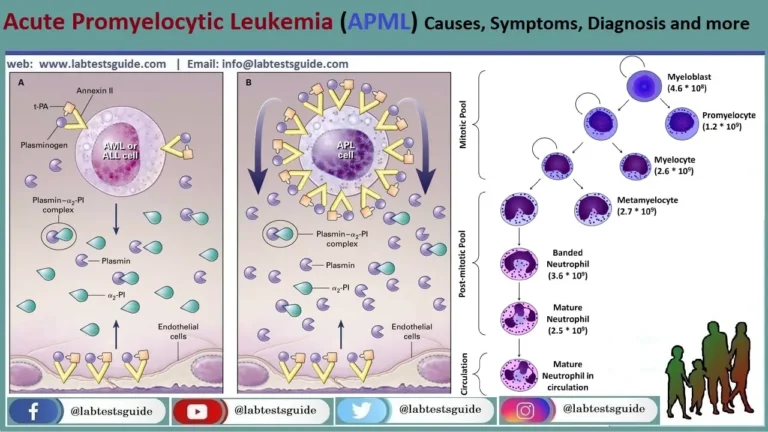
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease (STD) that can affect both men and women. It can cause infections in the penis, rectum and throat. This is a very common infection, especially in children aged 15-24.
Gonorrhea often spreads during vaginal, oral, or anal sex. But infected mothers may have infections during childbirth. In children, gonorrhea usually affects the eyes.
Symptoms:
Exposure usually occurs within two to 14 days after exposure. However, people with gonorrhea never develop prominent symptoms. It is important to remember that a person with gonorrhea who has no symptoms is also called a non-symptomatic carrier. When one person does not have any symptoms, then the other person gets the infection.
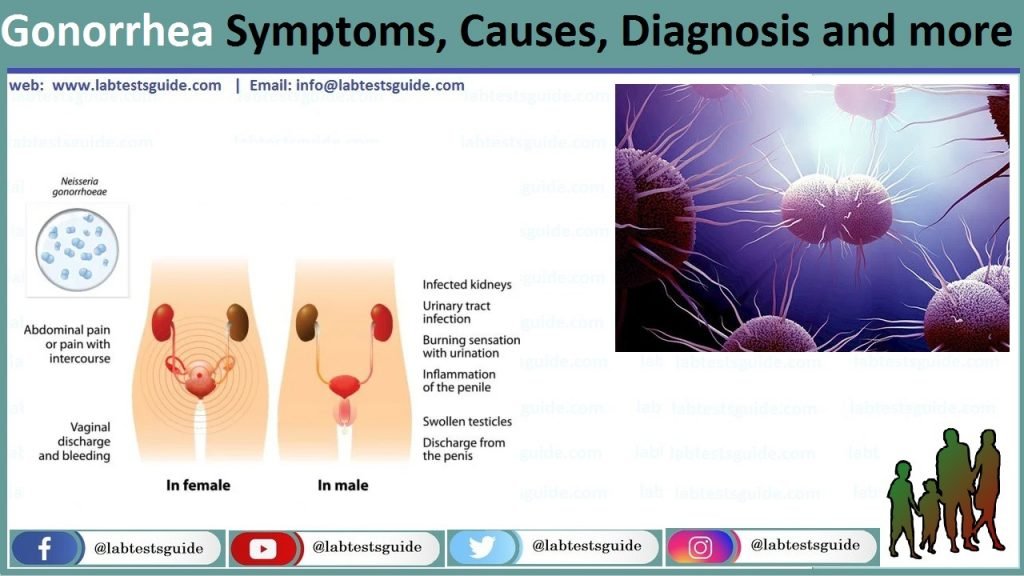
Symptoms in Men:
- Greater frequency or urgency of urination
- A pus-like discharge (or drip) from the penis (white, yellow, beige, or greenish)
- Swelling or redness at the opening of the penis
- Swelling or pain in the testicles
- A persistent sore throat
Symptoms in Women:
- Discharge from the vagina (watery, creamy, or slightly green)
- Pain or burning sensation while urinating
- The need to urinate more frequently
- Heavier periods or spotting
- Sore throat
- Pain upon engaging in sexual intercourse
- Sharp pain in the lower abdomen
- Fever
Causes:
- Gonorrhea Nausea is caused by gonorrhea bacteria.
- Inflammatory bacteria often pass from one person to another during sexual contact, including
- oral Sex
- Anal Sex
- Vaginal Sex
Risk factors:
Sexually active women under the age of 25 and men who have sex with men are at increased risk of becoming infected.
Other factors that may increase your risk include:
- Creating a New Sexual Partner
- Having a sexual partner who has other partners
- Having more than one sexual partner
- Gastric or other sexually transmitted infections.
Complications:
Treating gonorrhea can cause major complications, such as:
- Infertility in women. Gonorrhea can spread to the uterus and fallopian tubes, causing pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). PID can lead to tuberculosis, an increased risk of pregnancy complications and infertility. PID needs immediate treatment.
- Infertility In Men. Inflammation can cause a small spiral tube to flower in the back of the testicles where the epididymis (epididymis) is located. Untreated epidemics can cause infertility.
- Infection that spreads to the joints and other areas of your body. Bacteria that cause inflammation can spread to the bloodstream and affect other parts of the body, including the joints. Possible consequences are fever, irritation, skin lesions, joint pain, swelling and stiffness.
- Increased risk of HIV / AIDS. Gonorrhea makes you more prone to infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a virus that causes AIDS. People who have gonorrhea and HIV can easily transmit both diseases to their peers.
- Complications in children. Children who receive gonorrhea from their mothers during labor can develop blindness, scalp lesions and infections.
Prevention:
Follow these instructions to reduce the risk of gonorrhea ::
- If you have sex, use a condom. Avoiding sex is one of the surest ways to prevent gonorrhea. But if you do choose to have sex, use condoms during any sexual contact, including anal sex, oral or vaginal sex.
- Limit the number of sexual partners you have. Living in a sexual relationship where neither partner has sex with the other person can reduce their risk.
- Make sure that you and your partner are sexually transmitted infections. Before you have sex, test and share your results with each other.
- Do not have sex with anyone. who appears to have a sexually transmitted infection. If your partner has signs or symptoms of a sexually transmitted infection, such as urine burning or genetic itching or soreness, do not have sex with this person.
- Consider detecting gonorrhea regularly. Annual screening is recommended for sexually active women under 25 and older women at increased risk of infection. This includes women who have a new sexual partner, multiple sexual partners, have sexual partners with other partners, or have a sexual partner who is sexually transmitted.
Periodicals This review is also recommended for men who have sex with men, as well as for their partners.
Sample Required:
- The best sample for men is the urethral discharge smear.
- Females can make a smear from the vagina.
- In female cervical smear can also be taken.
- Anal canal smear can be taken.
Diagnoses:
Your doctor will examine the cell sample to determine if you have gonorrhea. Samples can be submitted by:
- Urine test. This can help identify the bacteria in your urinary tract.
- Swab from the affected area can collect bacteria from your throat, urinary tract, vagina or rectum that can be identified in the laboratory.