Biochemical Test of Listeria monocytogenes 50 FAQs and 25 MCQs:
Biochemical Test of Listeria monocytogenes 50 FAQs
Is Listeria monocytogenes Gram-positive or Gram-negative?
Does L. monocytogenes form spores?
No, it is non-sporing.
What is the shape of L. monocytogenes?
Rod-shaped (bacilli).
Is L. monocytogenes motile?
Yes, it is flagellated and motile at 20–28°C.
What type of hemolysis does L. monocytogenes exhibit?
Beta-hemolysis.
What is the CAMP test result for L. monocytogenes?
Positive (+ve).
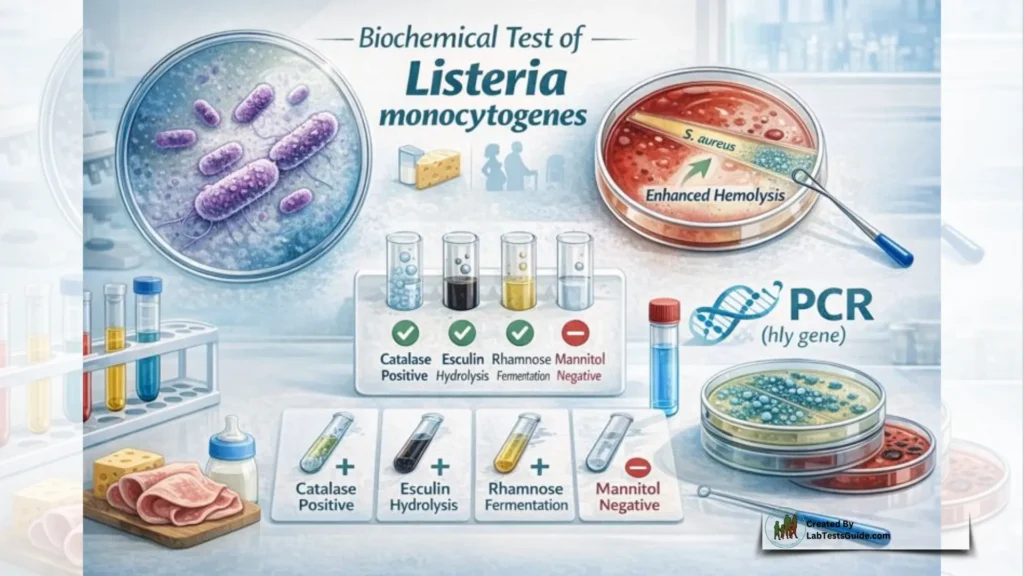
Does L. monocytogenes produce catalase?
Yes, catalase-positive.
Does L. monocytogenes ferment mannitol?
No, it is mannitol-negative.
Which carbohydrates does L. monocytogenes ferment?
Glucose, glycerol, lactose, maltose, rhamnose, sucrose, and trehalose.
What enzymes are produced by L. monocytogenes?
Lecithinase, esculin hydrolase, and arginine dehydrolase.
What disease does L. monocytogenes cause?
Listeriosis.
Who is most at risk for severe listeriosis?
Pregnant women, newborns, elderly, and immunocompromised individuals.
What are the symptoms of listeriosis?
Flu-like symptoms, fever, muscle aches, nausea, diarrhea, or neurological symptoms (e.g., meningitis).
How does L. monocytogenes infect humans?
Primarily through contaminated food (e.g., ready-to-eat meats, unpasteurized dairy).
Why is L. monocytogenes problematic in food?
It grows at refrigeration temperatures (4–8°C) and resists high salt/acid conditions.
What virulence factor is critical for L. monocytogenes pathogenesis?
Listeriolysin O (encoded by the hly gene).
Can L. monocytogenes cause miscarriage?
Yes, pregnant women may experience stillbirth or premature delivery.
Is L. monocytogenes zoonotic?
Yes, it can infect animals and humans.
What is the mortality rate of listeriosis?
20–30% in high-risk groups.
How many serotypes of L. monocytogenes exist?
13 (e.g., 1/2a, 1/2b, 4b).
What media are used to isolate L. monocytogenes?
Oxford agar, PALCAM agar, and chromogenic media (e.g., Ottavani-Agosti agar).
What is the role of chromogenic media in detection?
They differentiate pathogenic Listeria (blue-green colonies with halos) from non-pathogenic species.
How does the CAMP test work for L. monocytogenes?
It enhances hemolysis near Staphylococcus aureus streaks.
What biochemical tests confirm L. monocytogenes?
Catalase (+), oxidase (–), esculin hydrolysis (+), and rhamnose fermentation (+).
What molecular method detects L. monocytogenes?
PCR targeting the hly gene.
Can PCR detect L. monocytogenes directly in food?
Yes, rapid PCR kits (e.g., BAX® system) are used.
What is the ISO standard for Listeria detection?
ISO 11290 (Parts 1 & 2).
How is B. cereus differentiated from B. anthracis?
B. cereus is motile and hemolytic; B. anthracis is non-motile and non-hemolytic.
How long does traditional culture-based detection take?
Up to 6 days.
What is the DIM test in API-Listeria?
It detects arylamidase to differentiate L. monocytogenes from L. innocua.
Why is serotyping useful?
For epidemiological tracking (not speciation).
Which foods are commonly contaminated?
Ready-to-eat meats, raw milk, smoked fish, and soft cheeses.
Why are “ready-to-eat” foods high-risk?
No reheating kills Listeria before consumption.
Does cooking kill L. monocytogenes?
Yes, heating to ≥70°C destroys it.
Can Listeria grow in vacuum-packed foods?
Yes, it tolerates low-oxygen environments.
How can food industries prevent Listeria contamination?
Implement HACCP, GMP, and sanitation protocols.
What temperature inhibits Listeria growth?
Freezing (<0°C) stops growth but doesn’t kill it.
Is L. monocytogenes resistant to antibiotics?
Most strains are susceptible to penicillin/ampicillin but resistant to cephalosporins.
What sanitizers are effective against Listeria?
Quaternary ammonium compounds and chlorine-based sanitizers.
How does L. monocytogenes form biofilms?
It adheres to surfaces (e.g., processing equipment) and resists cleaning.
What is the “Cook Chill” process risk?
Improper cooling allows Listeria to multiply.
How many Listeria species are there?
8 (e.g., L. innocua, L. ivanovii, L. seeligeri).
Which Listeria species are pathogenic?
Primarily L. monocytogenes; rarely L. ivanovii or L. seeligeri.
What was the source of Brazil’s beef contamination?
Unhygienic free-fair butchers’ shops (study in Jiquiriçá, Bahia).
How prevalent is L. monocytogenes in humans?
1–10% may be asymptomatic intestinal carriers.
What was the 2008 Canadian outbreak linked to?
Processed meat (53 cases, 20 deaths).
Why is PCR better than culture methods?
Faster (hours vs. days) and detects non-viable bacteria.
What is the role of national reference labs?
Confirm outbreaks and track strains internationally.
Can Listeria survive in soil?
Yes, it is ubiquitous in soil, water, and plants.
What animal is L. ivanovii pathogenic to?
Sheep (causes abortions).
Why is listeriosis underreported in Brazil?
Lack of surveillance and diagnostic challenges.
Biochemical Test of Listeria monocytogenes 25 MCQs
- What is the Gram stain result for Listeria monocytogenes?
a) Gram-negative
b) Gram-positive ✔
c) Acid-fast
d) None of the above - Which of the following describes the shape of L. monocytogenes?
a) Spherical
b) Spiral
c) Rod-shaped ✔
d) Comma-shaped - Which enzyme is produced by L. monocytogenes?
a) Catalase ✔
b) Oxidase
c) Urease
d) Tryptophanase - What type of hemolysis does L. monocytogenes exhibit?
a) Alpha
b) Beta ✔
c) Gamma
d) Delta - Which carbohydrate is not fermented by L. monocytogenes?
a) Glucose
b) Mannitol ✔
c) Maltose
d) Sucrose
- Listeriosis primarily affects which population?
a) Healthy adults
b) Pregnant women and immunocompromised individuals ✔
c) Teenagers
d) Infants under 6 months - What is a common symptom of invasive listeriosis?
a) Skin rash
b) Neurological symptoms (e.g., meningitis) ✔
c) Jaundice
d) Hair loss - Which virulence factor is crucial for L. monocytogenes pathogenesis?
a) Coagulase
b) Listeriolysin O (hly gene) ✔
c) Enterotoxin
d) Hyaluronidase - How is L. monocytogenes primarily transmitted to humans?
a) Mosquito bites
b) Contaminated food ✔
c) Sexual contact
d) Airborne droplets - What is the mortality rate of listeriosis in high-risk groups?
a) 1–5%
b) 20–30% ✔
c) 50–60%
d) 80–90%
- Which agar is commonly used to isolate L. monocytogenes?
a) MacConkey agar
b) Blood agar
c) Oxford agar ✔
d) Sabouraud agar - What does a positive CAMP test indicate for L. monocytogenes?
a) Enhanced hemolysis near S. aureus ✔
b) Lactose fermentation
c) Gelatin liquefaction
d) Urea hydrolysis - Which molecular method is used for rapid detection of L. monocytogenes?
a) ELISA
b) PCR (hly gene) ✔
c) Western blot
d) Gram staining - What color do L. monocytogenes colonies appear on chromogenic media?
a) Pink
b) Blue-green with halos ✔
c) Yellow
d) Black - Which test differentiates L. monocytogenes from L. innocua?
a) Oxidase test
b) DIM test (arylamidase) ✔
c) Indole test
d) Citrate test
- Which food is not commonly associated with L. monocytogenes outbreaks?
a) Raw milk
b) Smoked salmon
c) Fresh apples ✔
d) Deli meats - At what temperature does L. monocytogenes grow in refrigerated food?
a) -20°C
b) 4–8°C ✔
c) 25°C
d) 37°C - Which antibiotic is ineffective against L. monocytogenes?
a) Ampicillin
b) Penicillin
c) Cephalosporins ✔
d) Gentamicin - What is the best way to kill L. monocytogenes in food?
a) Freezing
b) Heating to ≥70°C ✔
c) Salting
d) Drying - Which food safety system helps control Listeria in industries?
a) HACCP ✔
b) ISO 9001
c) Six Sigma
d) FDA-GMP
- How many serotypes of L. monocytogenes are known?
a) 5
b) 13 ✔
c) 20
d) 25 - Which Listeria species causes abortion in sheep?
a) L. innocua
b) L. ivanovii ✔
c) L. seeligeri
d) L. welshimeri - Which country reported a major listeriosis outbreak from processed meat in 2008?
a) USA
b) Canada ✔
c) Brazil
d) France - What is the incubation period for listeriosis?
a) 1–2 hours
b) 1–2 days
c) 3–70 days ✔
d) 6 months - Which regulatory body sets standards for Listeria detection in food?
a) WHO
b) ISO (11290) ✔
c) CDC
d) USDA






