Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) Test – Normal Range, Purpose, Procedure & Interpretation
The adenosine deaminase (ADA) test measures the level of the ADA enzyme in bodily fluids, primarily pleural fluid, to help quickly diagnose tuberculous pleurisy (TB of the lung lining), although it is also used for other infections or autoimmune diseases. An elevated ADA level strongly suggests TB, but it can also indicate lymphoma, cancer, or other inflammatory conditions, which require further testing for confirmation.
Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) Test Quick Facts:

What is Adenosine Deaminase Test ?
The Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) test measures the activity of the ADA enzyme in blood or body fluids. ADA plays a key role in immune system function, particularly in T-lymphocyte activity, and its level increases in conditions involving cellular immunity such as tuberculosis.
Why is Adenosine Deaminase Test Done ?
For Patients / General Use
- Persistent fever
- Chronic cough
- Chest pain with pleural effusion
- Unexplained weight loss
- Suspected tuberculosis
- Fluid accumulation around lungs or abdomen
For Doctors / Clinical Use
- Diagnosis of tuberculous pleural effusion
- Differentiation of TB from malignancy-related effusions
- Assessment of immune activation
- Supportive evidence in extrapulmonary TB
- Evaluation of lymphoproliferative disorders
How the Adenosine Deaminase Test Works (Principle / Methodology)
The ADA test is based on a colorimetric enzymatic method. ADA catalyzes the conversion of adenosine to inosine and ammonia. The ammonia produced reacts with reagents to form a colored complex, which is measured spectrophotometrically. The intensity of the color is directly proportional to ADA activity in the sample.
Adenosine Deaminase Test Specimen Requirements & Collection
- Specimen type: Serum, plasma, or body fluids (pleural/peritoneal/CSF)
- Tube type: Plain red-top or SST
- Volume: Minimum 1–2 mL
- Patient preparation: No fasting required
- Collection steps:
- Perform standard venipuncture
- Avoid hemolysis
- Allow blood to clot (for serum)
- Centrifuge and separate serum promptly
- Transport & storage:
- Store at 2–8°C
- Analyze within 24–48 hours
- Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles
Adenosine Deaminase Test Reference Ranges
| Population / Sample | Reference Range | Units |
|---|---|---|
| Adults (Serum) | < 30 | U/L |
| Pleural Fluid | < 40 | U/L |
| Children | Slightly higher | U/L |
Reference ranges may vary depending on laboratory method.
Adenosine Deaminase Test Interpretation of Results:
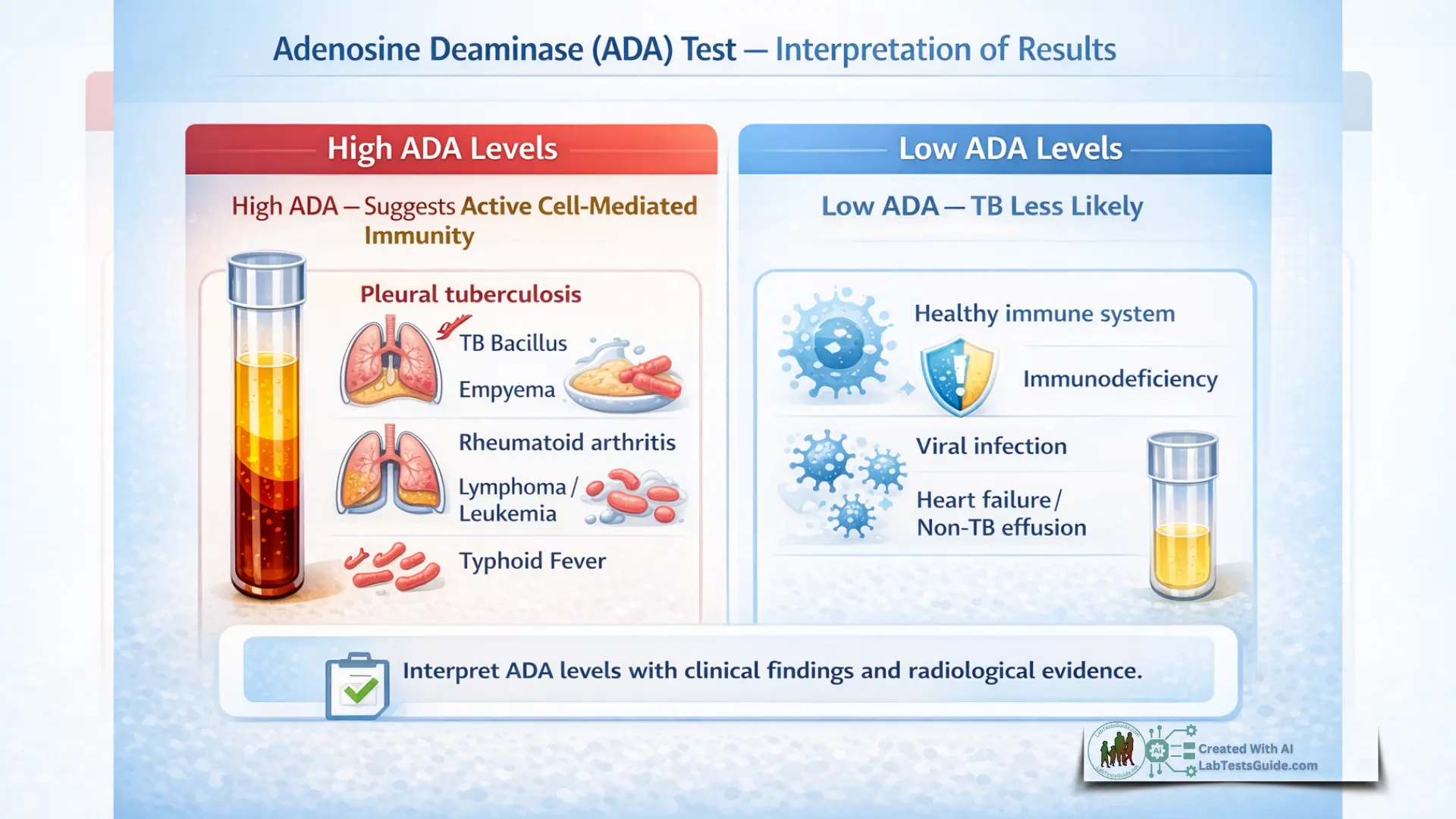
High Levels (Causes & Clinical Significance)
Causes
- Tuberculosis (especially pleural TB)
- Empyema
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- Typhoid fever
Differential Diagnoses
- Malignancy-related effusion
- Bacterial infections
Clinical Relevance
- Strongly supports TB diagnosis when correlated clinically and radiologically
Low Levels (Causes & Clinical Significance)
Causes
- Normal immune status
- Immunodeficiency
- Viral infections
Differential Diagnoses
- Non-TB effusions
- Transudative effusions (heart failure)
Clinical Relevance
- Makes TB less likely but does not exclude it
Adenosine Deaminase Test Interfering Factors / Pre-Analytical Errors
- Hemolysis: Falsely elevated results
- Lipemia: Interferes with colorimetric reading
- Icterus: Mild interference
- Medications: Immunosuppressants may reduce ADA
- Sample handling: Delayed processing increases error
- Biological variation: Age and immune status related
Critical Values / PANIC Values
- Pleural fluid ADA > 70 U/L – Highly suggestive of TB
Follow institution policy for urgent reporting.
🧠 AI-Powered Test Result Analysis:
Understand your Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) Test – Normal Range, Purpose, Procedure & Interpretation Results
AI-powered Lab Test Results Meaning tool 🤖
📥 Download Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) Test Lab Report Format
Get the demo report format for Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) Test in your preferred format. These templates are fully editable and professional.
How to Download?
| File Description | Format |
|---|---|
Adenosine Deaminase (ADA)Test Report Format (Image) | .PNG |
Adenosine Deaminase (ADA)Test Report Format (MS Word) | .DOCX |
Adenosine Deaminase (ADA)Test Report Format (MS Excel) | .XLSX |
Adenosine Deaminase (ADA)Test Report Format (PDF) |
Adenosine Deaminase Test Sample Lab Report:
Nursing / Phlebotomy Notes
- Use red or yellow-top tube
- Proper patient identification
- Avoid hemolysis
- Transport refrigerated
- Label with sample type clearly
Lab Student Key Points
- ADA is a marker of cell-mediated immunity
- Most useful in pleural fluid analysis
- High sensitivity for TB but not 100% specific
- Always interpret with clinical findings
Is fasting needed for ADA test?
No.
Does high ADA always mean TB?
No, but it strongly suggests TB.
Which fluid is best for ADA testing?
Pleural fluid.
Is this test confirmatory?
No, it is supportive.
Can children have higher ADA?
Yes, slightly.
How long does the result take?
Usually within 24 hours.