Simmons Citrate Agar 50 FAQs and 30 MCQs
Simmons Citrate Agar is a specialized differential medium used to identify bacteria capable of utilizing citrate as a sole carbon source. This test is critical for differentiating Enterobacteriaceae (e.g., Klebsiella vs. E. coli). This article compiles 50 FAQs clarifying principles, procedures, and interpretation, followed by 30 MCQs to test your knowledge. Ideal for microbiology labs and exam prep!

Simmons Citrate Agar is a cornerstone test in clinical microbiology. It exploits bacterial citrate permease activity and alkaline byproduct formation, turning the medium blue in positive results. Below, we address 50 FAQs for conceptual clarity and 30 MCQs for self-assessment.
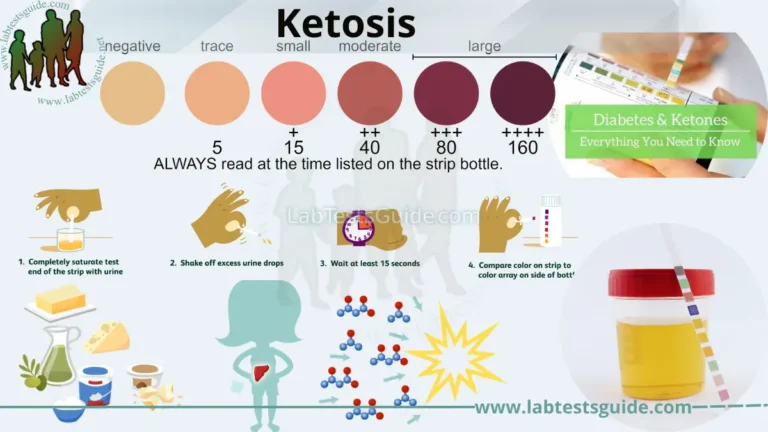
- 🔵 Blue = Positive (citrate utilized).
- 🟢 Green = Negative.
- ⚠️ Avoid contaminants and over-incubation.
- 🧪 QC with K. aerogenes (positive) and E. coli (negative).
Simmons Citrate Agar 50 FAQs
What is Simmons Citrate Agar?
A selective and differential medium used to test an organism’s ability to utilize citrate as a sole carbon source.
Who developed the original citrate medium?
Koser developed the liquid medium, and later Simmons modified it by adding agar and bromothymol blue.
What is the purpose of Simmons Citrate Agar?
To differentiate Gram-negative bacteria, especially Enterobacteriaceae, based on citrate utilization.
What type of medium is Simmons Citrate Agar?
It is both selective (tests for citrate utilization) and differential (color change indicates metabolic activity).
What is the final pH of Simmons Citrate Agar?
6.8 ± 0.2 (or 6.9 ± 0.2, depending on the formulation).
What is the carbon source in Simmons Citrate Agar?
Sodium citrate (2.0 g/L).
What is the nitrogen source in Simmons Citrate Agar?
Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (1.0 g/L).
What is the role of bromothymol blue in the medium?
It acts as a pH indicator, changing from green (neutral) to blue (alkaline, pH >7.6).
Why is magnesium sulfate added?
It serves as a cofactor for enzymatic reactions.
What maintains osmotic balance in the medium?
Sodium chloride (5.0 g/L).
What is the role of dipotassium phosphate?
It acts as a buffer to stabilize pH.
Why is agar included in the medium?
As a solidifying agent to create a slanted surface.
How is Simmons Citrate Agar prepared?
Suspend 24.28 g/L in distilled water, boil to dissolve, autoclave, and cool in slants.
What is the autoclaving condition for Simmons Citrate Agar?
121°C (15 psi) for 15 minutes.
How should the medium be cooled?
In a slanted position (long slant, shallow butt).
What is the shelf life of prepared slants?
6-8 weeks when stored refrigerated (4-8°C).
What is the initial color of uninoculated Simmons Citrate Agar?
Deep forest green.
Why must the pH of water be checked before preparation?
Improper pH (outside 6.5-7.0) can affect medium performance.
What type of inoculum should be used?
A pure, overnight culture from solid media (not broth).
How should the slant be inoculated?
Streak lightly in a fish-tail motion from bottom to top.
Why should a heavy inoculum be avoided?
It may cause false-positive results due to nutrient carryover.
What is the incubation temperature?
35°C (aerobic conditions).
How long should the medium be incubated?
24-48 hours (some citrate-positive organisms may take longer).
Why should caps be kept loose during incubation?
Tight caps may lead to false-negative results (prevents CO₂ release).
What indicates a positive citrate test?
Growth + color change from green to bright blue.
What indicates a negative citrate test?
No growth or no color change (remains green).
Which bacteria are typically citrate-positive?
Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Citrobacter, Serratia, Proteus, Providencia, Salmonella (except S. typhi).
Which bacteria are citrate-negative?
E. coli, Shigella, Yersinia, Edwardsiella, Morganella morganii.
Can growth without color change still be positive?
Yes, some organisms grow on citrate but do not change the color.
Why might a false-positive result occur?
Due to nutrient carryover from other media (always flame the loop before inoculation).
How is Simmons Citrate Agar used in IMViC tests?
It helps differentiate E. coli (IMViC: ++–) from Enterobacter (IMViC: –++).
How does it help distinguish Salmonella species?
Salmonella enteritidis (citrate +) vs. S. typhi (citrate –).
How is E. coli differentiated from Klebsiella?
E. coli (citrate –), Klebsiella (citrate +).
Can it differentiate Yersinia from Serratia?
Yes, Serratia is citrate +, while Yersinia is usually –.
What is its role in identifying Proteus species?
Proteus rettgeri (+) vs. Morganella morganii (–).
What causes false negatives?
Tight tube caps, improper incubation, or weak inoculum.
Why should broth cultures not be used?
They may introduce excess nutrients, causing false positives.
What happens if the medium turns blue before inoculation?
It may be due to improper storage or contamination.
Why must the medium be freshly prepared?
Old medium may show spontaneous color changes.
Can Simmons Citrate Agar identify species definitively?
No, additional biochemical/molecular tests are needed for confirmation.
What is the positive control organism?
Klebsiella pneumoniae (ATCC 13883) – growth with blue color.
What is the negative control organism?
Escherichia coli (ATCC 25922) – no growth/no color change.
How should QC be performed?
Test known positive and negative strains alongside samples.
What if the control results are incorrect?
The medium may be contaminated or improperly prepared.
What is the expected result for Enterobacter aerogenes?
Growth with blue color change (positive).
Can Simmons Citrate Agar be used for non-Enterobacteriaceae?
Rarely, as it is optimized for Enterobacteriaceae.
Why does Salmonella typhi test negative?
It lacks the citrate-permease enzyme needed for citrate utilization.
What if the slant shows weak blue color after 48 hours?
It may still be considered positive if growth is present.
Can Simmons Citrate Agar be used for environmental samples?
Yes, but additional tests are needed for confirmation.
Where can I purchase Simmons Citrate Agar?
Available from microbiological suppliers (e.g., Cat# TS62 for slants).
Simmons Citrate Agar 30 MCQs
What is the primary purpose of Simmons Citrate Agar?
a) To test for lactose fermentation
b) To differentiate bacteria based on citrate utilization✔
c) To detect hydrogen sulfide production
d) To identify Gram-positive cocci
2. Which pH indicator is used in Simmons Citrate Agar?
a) Phenol red
b) Methyl red
c) Bromothymol blue✔
d) Neutral red
3. A positive citrate test is indicated by a color change from green to:
a) Yellow
b) Red
c) Blue✔
d) Pink
4. Which of the following is the sole carbon source in Simmons Citrate Agar?
a) Glucose
b) Sodium citrate✔
c) Lactose
d) Sucrose
5. The nitrogen source in Simmons Citrate Agar is:
a) Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate✔
b) Potassium nitrate
c) Peptone
d) Urea
6. Which enzyme allows bacteria to utilize citrate in this medium?
a) Catalase
b) Citrate-permease✔
c) Oxidase
d) Urease
7. Which organism is typically citrate-positive?
a) Escherichia coli
b) Shigella spp.
c) Klebsiella pneumoniae✔
d) Yersinia enterocolitica
8. A negative citrate test shows:
a) Blue color
b) No growth
c) Green color (unchanged)
d) Both b & c✔
9. Simmons Citrate Agar is primarily used for which family of bacteria?
a) Staphylococcaceae
b) Enterobacteriaceae✔
c) Pseudomonadaceae
d) Streptococcaceae
10. What is the role of magnesium sulfate in the medium?
a) Carbon source
b) Cofactor for enzymes✔
c) pH indicator
d) Solidifying agent
11. Which Salmonella species is citrate-negative?
a) Salmonella enteritidis
b) Salmonella typhi✔
c) Salmonella paratyphi B
d) Salmonella choleraesuis
12. How should Simmons Citrate Agar slants be stored?
a) At room temperature
b) In a freezer
c) Refrigerated (4-8°C)✔
d) In direct sunlight
13. What is the incubation temperature for citrate agar?
a) 25°C
b) 35°C✔
c) 42°C
d) 55°C
14. A false-positive citrate test may occur due to:
a) Nutrient carryover from other media✔
b) Using a light inoculum
c) Incubating for less than 24 hours
d) Tightening the tube cap
15. Which of the following is a citrate-negative organism?
a) Enterobacter aerogenes
b) Citrobacter freundii
c) Escherichia coli✔
d) Serratia marcescens
16. The original citrate medium was developed by:
a) Simmons
b) Koser✔
c) Gram
d) MacConkey
17. What is the final pH of Simmons Citrate Agar?
a) 5.2 ± 0.2
b) 6.8 ± 0.2✔
c) 7.4 ± 0.2
d) 8.0 ± 0.2
18. Which component acts as a buffer in the medium?
a) Sodium chloride
b) Dipotassium phosphate✔
c) Bromothymol blue
d) Magnesium sulfate
19. How long should the medium be incubated before reading results?
a) 6 hours
b) 12 hours
c) 24-48 hours✔
d) 72 hours
20. Which organism is used as a positive control for citrate agar?
a) Escherichia coli
b) Pseudomonas aeruginosa
c) Klebsiella pneumoniae✔
d) Staphylococcus aureus
21. What is the purpose of sodium chloride in the medium?
a) Carbon source
b) Osmotic balance✔
c) Nitrogen source
d) pH indicator
22. Which of the following is NOT a citrate-positive genus?
a) Proteus
b) Shigella✔
c) Enterobacter
d) Citrobacter
23. Why must the inoculum be taken from a solid medium?
a) To avoid contamination
b) To prevent false positives from nutrient carryover✔
c) To enhance bacterial growth
d) To speed up the reaction
24. What happens if the tube cap is tightly closed during incubation?
a) Faster color change
b) False-negative result (no CO₂ release)✔
c) Medium turns red
d) No effect
25. Which metabolic cycle is involved in citrate utilization?
a) Glycolysis
b) Krebs cycle✔
c) Calvin cycle
d) Urea cycle
26. What is the shelf life of prepared citrate slants?
a) 1 week
b) 6-8 weeks✔
c) 6 months
d) 1 year
27. Which organism is citrate-variable?
a) Escherichia coli
b) Salmonella typhi
c) Proteus mirabilis✔
d) Yersinia pestis
28. What is the critical step before preparing the medium?
a) Adjusting water pH to 6.5-7.0✔
b) Adding extra glucose
c) Boiling for 30 minutes
d) Filter sterilization
29. Which of the following is a limitation of citrate agar?
a) Cannot differentiate Gram-positive bacteria✔
b) Requires anaerobic incubation
c) Only works for fungi
d) Must be read within 1 hour
30. Simmons Citrate Agar is part of which biochemical test series?
a) IMViC✔
b) API 20E
c) Oxidase test
d) Coagulase test
Simmons Citrate Agar remains essential for differentiating Gram-negative pathogens. Use these FAQs to solidify core concepts and MCQs to challenge your application skills. For lab professionals, meticulous technique ensures accuracy; for students, this content aligns with exam syllabi like USMLE and ASCP.