is surrounded by amniotic fluid within the amniotic sac. This fluid serves several purposes, including protecting the fetus, facilitating movement, and helping maintain a stable environment.
- Fetal Movement: As the fetus develops, expectant mothers can feel fetal movements, often referred to as “quickening.” These movements become more pronounced as the pregnancy progresses.
- Prenatal Monitoring: Healthcare providers use various methods to monitor fetal development, including ultrasound imaging, Doppler heartbeat monitoring, and measuring fundal height. These assessments help ensure the well-being of both the mother and the fetus.
- Teratogens: It’s crucial for expectant mothers to avoid exposure to harmful substances (teratogens) during pregnancy, as they can negatively impact fetal development. This includes avoiding smoking, alcohol, certain medications, and exposure to toxins.
Causes and Risk Factors:
Here are some common causes and risk factors.
Causes:
Placental Problems:
- Placental Abruption: When the placenta detaches from the uterine wall prematurely, it can lead to fetal distress and death.
- Placental Insufficiency: The placenta may not provide adequate oxygen and nutrients to the fetus, impairing growth and development.
Fetal Factors:
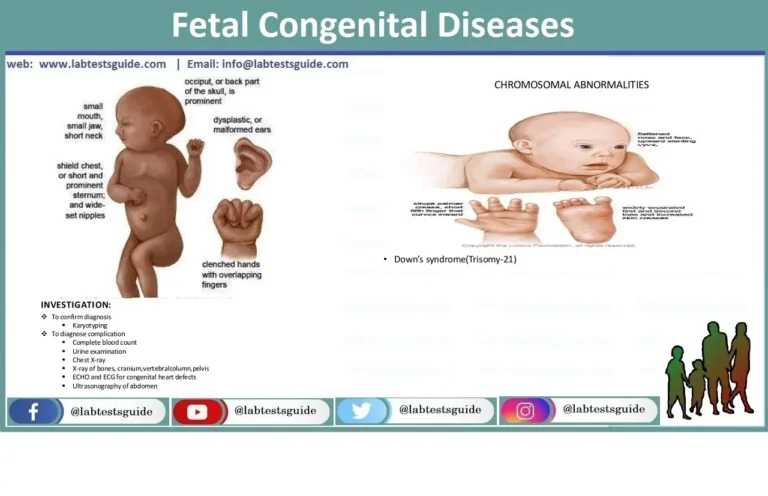
- Chromosomal Abnormalities: Genetic disorders or chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus can disrupt normal development and result in stillbirth.
- Congenital Anomalies: Structural defects or abnormalities in fetal organs or systems can lead to stillbirth.
Maternal Health Conditions:
- Diabetes: Poorly controlled diabetes can lead to complications that increase the risk of stillbirth.
- High Blood Pressure: Hypertension during pregnancy can affect placental function and fetal well-being.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Certain autoimmune conditions can increase the risk of pregnancy complications.
Thrombophilias.
- Blood clotting disorders can impair placental circulation.
Infections and Illnesses. - Infections: Maternal infections, such as toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus (CMV), and parvovirus B19, can be transmitted to the fetus and cause stillbirth.
Fever and Illness: High maternal fever during pregnancy can lead to fetal distress.
Umbilical Cord Issues:
- Cord Compression: Compression or entanglement of the umbilical cord can disrupt blood and oxygen flow to the fetus.
True Knot:
In rare cases, the umbilical cord may develop a true knot, which can impede blood flow.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors.
- Smoking: Maternal smoking during pregnancy is associated with an increased risk of stillbirth.
- Drug and Alcohol Use: Substance abuse during pregnancy can harm fetal development.
- Poor Nutrition: Inadequate maternal nutrition can affect fetal growth.
- Multiple Pregnancies: Twin or multiple pregnancies have a higher risk of complications, including stillbirth.
Advanced Maternal Age: Older mothers (typically over 35) may have a slightly higher risk of stillbirth.
Risk Factors:
While the above are specific causes, several risk factors may increase the likelihood of stillbirth without directly causing it. These include.
- Previous Stillbirth: A history of stillbirth increases the risk in subsequent pregnancies.
- Low Socioeconomic Status: Limited access to healthcare and resources can increase risk.
- Obesity: Maternal obesity is associated with an elevated risk of stillbirth.
- Late or No Prenatal Care: Inadequate prenatal care can lead to undetected issues.
- Race and Ethnicity: Disparities exist in stillbirth rates among different racial and ethnic groups.
- Poorly Managed Chronic Conditions: Chronic conditions like obesity, hypertension, or diabetes that are not well-managed during pregnancy can contribute to stillbirth risk.
Diagnosis and Detection:
Here are some key aspects of diagnosis and detection during pregnancy.
Prenatal Care: Regular prenatal care is the foundation for monitoring the progress of pregnancy. It involves a series of scheduled visits to a healthcare provider, typically an obstetrician or midwife. During these visits, the healthcare provider will perform various checks and tests to monitor the health of both the mother and the fetus.
Ultrasound Imaging: Ultrasound is a commonly used diagnostic tool during pregnancy. It uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the fetus and the uterus. Ultrasound can provide important information about the fetus’s size, development, and overall health. It is used at different stages of pregnancy for various purposes, including confirming pregnancy, estimating gestational age, checking fetal anatomy, and assessing amniotic fluid levels.
Doppler Heartbeat Monitoring: A Doppler ultrasound device is often used to listen to the baby’s heartbeat during prenatal visits. This non-invasive test allows healthcare providers to monitor the fetal heart rate and rhythm, which can provide valuable information about the baby’s well-being.
Maternal Blood Tests:
Blood tests can provide important information about both the mother’s and the fetus’s health.
Some common blood tests during pregnancy include.
Blood Type and Rh Factor: Determining the mother’s blood type and Rh factor can help identify potential compatibility issues.
Complete Blood Count (CBC): This test measures various components of the blood and can help detect conditions like anemia.
Blood Glucose Testing: Screening for gestational diabetes is typically performed during the second trimester.
Genetic Screening:
Genetic testing and screening may be offered to assess the risk of genetic disorders or chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus.
These tests can include.
- First-Trimester Screening: Combining a blood test and ultrasound to assess the risk of conditions like Down syndrome.
- Cell-Free DNA Testing: A non-invasive blood test to screen for certain genetic conditions.
- Amniocentesis: In some cases, when there are concerns about genetic abnormalities or other conditions, amniocentesis may be performed. This invasive procedure involves taking a sample of the amniotic fluid for genetic testing.
- Non-Stress Test (NST): NSTs are often performed in the third trimester to assess the baby’s heart rate in response to its movements. This test helps evaluate fetal well-being.
- Biophysical Profile (BPP): A BPP combines ultrasound and NST to assess fetal well-being by evaluating specific fetal movements and biophysical parameters.
- Fetal Movement Counting: Expectant mothers are encouraged to monitor their baby’s movements daily as an indicator of fetal well-being. A decrease in fetal movement may warrant further evaluation.
- Cervical Length Measurement: Transvaginal ultrasound can measure cervical length to assess the risk of preterm birth.
- Specialized Tests: In high-risk pregnancies or when specific concerns arise, specialized tests and consultations with maternal-fetal medicine specialists may be recommended.
Preventing Fetal Death:
Here are some important strategies for preventing fetal death.
Early and Regular Prenatal Care:
- Seeking prenatal care early in pregnancy allows healthcare providers to monitor both the mother’s and the baby’s health, detect and manage any underlying conditions, and provide guidance on a healthy lifestyle during pregnancy.
Manage Chronic Health Conditions:
- If a pregnant individual has pre-existing medical conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, or autoimmune disorders, it is essential to manage these conditions under the guidance of a healthcare provider. Proper management can reduce the risk of complications that may lead to stillbirth.
Avoid Harmful Substances:
- Smoking Cessation: Quit smoking if you smoke. Smoking during pregnancy is a significant risk factor for stillbirth.
- Alcohol and Drug Avoidance: Avoid alcohol and recreational drugs during pregnancy, as they can harm fetal development.
- Medication Review: Discuss all medications, including over-the-counter and prescription drugs, with a healthcare provider to ensure their safety during pregnancy.
Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle:
- Eat a balanced diet rich in nutrients, including folic acid.
- Exercise regularly with the guidance of a healthcare provider.
- Get adequate rest and manage stress through relaxation techniques.
- Stay hydrated and avoid excessive caffeine consumption.
Infection Prevention:
- Practice good hygiene to reduce the risk of infections. Wash hands regularly and avoid contact with individuals who have contagious illnesses.
- If you work in healthcare, childcare, or other high-risk environments, take necessary precautions to minimize exposure to infections.
- Genetic Counseling: Consider genetic counseling and testing if you have a family history of genetic disorders or if previous pregnancies have had chromosomal abnormalities.
- Monitoring Fetal Movement: Be attentive to the baby’s movements during pregnancy. Report any significant decrease in fetal movement to a healthcare provider promptly.
- Avoid Environmental Toxins: Minimize exposure to environmental toxins, such as lead and certain chemicals, which can be harmful during pregnancy.
- Prevent Trauma: Take precautions to prevent physical trauma, such as wearing seatbelts properly and avoiding risky activities.
- Multiple Pregnancy Monitoring: If you are expecting twins or multiples, your healthcare provider may recommend more frequent monitoring and specialized care.
- Fetal Kick Counts: Some healthcare providers recommend keeping track of fetal kick counts to monitor the baby’s activity regularly.
- Sleep Position: Sleep on your left side during the third trimester, as it may help improve blood flow to the fetus.
- Reduce Stress: Find ways to manage stress, such as mindfulness, yoga, or talking to a therapist. High stress levels may increase the risk of complications.
Medical Care and Management:
Here are key aspects of medical care and management during pregnancy.
Prenatal Care:
- Prenatal care is the foundation of medical management during pregnancy. It involves regular check-ups and consultations with healthcare providers to monitor the progress of the pregnancy.
- Prenatal care typically includes physical exams, health assessments, and discussions about nutrition, lifestyle, and any existing medical conditions.
- Expectant parents should schedule their first prenatal visit as soon as they learn they are pregnant and continue to attend regular appointments throughout pregnancy.
Medical History and Assessments:
- Healthcare providers will obtain a comprehensive medical history from the pregnant individual, including any pre-existing medical conditions, previous pregnancies, surgeries, and family medical history.
- Assessments may include blood pressure monitoring, weight checks, and urine tests.
Nutritional Guidance:
- Healthcare providers offer dietary guidance to ensure that pregnant individuals are getting proper nutrition.
- Folic acid supplementation and iron supplements may be recommended.
Monitoring Fetal Development:
- Regular ultrasound examinations are conducted to assess fetal growth, development, and well-being.
- Doppler ultrasound can be used to monitor the fetal heart rate and circulation.
Screening and Testing:
- Genetic screening tests may be offered to assess the risk of chromosomal abnormalities or genetic disorders.
- Blood tests for conditions like gestational diabetes and anemia may be performed.
- Other screenings, such as Group B Streptococcus (GBS) testing, may be done in the later stages of pregnancy.
Management of High-Risk Pregnancies:
- Some pregnancies are considered high-risk due to factors such as advanced maternal age, multiple pregnancies, or pre-existing health conditions.
- High-risk pregnancies often require specialized care, additional monitoring, and more frequent check-ups.
Managing Pregnancy Complications:
- If complications arise during pregnancy, such as preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, or placental issues, healthcare providers will develop management plans to mitigate risks and provide appropriate treatments.
Labor and Delivery Planning:
- Healthcare providers work with expectant parents to create a birth plan that outlines preferences for labor and delivery.
- In cases of high-risk pregnancies, a team of specialists, including obstetricians and neonatologists, may be involved in planning for a safe delivery.
- Pain Management and Comfort Measures: Expectant parents are educated about pain management options during labor and childbirth, including natural techniques, epidurals, and other medical interventions.
- Postpartum Care Planning: Preparing for postpartum care is an important aspect of pregnancy management. Healthcare providers discuss postpartum recovery, breastfeeding, and emotional well-being.
- Emotional and Psychological Support: Emotional and psychological support is essential throughout pregnancy. Expectant parents should feel comfortable discussing their concerns and fears with healthcare providers, and counseling or therapy may be recommended if needed.
Coping with Fetal Death:
Here are some strategies and considerations for coping with fetal death.
- Acknowledge Your Grief: It’s important to recognize and accept the depth of your grief. Understand that the pain and sadness you’re feeling are natural reactions to the loss.
- Seek Support: Reach out to supportive friends and family members who can offer comfort and a listening ear.
Consider joining a support group for parents who have experienced stillbirth or infant loss. Sharing your experiences with others who have been through similar situations can be comforting. - Talk to a Professional: Grief counseling or therapy can provide a safe space to express your emotions and work through the grieving process. Mental health professionals can offer coping strategies and support tailored to your needs.
- Memorialize Your Baby: Create a memorial or a remembrance ceremony to honor your baby’s memory. This can involve planting a tree, holding a memorial service, or creating a scrapbook or memorial website.
Some parents choose to name their baby, write letters to them, or keep a journal of their feelings and memories. - Lean on Your Partner: Share your grief with your partner, and be receptive to their feelings and needs as well. Grieving together can help strengthen your bond.
- Take Care of Your Physical Health: Grief can take a toll on your physical health. Ensure you’re eating well, getting enough rest, and engaging in gentle physical activity when you feel up to it.
- Express Your Emotions: Give yourself permission to express your emotions, whether that involves crying, screaming, or simply sitting in silence. Expressing your feelings can be cathartic.
- Be Patient with Yourself: Grief doesn’t have a timetable, and everyone experiences it differently. Allow yourself the time and space to grieve at your own pace.
- Educate Yourself: Understanding the causes and potential risk factors for stillbirth can help some parents find closure or peace of mind. Consider discussing the details of the loss with your healthcare provider if it’s something that would be beneficial for you.
Connect with Others Who Have Experienced Stillbirth:
Online forums, social media groups, and local support groups can connect you with others who have gone through similar experiences. Sharing your story and hearing theirs can be comforting and validating.
- Consider Future Pregnancy: If you plan to have more children, discuss your concerns, fears, and medical history with your healthcare provider. They can provide guidance and support for future pregnancies.
- Remember That It’s Okay to Smile: While grieving, it’s important to allow yourself moments of happiness and laughter. It doesn’t diminish your love for your lost baby.
Seek Legal and Practical Support: Be aware of your legal rights and responsibilities, such as obtaining a birth certificate or death certificate for your baby.
Consider practical matters, such as funeral arrangements or financial concerns, and seek assistance as needed.
Investigation and Autopsy:
Here are key aspects of investigation and autopsy in cases of fetal death.
Medical Evaluation and Records Review:
- Healthcare providers will begin by reviewing the medical history of the mother and the prenatal care received. This includes assessing risk factors, prenatal tests, ultrasounds, and maternal health during pregnancy.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination of the baby, including measurements and visual inspection, may be performed to look for any visible abnormalities or signs of distress.
Autopsy (Postmortem Examination):
- An autopsy is a thorough medical examination of the baby’s body to identify any underlying medical conditions, abnormalities, or causes of death. This examination is usually conducted by a perinatal pathologist.
- The autopsy can include a detailed examination of the baby’s organs, tissues, and placenta.
- Genetic testing, including chromosomal analysis, may be performed during the autopsy to identify any genetic abnormalities.
- Placental Examination: The placenta is examined to assess its condition, including any signs of placental abruption, infection, or other abnormalities that may have contributed to the fetal death.
- Cord Blood and Tissue Analysis: Samples of cord blood and cord tissue may be collected and analyzed to check for infections, genetic conditions, or other abnormalities.
- Toxicology Testing: Toxicology testing of the baby’s blood or tissues may be conducted to rule out exposure to harmful substances.
- Microscopic Examination: Microscopic examination of tissues and organs can reveal microscopic abnormalities that may not be visible to the naked eye.
- Photographic Documentation: Photographs of the baby, placenta, and any abnormalities found during the autopsy may be taken for documentation.
- Detailed Report: Following the investigation and autopsy, a detailed report is typically provided to the parents and their healthcare providers. This report summarizes the findings and may include a definitive cause of death or, in some cases, inconclusive results.
- Counseling and Discussion: Healthcare providers, including perinatal pathologists and genetic counselors, can discuss the findings with the parents. This discussion can help parents understand the cause of the fetal death and provide closure.
- Legal and Ethical Considerations: Depending on the jurisdiction, there may be legal requirements for documenting and reporting fetal deaths. Parents should be informed of their rights and responsibilities during this process.
- Research and Data Collection: In some cases, the information gathered during an investigation and autopsy may contribute to medical research and data collection to better understand stillbirth and improve prenatal care.
FAQs:
What is stillbirth?
Stillbirth, also known as fetal death, refers to the loss of a pregnancy after 20 weeks of gestation or when the fetus reaches a weight of 500 grams (approximately 1.1 pounds) or more before birth.
What is the difference between a stillbirth and a miscarriage?
A miscarriage typically refers to the loss of a pregnancy before the 20th week of gestation or when the fetus weighs less than 500 grams. A stillbirth occurs after these milestones.
What are the common causes of stillbirth?
Common causes of stillbirth include placental problems, fetal factors (such as genetic abnormalities), maternal health conditions (e.g., diabetes, hypertension), infections, umbilical cord issues, and lifestyle factors (e.g., smoking, substance abuse).
How is stillbirth diagnosed and detected?
Stillbirth is typically diagnosed through ultrasound imaging, Doppler heartbeat monitoring, and medical examinations. Fetal movement counting and various tests, including genetic screening and blood tests, may also be part of the diagnostic process.
What can pregnant individuals do to reduce the risk of stillbirth?
Pregnant individuals can reduce the risk of stillbirth by attending regular prenatal care, managing chronic health conditions, avoiding harmful substances (e.g., smoking, alcohol), maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and following healthcare provider recommendations.
What happens during an autopsy after a stillbirth?
An autopsy, also known as a postmortem examination, involves a thorough medical examination of the baby’s body to determine the cause of death. It may include the examination of organs, tissues, and genetic testing.
What legal and regulatory aspects are associated with stillbirth?
Legal aspects of stillbirth can include reporting requirements, issuance of a fetal death certificate, disposition of fetal remains, and parental rights and responsibilities. These aspects vary by jurisdiction.
How can parents cope with the grief of stillbirth?
Coping with stillbirth involves acknowledging grief, seeking emotional support from loved ones and professionals, creating memorials, and allowing oneself to grieve in one’s own way and time.
Are there advances in stillbirth research and prevention?
Yes, ongoing research aims to better understand the causes and risk factors of stillbirth, improve prenatal care and monitoring, and develop prevention strategies. Advances in genetic testing, placental assessment, and psychological support are also ongoing.
What resources are available for parents who have experienced stillbirth?
There are various support groups, counseling services, and organizations that provide resources and emotional support for parents and families who have experienced stillbirth. Healthcare providers can often connect parents with these resources.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, fetal death, or stillbirth, is a deeply tragic and emotionally challenging event that affects expectant parents and families around the world. It’s characterized by the loss of a pregnancy after 20 weeks of gestation and can be caused by a variety of factors, including placental problems, maternal health conditions, genetic abnormalities, and lifestyle factors. While not all cases of stillbirth can be prevented, advances in medical care, research, and emotional support have contributed to improving outcomes and helping grieving parents navigate this difficult journey. Legal and regulatory aspects related to stillbirth vary by region, and parents should be aware of their rights and responsibilities. Ultimately, awareness, education, early prenatal care, and compassionate support are essential in addressing stillbirth and promoting the well-being of expectant families.
Possible References Used