Radiology
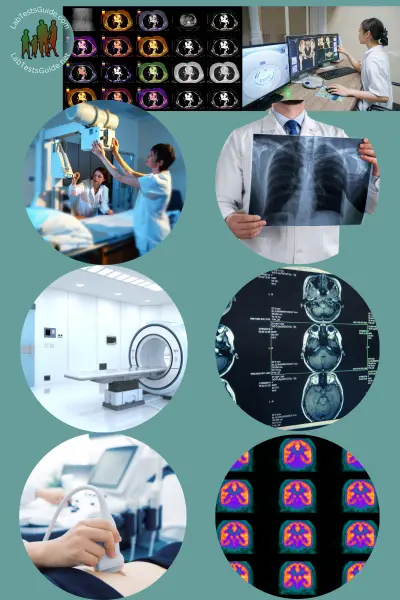 Radiology is a medical specialty that uses various imaging techniques to diagnose and treat diseases and injuries. Radiologists are physicians who specialize in interpreting medical images and providing clinical evaluations based on these images. Radiology plays a crucial role in modern medicine by helping healthcare professionals visualize the inside of the body without invasive procedures.
Radiology is a medical specialty that uses various imaging techniques to diagnose and treat diseases and injuries. Radiologists are physicians who specialize in interpreting medical images and providing clinical evaluations based on these images. Radiology plays a crucial role in modern medicine by helping healthcare professionals visualize the inside of the body without invasive procedures.
- Medical Imaging: Radiology is a medical specialty that uses various imaging techniques to visualize the inside of the body.
- Radiologists: Radiologists are physicians who specialize in interpreting medical images and providing clinical assessments based on those images.
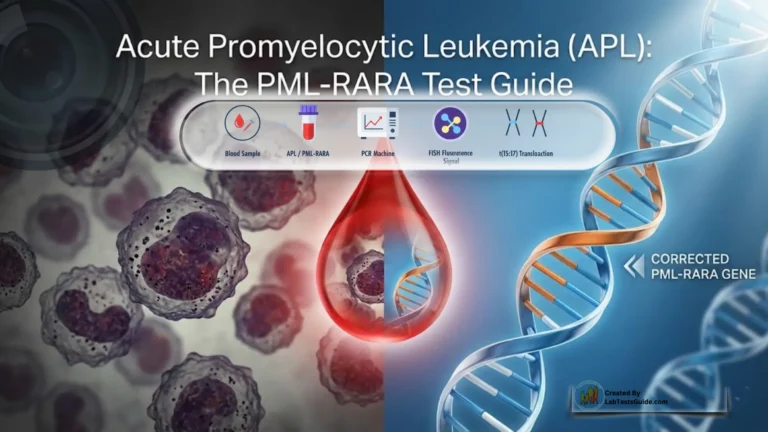
- Diagnostic Radiology: This branch of radiology focuses on using imaging to diagnose diseases, injuries, and medical conditions.
- Imaging Modalities: Radiology includes various imaging modalities, such as X-ray, CT, MRI, ultrasound, nuclear medicine, and fluoroscopy.
- X-ray: X-ray imaging uses ionizing radiation to create images of bones and some soft tissues, making it useful for diagnosing fractures and certain conditions.
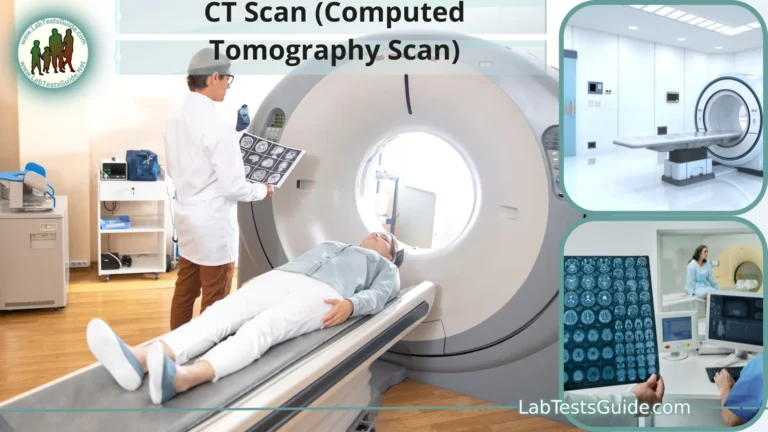
- Computed Tomography (CT): CT scans combine X-rays with computer technology to produce detailed cross-sectional images of the body, helping diagnose a wide range of conditions.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of soft tissues like the brain, muscles, and organs.
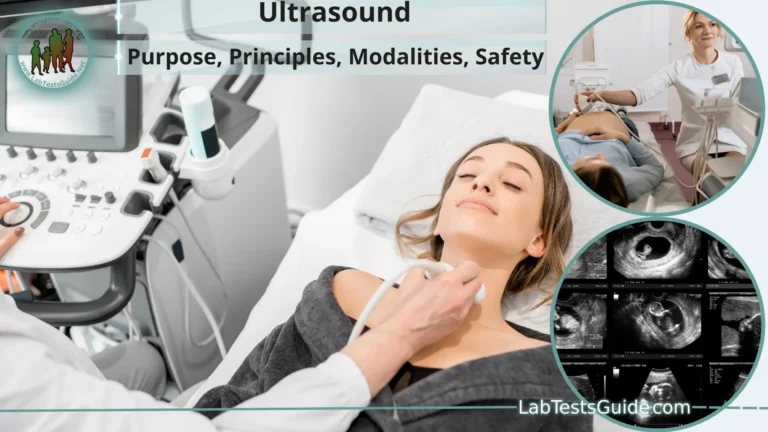
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound imaging employs high-frequency sound waves to generate images of internal structures, often used for monitoring pregnancy and assessing abdominal organs.
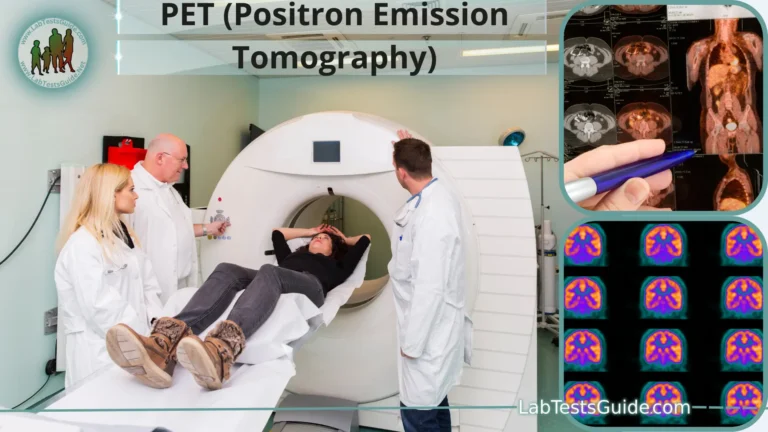
- Nuclear Medicine: Involves the use of radioactive materials (radiotracers) to diagnose and treat diseases like cancer and heart conditions.
- Interventional Radiology (IR): IR uses imaging guidance to perform minimally invasive procedures, including angioplasty, embolization, and biopsies.
- Radiation Safety: Radiologic professionals are trained to ensure patient and staff safety when using ionizing radiation, employing methods to minimize radiation exposure.
- Digital Imaging: Radiology has transitioned from film-based to digital imaging, allowing for easier storage, retrieval, and sharing of medical images.
- 3D Imaging: Advances in technology have enabled three-dimensional imaging, which provides more detailed views of anatomical structures.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is increasingly being used in radiology to assist radiologists in image interpretation, speeding up diagnosis and improving accuracy.
- Subspecialties: Radiologists can specialize in various areas, such as neuroradiology, musculoskeletal radiology, and breast imaging, tailoring their expertise to specific medical conditions and patient populations.
Radiology is a critical component of modern healthcare, aiding in the diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of a wide range of medical conditions. It continues to evolve with technology and plays an essential role in patient care.