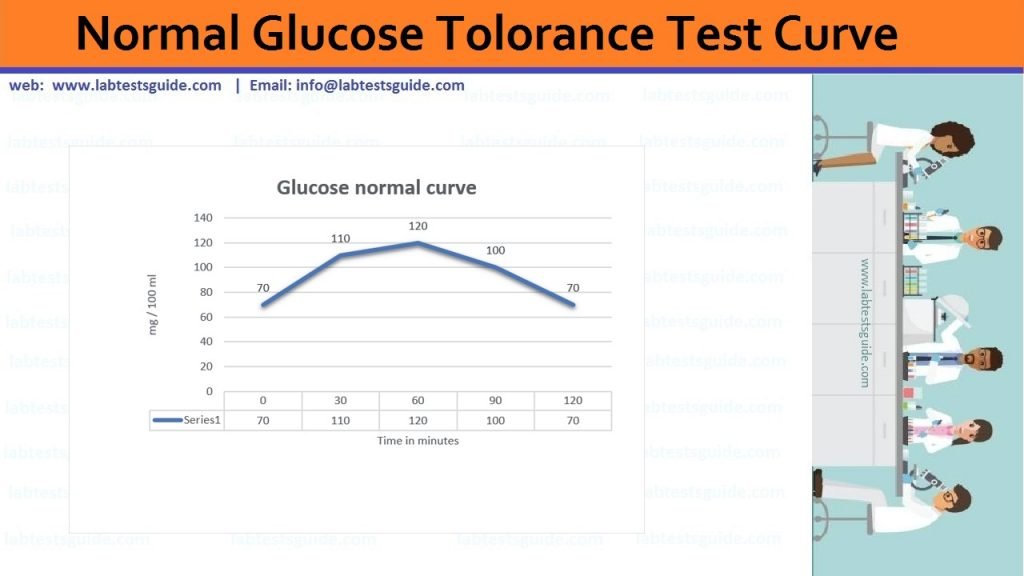
The Glucose Tolerance Test (GTT) is the most sensitive test for detecting borderline diabetes mellitus. Glucose tolerance means ability of the body to utilize glucose in the circulation. It is indicated by the nature of blood glucose curve following the administration of glucose. Thus “glucose tolerance test” is a valuable diagnostic aid in the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus, insulin resistance, impaired beta-cell functionnand sometimes reactive hypoglycemia and acromegaly. GTT is of two types depending upon the route of glucose administration :
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
- Intravenous Glucose Tolerance Test (IVGTT)
OGTT is mostly preferred and is explained in detail here. IVGTT may be chosen for patients who are unable to absorb an oral dose of glucose (eg. malabsorption syndrome).
Principle of Glucose Tolerance Test
Following a standard oral dose of glucose, plasma and urine glucose levels are monitored at regular intervals, in order to measure tolerance under defined conditions.
Samples and Procedure
- The patient is advised to come to the laboratory in a fasting state, where after taking a fasting blood sample, the patient is given 75 grams of glucose.
- It is better to give in 7-up where it will be well tolerated.
- Collect fasting blood and then collect blood samples at 30, 60, 90, 120 minutes.
- Multiple samples are taken at half-hour intervals along with the urine sample.
- In pregnant lady collect blood at 60, 120 and 180 min after glucose.
- some time the sample is taken at 1, 2, 3, and up to 4 hours.
Precautions
- Stress can increase the glucose level.
- If the patient does not tolerate the glucose and vomit out, that may give a false result.
Purpose of the test
- It is used to diagnose Diabetes mellitus.
- It is also used to evaluate hypoglycemia.
- Patient with family H/o diabetes.
- patients with obesity.
- Patients with H/O recurrent infection.
- Patients with H/O delayed wound healing.
- Ladies with H/O stillbirths or delivering obese babies.
- Patients with H/O random glycosuria, or hyperglycemia during pregnancy or after myocardial infarction, surgery or stress.
Important facts for GDM:
- OGTT is not recommended to see the complications of Diabetes mellitus.
- Its use also discouraged for the fasting hypoglycemia.
- In non-pregnant ladies and children, the OGTT is not recommended as a screening test.
- For pregnant lady 50 G glucose is recommended for screening.
- The serum glucose level of >150 mg/dl at 1 hour, is considered for further testing.
- There is a rapid response to insulin to oral glucose and the peak is 30 and 60 minutes.
- Glucose comes to normal in 3 hours.
- Glucose will not appear in the urine in a normal pattern.
Normal Values:
| Time | Glucose value | Urine glucose |
|---|---|---|
| Fasting | <110 mg/dL or 6.1 mmol/L (70 to 105 mg/dl) | negative |
| 30 min | 110 to 170 mg/dL ( 11.1 mmol/L) | negative |
| one hour | 120 to 170 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) | negative |
| 2 hours | <140 mg/dL or 7.8 mmol/L (70 to 120 mg/dL) | negative |
| 3 hours | 70 to 115 mg/dL or <6.4 mmol/L | negative |
| 4 hours | 70 to 115 mg/dL or <6.4 mmol/L | negative |