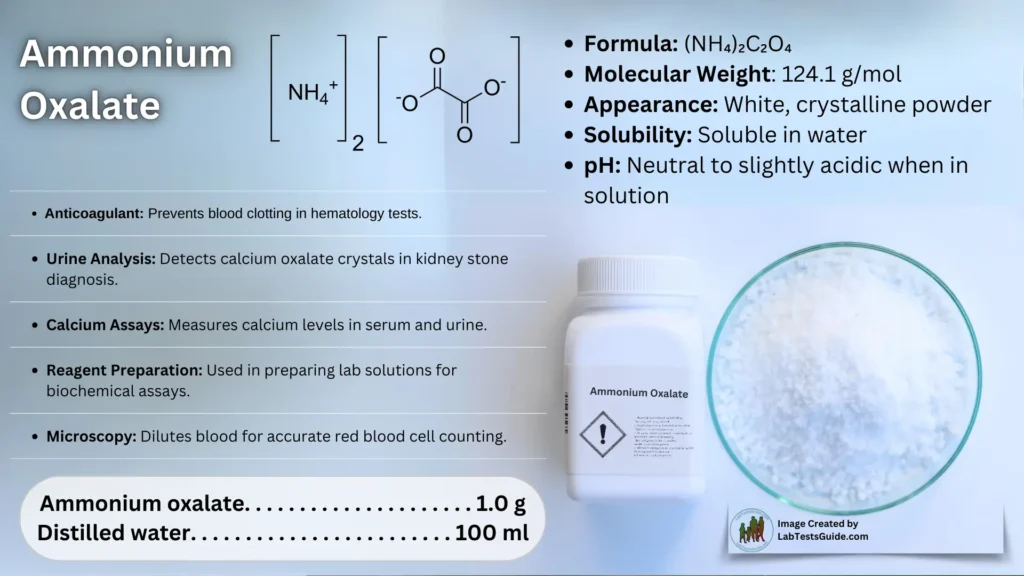
Ammonium oxalate, C2H8N2O4 – more commonly written as (NH4)2C2O4 – is an oxalate salt with ammonium (sometimes as a monohydrate). It is a colorless (white) salt under standard conditions and is odorless and non-volatile. It is the ammonium salt of oxalic acid, and occurs in many plants and vegetables.
It and other oxalates are used as anticoagulants, to preserve blood outside the body.
Chemical Properties of Ammonium Oxalate:
- Formula: (NH₄)₂C₂O₄
- Molecular Weight: 124.1 g/mol
- Appearance: White, crystalline powder
- Solubility: Soluble in water
- pH: Neutral to slightly acidic when in solution
Uses of Ammonium Oxalate in Laboratories:
- Ammonium oxalate is used as an analytical reagent and general reducing agent. It and other oxalates are used as anticoagulants to keep blood out of the body.
- Ammonium oxalate is used in blood tests where it helps prevent or inhibit blood plasma clotting.
- Hematologic anticoagulant: Used to prevent blood clotting in microhematocrit procedures by binding calcium, allowing for accurate blood counts.
- Urine analysis: Helps precipitate calcium ions to detect calcium oxalate crystals, essential for diagnosing kidney stones.
- Calcium quantification: Used in assays to measure calcium levels in serum and urine to diagnose metabolic disorders.
- Reagent preparation: Key ingredient in creating standard buffer solutions and titration solutions for biochemical analysis.
- Microscopy: Used to dilute blood to count red blood cells under the microscope in CBC tests.
Ammonium oxalate Reagent Preparation:
Ammonium oxalate, 10g/l (1% w/v) Reagent Preparation.
To make 100 ml:
- Ammonium oxalate. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 g
- Distilled water. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100 ml
- Weigh the chemical and transfer it to a completely clean screw-cap container.
- Add the water and mix until the chemical is completely dissolved. Label the bottle and store at 2–8°C.
Filter immediately before use to ensure the reagent is free from particles which could be mistaken for platelets.








0 Comments