Bird Seed Agar 50 FAQs and 30 MCQs
Discover everything about Bird Seed Agar, the specialized medium for isolating Cryptococcus neoformans, with our comprehensive 50 frequently asked questions (FAQs) covering its composition, preparation, interpretation, and clinical significance. Test your knowledge further with 30 multiple-choice questions (MCQs) designed for medical lab technicians, microbiologists, and mycology students. Whether you’re preparing for exams or enhancing your diagnostic skills, this resource on LabTestsGuide.com provides essential insights into this unique fungal culture medium.

Bird Seed Agar 50 FAQs:
What is Bird Seed Agar?
A selective and differential medium for isolating Cryptococcus neoformans.
Why is it called Bird Seed Agar?
It contains Guizotia abyssinica (niger seed), commonly used as bird feed.
Who developed Bird Seed Agar?
Staib in 1962; later modified by Shields & Ajello (1966) with antibiotics.
What is the primary purpose of Bird Seed Agar?
Selective isolation and differentiation of C. neoformans and C. gattii.
What is the key component in Bird Seed Agar?
Guizotia abyssinica seeds (source of caffeic acid).
Why is caffeic acid important?
Substrate for phenoloxidase enzyme, leading to melanin production.
What role does creatinine play?
Enhances melanization in some C. neoformans strains.
Which antibiotics are added to Bird Seed Agar?
Penicillin G and gentamicin (or chloramphenicol in some formulations).
What is the pH of Bird Seed Agar?
6.5 ± 0.3 (varies slightly by formulation).
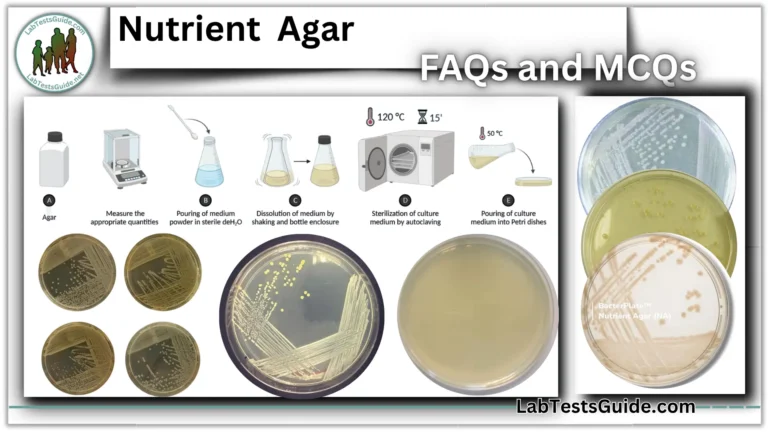
How are Guizotia abyssinica seeds prepared?
Ground finely, boiled in water, and filtered.
At what temperature is Bird Seed Agar autoclaved?
110–121°C for 15–20 minutes.
When are antibiotics added?
After cooling to 48°C before pouring plates.
What is the alternative to penicillin/gentamicin?
Some formulations use chloramphenicol or diphenyl.
Can Bird Seed Agar be stored after preparation?
Yes, at 2–8°C if unused.
How does C. neoformans appear on Bird Seed Agar?
Brown to black pigmented colonies due to melanin.
What enzyme causes pigmentation?
Phenoloxidase (acts on caffeic acid).
Which organisms show negative results?
Cryptococcus laurentii, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, E. coli.
Why might some C. neoformans strains not pigment?
Rare strains lack phenoloxidase activity.
Can other fungi produce dark colonies?
Yes (e.g., Aureobasidium, Sporothrix), but pigment is non-enzymatic.
What samples can be tested with Bird Seed Agar?
Clinical specimens (sputum, CSF, urine, tissue).
Is it used for environmental samples?
Yes (e.g., soil, bird droppings).
How does it differentiate C. neoformans from other yeasts?
Melanin production is unique to C. neoformans/gattii.
Can it detect Cryptococcus gattii?
Yes, both C. neoformans and C. gattii produce melanin.
Is Bird Seed Agar used for bacterial isolation?
No, antibiotics inhibit bacteria.
What is a positive control for Bird Seed Agar?
C. neoformans ATCC 32045 (brown colonies).
What is a negative control?
E. coli ATCC 25922 (growth inhibited).
How long should cultures be incubated?
Up to 2 weeks at 30°C.
What if bacterial contamination obscures results?
Repeat with proper antibiotic additives.
How is pH verified?
Should be 6.5–6.7 after preparation.
Bird Seed Agar 30 MCQs:
- What is the primary purpose of Bird Seed Agar?
a) Isolate Candida albicans
b) Selectively grow Cryptococcus neoformans
c) Detect bacterial endospores
d) Culture Aspergillus species - Which enzyme produced by C. neoformans causes pigmentation on Bird Seed Agar?
a) Catalase
b) Phenoloxidase
c) Amylase
d) Coagulase - What is the key substrate in Bird Seed Agar for melanin production?
a) Glucose
b) Caffeic acid
c) Lactose
d) Sucrose - Who first observed C. neoformans pigmentation on Guizotia seed media?
a) Robert Koch
b) Louis Pasteur
c) Staib
d) Alexander Fleming - Which antibiotic is commonly added to Bird Seed Agar to inhibit bacteria?
a) Vancomycin
b) Penicillin G
c) Tetracycline
d) Erythromycin
- What is the concentration of Guizotia abyssinica seeds in Bird Seed Agar?
a) 10 g/L
b) 50 g/L
c) 100 g/L
d) 5 g/L - Which component enhances melanization in some C. neoformans strains?
a) Agar
b) Creatinine
c) Glucose
d) KH₂PO₄ - At what temperature should Bird Seed Agar be autoclaved?
a) 100°C
b) 110–121°C
c) 130°C
d) 80°C - When are antibiotics added during preparation?
a) Before autoclaving
b) After cooling to 48°C
c) During seed grinding
d) After solidification - What is the pH range of Bird Seed Agar?
a) 4.5–5.5
b) 6.5 ± 0.3
c) 7.2–7.6
d) 8.0–9.0
- How does C. neoformans appear on Bird Seed Agar?
a) White colonies
b) Green colonies
c) Brown to black colonies
d) Yellow colonies - Which organism is a negative control for Bird Seed Agar?
a) Cryptococcus neoformans
b) Escherichia coli
c) Candida albicans
d) Aspergillus niger - What indicates a positive result on Bird Seed Agar?
a) Non-pigmented colonies
b) Red blood cell lysis
c) Melanin production
d) Gas bubbles - Which yeast does NOT produce pigment on Bird Seed Agar?
a) Cryptococcus neoformans
b) Cryptococcus laurentii
c) Cryptococcus gattii
d) Saccharomyces cerevisiae - How long should Bird Seed Agar be incubated for C. neoformans detection?
a) 24 hours
b) 48 hours
c) 1 week
d) Up to 2 weeks
- Which fungus can produce dark colonies but lacks phenoloxidase?
a) Aureobasidium
b) Cryptococcus neoformans
c) Candida albicans
d) Saccharomyces cerevisiae - What may obscure C. neoformans growth on Bird Seed Agar?
a) High glucose
b) Bacterial contamination
c) Low pH
d) Excess agar - Which factor does NOT affect melanin production in C. neoformans?
a) Caffeic acid
b) Creatinine
c) Phenoloxidase
d) Catalase - What should be done if colonies lack pigment?
a) Incubate longer
b) Add more glucose
c) Repeat with Sabouraud Agar
d) Discard the culture - Which component is NOT part of Bird Seed Agar?
a) Guizotia seeds
b) Chloramphenicol
c) Blood
d) Creatinine
- Which modification did Shields & Ajello make to Staib’s agar?
a) Added blood
b) Added antibiotics
c) Removed glucose
d) Reduced pH - What is the teleomorph name of C. neoformans?
a) Aspergillus fumigatus
b) Filobasidiella neoformans
c) Candida tropicalis
d) Histoplasma capsulatum - Which clinical specimen is NOT suitable for Bird Seed Agar?
a) CSF
b) Sputum
c) Blood agar
d) Urine - What is the role of KH₂PO₄ in Bird Seed Agar?
a) Energy source
b) Buffer
c) Pigment enhancer
d) Solidifying agent - Which organism is inhibited by gentamicin in Bird Seed Agar?
a) C. neoformans
b) E. coli
c) C. albicans
d) A. niger
- What is the ATCC number for C. neoformans positive control?
a) ATCC 25922
b) ATCC 32045
c) ATCC 10231
d) ATCC 90028 - How should used Bird Seed Agar plates be disposed of?
a) Autoclave
b) Freeze
c) Incinerate directly
d) Discard in trash - What temperature is ideal for storing prepared plates?
a) 2–8°C
b) 25°C
c) 37°C
d) -20°C - Which organism is used to test antibiotic inhibition in Bird Seed Agar?
a) Staphylococcus aureus
b) Pseudomonas aeruginosa
c) Escherichia coli
d) Klebsiella pneumoniae - What precaution is needed when handling Guizotia seeds?
a) Avoid inhalation
b) Use UV light
c) Freeze before use
d) Mix with acid
Bird Seed Agar: A Selective Medium for Cryptococcus neoformans
Bird seed agar (also known as niger seed agar or Staib agar) is a specialized fungal culture medium used primarily for the selective isolation and identification of Cryptococcus neoformans, an encapsulated yeast that can cause severe infections, particularly in immunocompromised individuals. The medium derives its name from its key ingredient—Guizotia abyssinica (niger seed) extract—which contains phenol oxidase substrates that allow C. neoformans to produce melanin, resulting in brown to black colonies due to the oxidation of caffeic acid.
Unlike general fungal media, bird seed agar is selective because its composition (including chloramphenicol and sometimes cycloheximide) inhibits bacterial and saprophytic fungal growth while promoting Cryptococcus species. C. neoformans is distinguished from other yeasts by its dark pigment production, whereas non-pathogenic Cryptococcus species (like C. albidus) typically remain unpigmented. This medium is particularly useful in clinical mycology for diagnosing cryptococcal meningitis and in environmental studies to detect the yeast in pigeon droppings and soil.
Composition and Mechanism of Bird Seed Agar
The standard bird seed agar recipe includes:
- Guizotia abyssinica (niger seed) extract (primary substrate for melanin production)
- Glucose (carbon source)
- Chloramphenicol (inhibits bacteria)
- Caffeic acid or creatinine (enhances melanin formation)
- Agar (solidifying agent)
When Cryptococcus neoformans grows on this medium, it oxidizes phenolic compounds in the seeds, leading to melanin deposition in the cell wall, which gives colonies their characteristic dark color. Other fungi, such as Candida species, may grow but do not produce pigment, helping in differentiation.
Applications and Limitations
Bird seed agar is widely used in:
- Clinical labs – For detecting C. neoformans in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), blood, and respiratory samples from HIV/AIDS or transplant patients.
- Environmental studies – To isolate Cryptococcus from bird droppings, soil, and decaying wood.
- Research – Studying melanin production as a virulence factor in Cryptococcus.
Limitations:
- Some non-pathogenic Cryptococcus species may grow but lack pigment.
- Requires 48–72 hours of incubation at 25–30°C for optimal results.
- Less effective for non-neoformans Cryptococcus (e.g., C. gattii), which may need additional tests.
Comparison with Other Fungal Media
| Medium | Selective For | Differentiation Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Bird Seed Agar | Cryptococcus neoformans | Brown/black colonies (melanin) |
| Sabouraud Dextrose Agar (SDA) | General fungi | Non-selective, supports most yeasts/molds |
| CHROMagar Candida | Candida species | Color-based species differentiation |
| Cornmeal Agar | Fungal morphology (hyphae, chlamydospores) | No melanin production |
Conclusion
Bird seed agar remains a gold-standard medium for identifying Cryptococcus neoformans due to its melanin-based differentiation. While newer molecular methods (e.g., PCR, antigen testing) are faster, bird seed agar is still valuable for low-resource labs and environmental sampling. For confirmation, labs often pair it with India ink staining (for capsule visualization) or MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry.