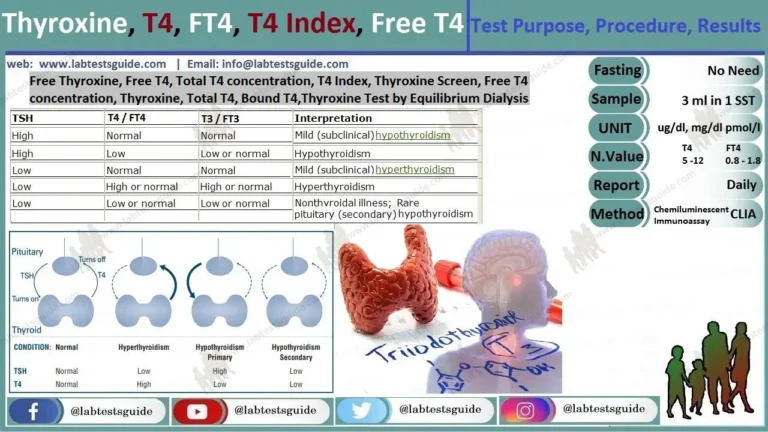
The osmolal gap measures the difference between measured serum osmolality (lab-tested) and calculated serum osmolality. It helps detect unmeasured osmoles like methanol, ethylene glycol, or ethanol in poisoning cases.
Formula:
Osmolal Gap = Measured Serum Osmolality − Calculated Serum Osmolality

Formulas & Units:
Calculated Serum Osmolality
- Using mg/dL (Conventional Units):
- Using mmol/L (SI Units):
*Conversion: 1 mmol/L ethanol = 4.6 mg/dL
Note: Ethanol (if present) can be added to the formula:
🧮 Osmolal Gap Calculator (Conventional & SI Units)
📐 Formula:
- Osmolal Gap = Measured Osmolality - Calculated Osmolality
- Conventional: (2 × Na) + (Glucose / 18) + (BUN / 2.8) [+ Ethanol / 4.6 (optional)]
- SI Units: (2 × Na) + Glucose + BUN [+ Ethanol × 1.25 (optional)]
📊 Normal Values:
- Measured Osmolality: 275 - 295 mOsm/kg
- Osmolal Gap: 0 - 10 mOsm/kg (higher values may indicate toxins)
🖊️ Enter the Values:
Purpose
- Screen for toxic alcohol ingestion (methanol, ethylene glycol).
- Identify osmotically active substances (e.g., mannitol, acetone).
- Evaluate electrolyte imbalances or lab errors.
Normal Value
- Normal Osmolal Gap: < 10 mOsm/kg.
- Clinically Significant Gap: > 10 mOsm/kg (suggests unmeasured osmoles).
Example Calculation (mg/dL)
- Lab Values:
- Na⁺ = 140 mEq/L
- Glucose = 180 mg/dL
- BUN = 28 mg/dL
- Measured Osmolality = 320 mOsm/kg
- Calculated Osmolality:
- Osmolal Gap:
Osmolal Gap = Measured Serum Osmolality − Calculated Serum Osmolality
Osmolal Gap = 320 − 300 = 20mOsm/kg
How to Use the Calculator
- Input Values:
- Enter serum Na⁺, glucose, BUN, and measured osmolality.
- Select units (mg/dL or mmol/L).
- Calculate: Automatically computes the osmolal gap.
- Interpretation:
- Gap > 10: Investigate for toxins, ketoacidosis, or lab error.
- Gap < 10: Likely no significant unmeasured osmoles.
Clinical Considerations
- Toxic Alcohols: Methanol, ethylene glycol, isopropanol.
- Other Causes:
- Ketoacidosis (elevated ketones).
- Lactic acidosis.
- Hyperlipidemia (pseudohyponatremia).
- Limitations:
- Ethanol may mask the gap if not included in the calculation.
- Formulas assume normal serum proteins and lipids.
Excluded Factors
- Does not account for volatile alcohols (e.g., acetone) unless specified.
- Non-toxin causes (e.g., hypertriglyceridemia) may require additional testing.
Key Takeaway: The osmolal gap is a rapid screening tool for toxins but must be interpreted alongside clinical history and confirmatory tests (e.g., anion gap, blood gas).
🔬 Lab Pro Tip: Always verify units (mg/dL vs. mmol/L) and include ethanol in the calculation if intoxication is suspected!