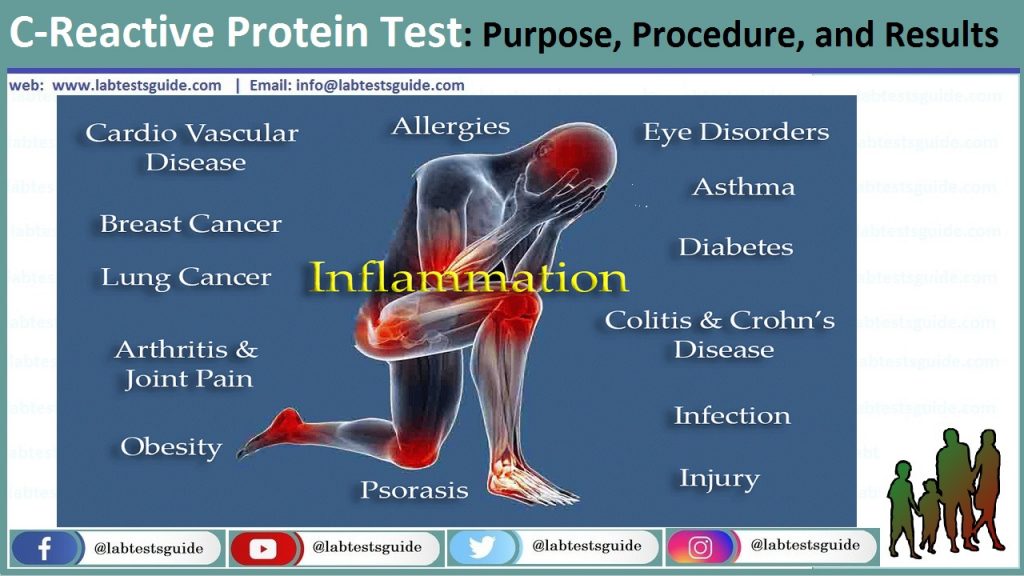
C-reactive protein (CRP) is an acute-phase protein produced by the liver in response to inflammation, infection, and tissue damage. Discovered in 1930, CRP plays a vital role in the immune response by binding to phosphocholine on microbes, enhancing phagocytosis, and aiding in the clearance of dead cells. Elevated CRP levels are a significant marker for various inflammatory conditions, making it a crucial tool in diagnosing and monitoring disease progression.
PRINCIPLE:
It is a slide agglutination test. Latex particles coated with CRP antiserum are allowed to react with test serum. Agglutination is observed if CRP is present in a concentration of 6 mg/L or above.
REQUIREMENTS:
- Serum sample
- CRP latex reagent
- Positive and negative controls (PC; NC)
- Test card and Test Tubes
- Normal saline
- Disposable mixing sticks
- Mechanical rotator (80-100 rpm)
PROCEDURE:
- Bring the kit reagents and sample to room temperature.
- Place 0.05 ml of the serum into one circle of slide.
- Place similar quantities of positive and negative controls in separate circles.
- Gently mix the latex reagent vial (to ensure homogeneity) and place one drop to each of the circle.
- Mix the contents of each circle evenly with disposable sticks and spread over the complete area of the circle.
- Place the slide on mechanical rotator (80-100 rpm) for 2 minutes.
- Examine for agglutination macroscopically.
- Compare the results with positive and negative controls.
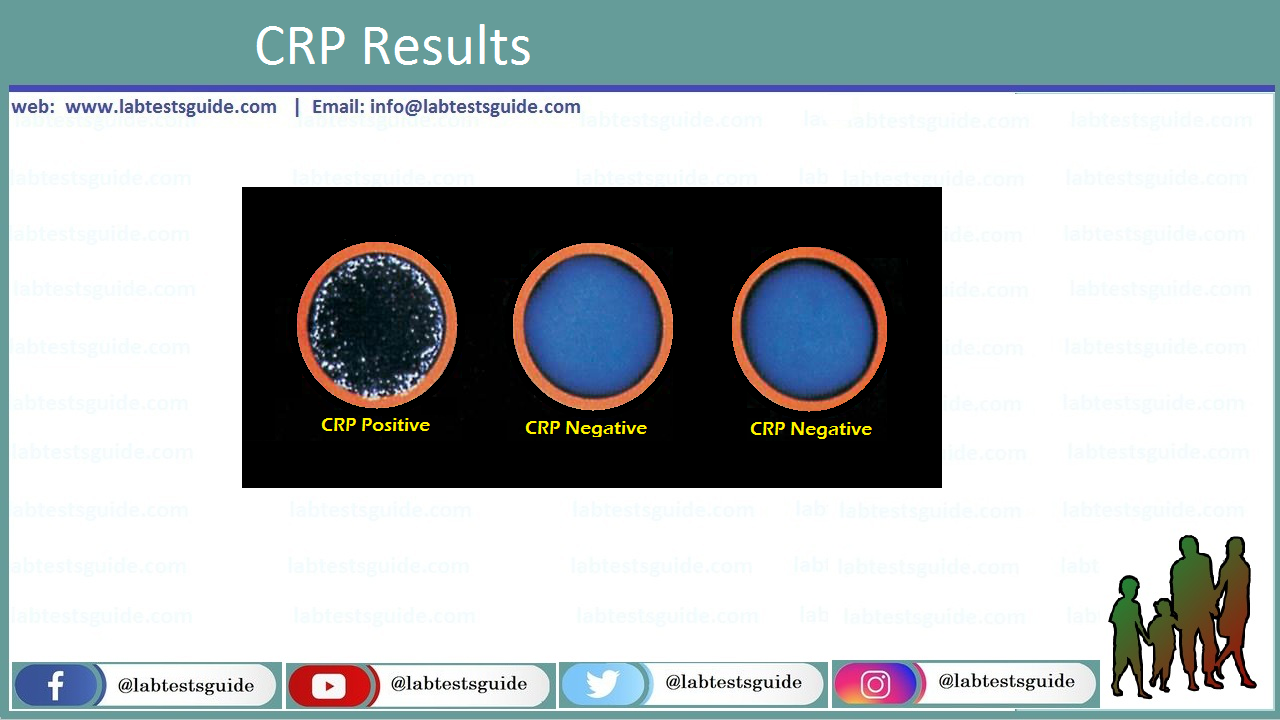
RESULTS:
- Agglutination indicates a positive reaction.
- If CRP test is positive, the amount of CRP will be equal to 6 mg/L or above while in case of a negative reaction (no agglutination) less than 6 mg/L.
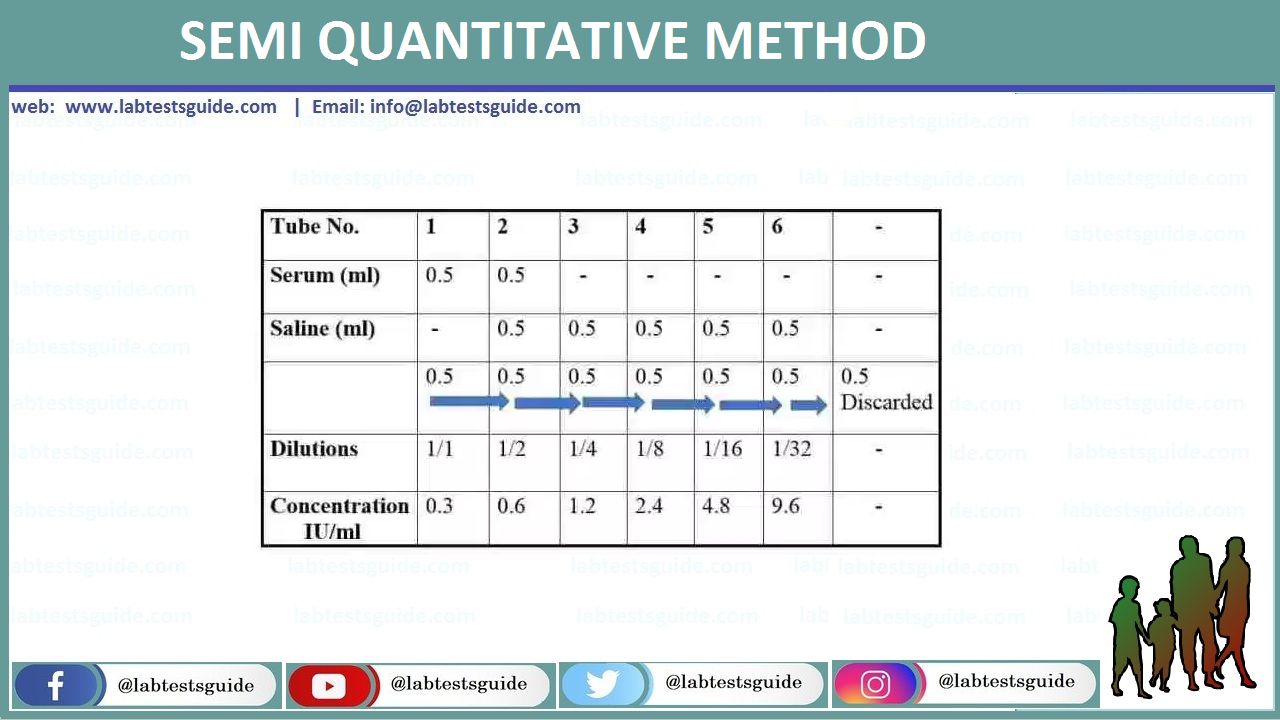
SEMI QUANTITATIVE METHOD:
- If CRP test is positive, serial dilutions of the serum are tested.
- The highest dilution of the serum giving positive result will be the titre.
Prepare double dilutions of serum as follows.
QUALITY CONTROL:
Every test kit have Positive and Negative controls which are run parallel to all tests which are being run or perform routinely.
INTERPRETATION OF CRP TEST:
- The increased level of CRP indicates inflammation and tissue damage.
- The progression of an infection is also monitored
- False negative results are seen due to prozone phenomenon.
- It is recommended to make the final diagnosis with clinical examination and other laboratory data.
COMPARISON OF CRP AND ESR TEST:
CRP has some advantages over Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR), though both are used as a marker of inflammation.
- CRP is a direct measure of inflammation whereas ESR is a indirect one.
- CRP has a more rapid response to inflammation than ESR and also returns to normal when the inflammatory condition is resolved.
- CRP is comparatively less affected by age.
- CRP is not raised in non-inflammatory conditions but ESR is elevated in some.