Biochemical Test of Corynebacterium Diphtheriae 50 FAQs and 30 MCQs:
Biochemical Test of Corynebacterium Diphtheriae 50 FAQs
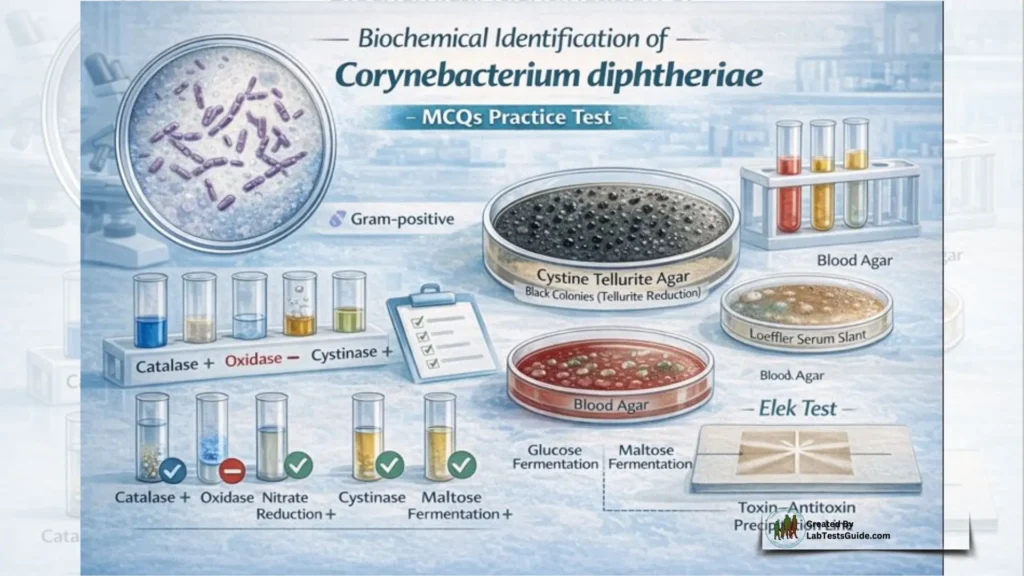
What is the Gram stain result for C. diphtheriae?
Gram-positive.
Describe the shape and arrangement of C. diphtheriae.
Club-shaped rods in “Chinese character” or palisade arrangements.
Is C. diphtheriae capsulated?
No, it is non-capsulated.
Does C. diphtheriae produce spores?
No, it is non-sporing.
Is C. diphtheriae motile?
No, it is non-motile and non-flagellated.
What is the catalase test result for C. diphtheriae?
Positive.
What is the oxidase test result?
Negative (lacks cytochrome oxidase).
Does C. diphtheriae reduce nitrate?
Yes, nitrate reduction is positive.
What is the urease test result?
Negative (lacks urease enzyme).
Is C. diphtheriae coagulase-positive?
No, coagulase test is negative.
Does it hydrolyze gelatin?
No, gelatin hydrolysis is negative.
What is the methyl red (MR) test result?
Positive.
Does it produce hydrogen sulfide (H₂S)?
Yes, H₂S test is positive.
What is the CAMP test result?
Negative.
Does it hydrolyze starch?
No, starch hydrolysis is negative.
What is the cystinase test result?
Positive (forms black colonies on cystine tellurite agar).
What is the pyrazinamidase test result?
Positive.
Does it hydrolyze esculin?
No, esculin hydrolysis is negative.
Does it hydrolyze casein?
No, casein hydrolysis is negative.
Does it hydrolyze tyrosine?
No, tyrosine hydrolysis is negative.
What is the ornithine decarboxylase result?
Negative.
What is the alkaline phosphatase result?
Negative.
What is the cetrimide test result?
Negative.
Which carbohydrates does C. diphtheriae ferment?
Glucose, maltose, dextrose, fructose, galactose, arabinose, mannose, rhamnose, and salicin.
Which carbohydrates does it NOT ferment?
Lactose, sucrose, trehalose, xylose, glycogen, mannitol, and hippurate.
Does it ferment glucose?
Yes, with acid production.
Does it ferment maltose?
Yes.
Does it ferment lactose?
No.
Does it ferment sucrose?
No (strain-dependent variability).
Does it ferment mannitol?
No
Does it ferment raffinose?
Variable (strain-dependent).
Does it produce gas during fermentation?
Gas production is variable
What is the Elek test used for?
To detect diphtheria toxin production.
How is the Elek test performed?
Streak bacteria perpendicular to an antitoxin-embedded strip; toxin-antitoxin interaction forms a precipitation line.
Why is toxigenicity testing critical for diagnosis?
Only toxin-producing strains cause clinical diphtheria.
Which gene confirms toxigenicity?
The tox gene (detected via PCR).
What hemolysis pattern does C. diphtheriae show?
Weak beta-hemolysis.
Does it produce pigment?
Yes.
What is its oxygen requirement?
Fermentative (facultative anaerobe).
Is it citrate utilization-positive?
No, citrate test is negative.
Does it grow on tellurite media?
Yes (tellurite reduction is positive).
How does C. diphtheriae differ from C. ulcerans and C. pseudotuberculosis?
C. diphtheriae is urease-negative; others are urease-positive.
Which tests help differentiate toxic Corynebacterium species?
Urease, pyrazinamidase, and nitrate reduction tests.
Are all toxic Corynebacterium species pyrazinamidase-positive?
No, they are pyrazinamidase-negative.
What initial tests suggest C. diphtheriae?
Gram stain (club-shaped rods), catalase-positive, oxidase-negative.
Which tests are used for presumptive identification?
Carbohydrate fermentation (glucose/maltose +ve; sucrose -ve), nitrate reduction, cystinase.
How is identification confirmed?
Molecular methods (PCR for tox gene).
Why is colony morphology important?
Supports biochemical findings (e.g., black colonies on tellurite media).
Can biochemical test results vary?
Yes, depending on strain and laboratory protocols.
What is the role of the indole test?
Negative for C. diphtheriae (helps rule out other species).
Biochemical Test of Corynebacterium diphtheriae 30 MCQs
- What is the Gram reaction of C. diphtheriae?
a) Gram-negative
b) Gram-variable
c) Gram-positive✔
d) Acid-fast - What is the characteristic cellular arrangement of C. diphtheriae?
a) Chains
b) Clusters
c) Palisades/”Chinese characters”✔
d) Tetrads - Is C. diphtheriae motile?
a) Yes
b) No✔
c) Only in liquid media
d) Variable - Does C. diphtheriae produce spores?
a) Yes
b) No✔
c) Only under stress
d) Variable - 5. Catalase test result for C. diphtheriae is:
a) Negative
b) Positive✔
c) Weakly positive
d) Variable
- The oxidase test for C. diphtheriae is:
a) Negative✔
b) Positive
c) Delayed positive
d) Strain-dependent - Urease test result for C. diphtheriae is:
a) Positive
b) Negative✔
c) Variable
d) Weakly positive - Nitrate reduction by C. diphtheriae is:
a) Negative
b) Positive✔
c) Variable
d) Not tested - The CAMP test for C. diphtheriae is:
a) Positive
b) Negative✔
c) Weakly positive
d) Inconclusive - Gelatin hydrolysis by C. diphtheriae is:
a) Positive
b) Negative✔
c) Variable
d) Slow positive - 11. Which sugar is consistently fermented by C. diphtheriae?
a) Lactose
b) Sucrose
c) Glucose✔
d) Mannitol
- Maltose fermentation by C. diphtheriae is:
a) Negative
b) Positive✔
c) Variable
d) Not reported - Sucrose fermentation by C. diphtheriae is typically:
a) Positive
b) Negative✔
c) Variable
d) Acid-only - Lactose fermentation by C. diphtheriae is:
a) Positive
b) Negative✔
c) Variable
d) Slow - Raffinose fermentation is:
a) Positive
b) Negative
c) Variable✔
d) Not tested - 16. The cystinase test for C. diphtheriae is:
a) Negative
b) Positive✔
c) Variable
d) Equivocal
- Pyrazinamidase test result for toxigenic Corynebacterium spp. is:
a) Positive
b) Negative✔
c) Variable
d) Not applicable - Starch hydrolysis by C. diphtheriae is:
a) Positive
b) Negative✔
c) Variable
d) Slow - H₂S production by C. diphtheriae is:
a) Negative
b) Positive✔
c) Variable
d) Weak - The methyl red (MR) test is:
a) Negative
b) Positive✔
c) Variable
d) Not defined - 21. The Elek test detects:
a) Bacterial capsule
b) Diphtheria toxin✔
c) Catalase enzyme
d) Nitrate reductase
- Confirmation of toxigenicity requires:
a) Catalase test
b) Gram stain
c) PCR for tox gene✔
d) Urease test - On cystine tellurite agar, C. diphtheriae produces:
a) Yellow colonies
b) Red colonies
c) Black colonies✔
d) Green colonies - 24. Which test best differentiates C. diphtheriae from C. ulcerans?
a) Catalase
b) Urease✔
c) Oxidase
d) Nitrate reduction - All toxigenic Corynebacterium species are:
a) Urease-positive
b) Pyrazinamidase-negative✔
c) Sucrose fermenters
d) Motile - Hemolysis pattern of C. diphtheriae is:
a) Alpha-hemolysis
b) Weak beta-hemolysis✔
c) Gamma-hemolysis
d) Strong beta-hemolysis
- Citrate utilization by C. diphtheriae is:
a) Positive
b) Negative✔
c) Variable
d) Slow - The OF (Oxidative-Fermentative) profile is:
a) Oxidative
b) Fermentative✔
c) Inert
d) Variable - Tellurite reduction by C. diphtheriae is:
a) Negative
b) Positive✔
c) Variable
d) Not tested - Biochemical tests for C. diphtheriae provide:
a) Definitive diagnosis
b) Presumptive identification✔
c) Toxigenicity confirmation
d) Antibiotic sensitivity