Activated Coagulation Time Test Purpose, Procedure, Result Interpretation and Your Test Result Meaning
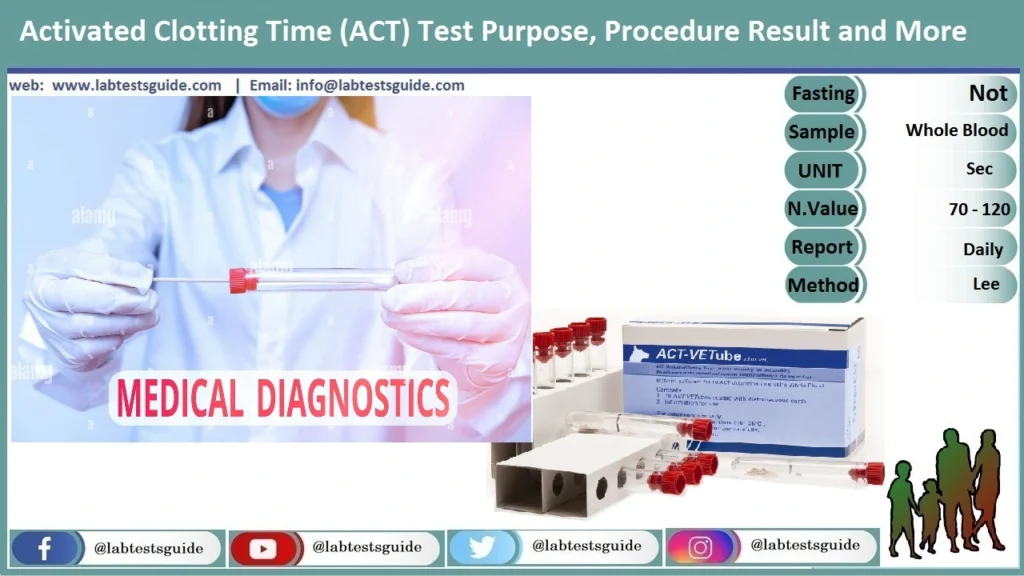
The Activated Coagulation Time (ACT) test is a laboratory test used to assess the anticoagulant effect of medications, such as heparin, during cardiac procedures like cardiac catheterization, angioplasty, or bypass surgery. It measures the time it takes for blood to clot after a specific activator is added.
Understand Your Test Results:
Understand your Activated Coagulation Time Test Results
AI-powered Lab Test Results Meaning tool 🤖
| Also Known as | Activated Clotting Time, ACT, Activated Coagulation Time |
| Test Purpose | To monitor treatment with heparin or other blood-thinning medications (anticoagulants) when undergoing heart bypass surgery, coronary angioplasty, or dialysis |
| Test Preparations | No Preparation Required |
| Test Components | ACT Test |
| Specimen | Whole Blood |
| Stability Room | N/A |
| Stability Refrigerated | N/A |
| Stability Frozen | N/A |
| Method | Lee and white |
| Download Report | Download Report |
During the ACT test, a blood sample is drawn from the patient and mixed with an activator substance that initiates the clotting process. The activator used can vary depending on the laboratory or hospital protocol but often includes substances like celite, kaolin, or ellagic acid.
Why get tested?
To monitor treatment with heparin or other anticoagulant drugs (anticoagulants) when undergoing heart bypass surgery, coronary angioplasty, or dialysis
When to get tested?
When you are receiving high doses of heparin to prevent clotting during and after surgical procedures such as heart bypass.
when heparin levels are too high to allow monitoring with a partial thromboplastin time (PTT).
When a quick result is necessary to control the treatment.
Interpretation
A normal activated clotting time (ACT) indicates that the blood tested does not contain heparin or that all heparin is inhibited by protamine (reversal of postoperative anticoagulation).
ACT is intended to monitor the anticoagulant effect of unfractionated heparin. ACT target values may depend on the specific device and clinical scenario. ACT prolongation may also indicate coagulation factor deficiency, severe thrombocytopenia, or severe platelet dysfunction.
Sample Required:
Specimen: Whole blood
Collection: Blood (usually 0.5-1 mL) from venous/arterial vessel; indwelling or extracorporeal line is collected into the plastic syringe/tube (see image below) and immediately placed/poured into the device cuvette/cartridge
Storage: Whole blood specimen should be processed within 1 minute (or 2 min if specimen contains therapeutic level of unfractionated heparin)
Normal values:
Source 1
The normal range for ACT is 70-120 Second
Source 2
- 70 to 120 seconds is the usual amount of time for blood to clot without heparin.
- 180 to 240 seconds is the usual amount of time for blood to clot with heparin. This is called the therapeutic range.
Understand Your Test Results:
Understand your Activated Coagulation Time Test Results
AI-powered Lab Test Results Meaning tool 🤖