Biochemical Test of Bordetella Pertussis 50 FAQs and 30 MCQs:
Biochemical Test of Bordetella Pertussis 50 FAQs
What bacterium causes whooping cough?
Bordetella pertussis.
What shape is Bordetella pertussis?
Minute coccobacilli (tiny rods/cocci).
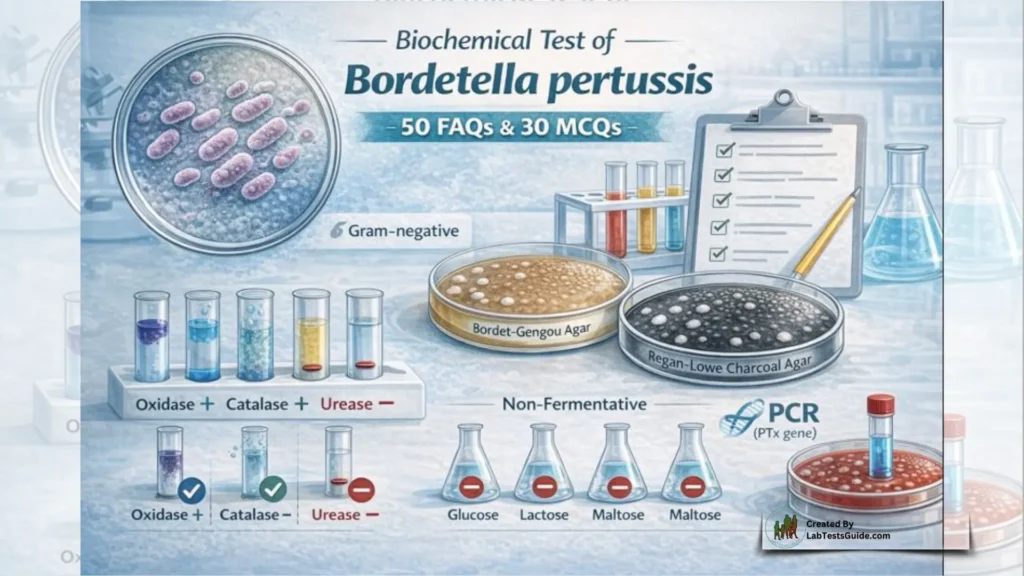
Is B. pertussis Gram-positive or Gram-negative?
Gram-negative.
Does B. pertussis have a capsule?
Yes, it is capsulated (+ve).
Is B. pertussis motile? .
No, it is non-motile (-ve flagella, -ve motility)
Does B. pertussis form spores?
No, it is non-spore-forming (-ve).
What color pigment does B. pertussis produce?
It does not produce pigment (-ve).
Why is B. pertussis considered fastidious?
It has very specific and demanding growth requirements.
Can B. pertussis grow in standard nutrient broth?
No, growth in nutrient broth is negative (-ve).
What type of media is essential for growing B. pertussis?
Bordet-Gengou agar or Regan-Lowe charcoal agar supplemented with blood and antibiotics.
Does B. pertussis require special atmospheric conditions?
It is aerobic but often benefits from increased CO2 (microaerophilic conditions) for initial isolation.
What is the typical hemolysis pattern of B. pertussis?
It exhibits beta-hemolysis (+ve), meaning it completely lyses red blood cells around colonies.
How long does it take for B. pertussis to grow on culture?
Colonies can take 3-7 days to appear.
Is B. pertussis catalase positive?
Yes (+ve).
Is B. pertussis oxidase positive?
Yes (+ve).
Does B. pertussis have chymotrypsin activity?
Yes (+ve).
Does B. pertussis have esterase (C8) lipase activity?
Yes (+ve).
Does B. pertussis have Naphthol-AS-B1 phosphohydrolase activity?
Yes (+ve).
Can B. pertussis use citrate as a sole carbon source?
No, citrate test is negative (-ve).
Does B. pertussis hydrolyze gelatin?
No (-ve).
Can B. pertussis reduce nitrate to nitrite?
No, nitrate reduction is negative (-ve).
Does B. pertussis produce urease?
No (-ve).
Does B. pertussis produce alkaline phosphatase?
No (-ve).
Can B. pertussis hydrolyze esculin?
No (-ve).
Does B. pertussis have lipase (C14) activity?
No (-ve).
Does B. pertussis produce lysine decarboxylase?
No (-ve).
Does B. pertussis produce trypsin?
No (-ve).
Can B. pertussis ferment glucose?
No (-ve).
Can B. pertussis ferment lactose?
No (-ve).
Can B. pertussis ferment maltose?
No (-ve).
Can B. pertussis ferment mannitol?
No (-ve).
Can B. pertussis ferment sucrose?
No (-ve).
Can B. pertussis ferment xylose?
No (-ve).
Does B. pertussis ferment any common sugars?
No, it is generally non-fermentative for carbohydrates listed (Glucose, Lactose, Maltose, Mannitol, Sucrose, Xylose all -ve).
Can B. pertussis utilize adipate?
No (-ve).
Can B. pertussis utilize caprate?
No (-ve).
Can B. pertussis utilize gluconate?
No (-ve).
Can B. pertussis utilize malate?
No (-ve).
Can B. pertussis utilize phenylacetate?
No (-ve).
Is culture the primary method for diagnosing pertussis today?
No, PCR and serology are more common due to the fastidious nature of the bacterium and slow culture growth.
Why is biochemical testing still important for B. pertussis?
It helps confirm identity, especially from culture, and differentiate from similar species.
What are the key biochemical tests to identify B. pertussis?
Oxidase (+ve), Catalase (+ve), Urease (-ve), Nitrate Reduction (-ve), and its inability to grow on nutrient agar/broth and lack of carbohydrate fermentation are crucial.
How does B. pertussis differ biochemically from B. parapertussis?
B. parapertussis is usually urease positive (+ve) and can produce brown pigment on media, unlike B. pertussis.
How does B. pertussis differ biochemically from B. bronchiseptica?
B. bronchiseptica is motile (+ve), urease positive (+ve), grows on nutrient agar, and reduces nitrate (+ve).
What is the significance of a positive oxidase test for B. pertussis?
It helps place it among Gram-negative bacteria and differentiate it from some other respiratory pathogens.
Do the biochemical characteristics relate to how B. pertussis causes disease?
Yes, characteristics like toxin production (not directly tested here), adhesion factors, and evasion mechanisms (capsule) are crucial for pathogenesis.
Why can’t B. pertussis ferment sugars?
It primarily utilizes amino acids and organic acids as energy sources, aligning with its niche in the respiratory tract.
What does the lack of motility mean for B. pertussis infection?
It relies on other mechanisms (e.g., adhesins, toxins) to colonize and damage the respiratory epithelium, not self-propulsion.
Is the capsule important for B. pertussis virulence?
Yes, it helps resist phagocytosis by the host immune system.
Why is identifying B. pertussis accurately important?
For appropriate treatment (specific antibiotics), infection control (highly contagious), public health reporting, and vaccination strategies.
Biochemical Test of Bordetella Pertussis 30 MCQs
- What is the Gram stain reaction of Bordetella pertussis?
a) Gram-positive
b) Gram-variable
c) Gram-negative✔
d) Acid-fast - Which of the following enzymes is POSITIVE in B. pertussis?
a) Urease
b) Citrate utilization
c) Catalase✔
d) Nitrate reductase - B. pertussis is characterized by:
a) Motility
b) Spore formation✔
c) Capsule presence
d) Pigment production - Growth of B. pertussis in standard nutrient broth is:
a) Positive
b) Negative✔
c) Variable
d) Requires CO2 enrichment - The oxidase test result for B. pertussis is:
a) Positive✔
b) Negative
c) Weakly positive
d) Not applicable - Which carbohydrate can B. pertussis ferment?
a) Glucose
b) Lactose
c) Maltose
d) None of the above✔ - The hemolysis pattern exhibited by B. pertussis on blood-containing media is:
a) Alpha-hemolysis
b) Beta-hemolysis✔
c) Gamma-hemolysis
d) Delta-hemolysis - The gelatin hydrolysis test for B. pertussis is:
a) Positive
b) Negative✔
c) Slowly positive
d) Not determined - Which of the following enzymatic activities is POSITIVE in B. pertussis?
a) Alkaline Phosphatase
b) Esterase (C8) lipase✔
c) Lipase (C14)
d) Trypsin - The citrate utilization test for B. pertussis is:
a) Positive
b) Negative✔
c) Variable
d) Requires prolonged incubation
- A gram-negative coccobacillus isolated from a whooping cough suspect is non-motile, urease-negative, and nitrate reduction negative. It is most likely:
a) Bordetella bronchiseptica
b) Bordetella parapertussis
c) Bordetella pertussis✔
d) Haemophilus influenzae - Which biochemical test is MOST useful to differentiate B. pertussis from B. parapertussis?
a) Catalase
b) Oxidase
c) Urease✔ - A bacterium grows on nutrient agar, is motile, urease-positive, and reduces nitrate. It is likely:
a) Bordetella pertussis
b) Bordetella parapertussis
c) Bordetella bronchiseptica✔
d) Bordetella holmesii - B. pertussis can be differentiated from Haemophilus influenzae because B. pertussis:
a) Requires X and V factors
b) Is oxidase negative
c) Does not require X and V factors✔
d) Ferments sucrose
- The preferred medium for isolating B. pertussis is:
a) MacConkey Agar
b) Blood Agar
c) Bordet-Gengou Agar✔
d) Chocolate Agar - Colonies of B. pertussis typically appear on culture media after:
a) 12-24 hours
b) 24-48 hours
c) 3-7 days✔
d) >10 days - Why is B. pertussis considered a fastidious organism?
a) It grows rapidly on all media
b) It has complex and specific nutritional requirements✔
c) It is highly resistant to antibiotics
d) It produces abundant spores
- The capsule of B. pertussis is important for virulence because it:
a) Enhances motility
b) Facilitates sugar fermentation
c) Protects against phagocytosis✔
d) Produces toxins - The inability of B. pertussis to ferment sugars is related to its:
a) Fast growth rate
b) Preference for amino acids/organic acids as energy sources✔
c) Aerobic metabolism
d) Toxin production - Which virulence factor is NOT directly indicated by the provided biochemical profile?
a) Capsule
b) Pertussis Toxin✔
c) Beta-hemolysin
d) Enzymes like Chymotrypsin
- The primary diagnostic method for pertussis in most clinical settings today is:
a) Culture on Bordet-Gengou agar
b) Gram stain of sputum
c) PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)✔
d) Biochemical test panel - Biochemical testing of B. pertussis remains important primarily for:
a) Initial rapid diagnosis from patient samples
b) Confirming the identity of isolates obtained from culture✔
c) Determining antibiotic susceptibility
d) Measuring toxin levels - Accurate identification of B. pertussis is critical for all EXCEPT:
a) Selecting appropriate antibiotic therapy
b) Implementing effective infection control measures
c) Monitoring vaccine effectiveness & epidemiology
d) Determining patient blood type✔.
- B. pertussis shows POSITIVE activity for which enzyme?
a) Alkaline Phosphatase
b) Esculin Hydrolysis
c) Naphthol-AS-B1-phosphohydrolase✔
d) Lysine decarboxylase - Which substrate utilization test is NEGATIVE for B. pertussis?
a) Adipate
b) Caprate
c) Malate
d) All of the above✔ - Chymotrypsin activity in B. pertussis is:
a) Positive✔
b) Negative
c) Variable
d) Not tested - The shape of Bordetella pertussis cells is described as:
a) Long rods
b) Cocci in chains
c) Minute coccobacilli✔
d) Spirochetes
- B. pertussis is non-motile.
a) True✔
b) False - B. pertussis can reduce nitrate to nitrite.
a) True
b) False✔ - B. pertussis produces a pigment.
a) True
b) False✔