Biochemical Test of Helicobacter pylori 50 FAQs and 30 MCQs
Biochemical Test of Helicobacter pylori 50 FAQs
What shape is H. pylori?
Spiral/Helical (Rod-shaped per Gram stain description).
Is H. pylori Gram-positive or Gram-negative?
Gram-negative.
Does H. pylori have a capsule?
No, it is non-capsulated.
Is H. pylori motile?
Yes, it is motile.
What allows H. pylori to be motile?
It possesses flagella (multiple).
Does H. pylori form spores?
No, it is non-sporing.
What oxygen requirement does H. pylori have?
It is microaerophilic (requires low oxygen).
Where does H. pylori primarily live in humans?
In the stomach.
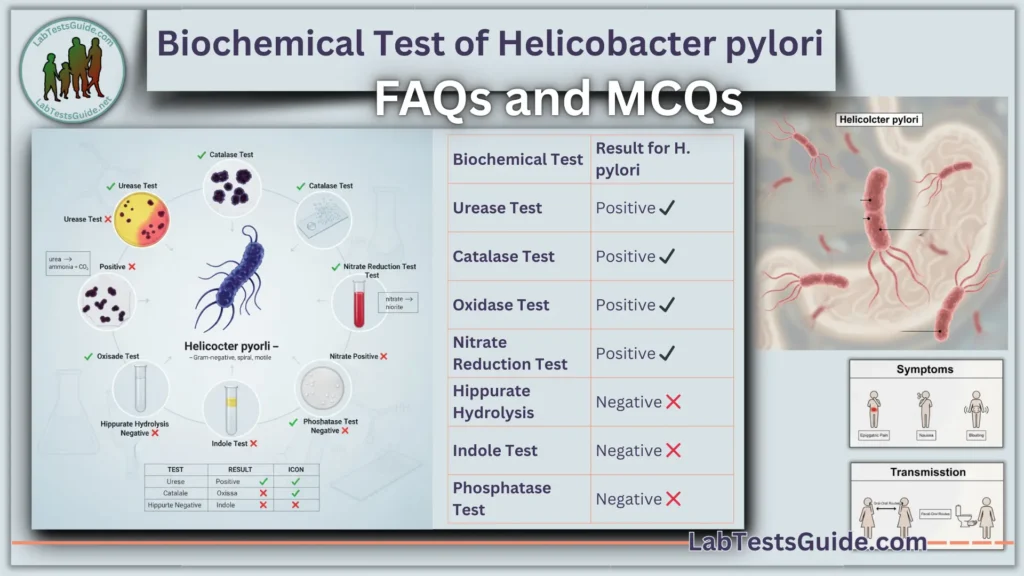
Is the Catalase test positive or negative for H. pylori?
Positive (+ve).
Is the Oxidase test positive or negative for H. pylori?
Positive (+ve).
Is the Urease test positive or negative for H. pylori?
Positive (+ve).
What is the significance of H. pylori‘s urease production?
It breaks down urea into ammonia, neutralizing stomach acid for survival.
Does H. pylori reduce Nitrate?
No, Nitrate Reduction is Negative (-ve).
Does H. pylori produce H2S?
Yes, H2S test is Positive (+ve).
Can H. pylori tolerate 1% Glycine?
No, Glycine (1%) Tolerance is Negative (-ve).
Does H. pylori ferment Glucose?
Yes, Glucose fermentation is Positive (+ve).
Is the Hippurate hydrolysis test positive for H. pylori?
No, Hippurate is Negative (-ve).
Is the Indoxyl Acetate hydrolysis test positive for H. pylori?
No, Indoxyl Acetate is Negative (-ve).
Is Alkaline Phosphatase produced by H. pylori?
Yes, Alkaline Phosphatase test is Positive (+ve).
Can H. pylori grow at 25°C, 30°C, or 45°C?
No, Growth is Negative (-ve) at these temperatures.
At what temperatures can H. pylori grow?
It grows at 35°C and 40°C (Positive +ve).
Can H. pylori grow in 0.5% or 0.75% NaCl?
Yes, Growth is Positive (+ve).
Can H. pylori grow in 1.00% or 1.25% NaCl?
Yes, Growth is Positive (+ve).
Can H. pylori grow in 1.5% NaCl?
No, Growth is Negative (-ve).
What major diseases is H. pylori associated with?
Chronic gastritis, peptic ulcers, gastric cancer, MALT lymphoma.
How does H. pylori cause gastritis?
It infects and inflames the stomach lining.
What are symptoms of H. pylori-induced gastritis?
Stomach pain, nausea, bloating.
What type of ulcers does H. pylori cause?
Peptic ulcers (stomach or upper small intestine).
How does H. pylori contribute to peptic ulcer formation?
It erodes the protective stomach/duodenal lining, making it vulnerable to acid.
Does H. pylori infection increase cancer risk?
Yes, chronic infection increases the risk of gastric cancer.
What specific type of stomach cancer is linked to chronic H. pylori?
Gastric cancer (adenocarcinoma).
What type of lymphoma is associated with H. pylori?
MALT lymphoma (Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue lymphoma).
Is H. pylori considered a pathogen?
Yes, it is a significant human pathogen.
How does H. pylori survive in the acidic stomach?
Primarily by producing urease to neutralize acid.
How does the spiral shape help H. pylori?
It allows the bacterium to pierce the stomach’s mucous membrane.
How do flagella help H. pylori?
They enable motility to move through the stomach’s mucous layer.
How does H. pylori adhere to the stomach lining?
It produces adhesins that bind to gastric epithelial cells.
Can H. pylori evade the immune system?
Yes, it can modify surface antigens and produce factors to evade immunity.
How is H. pylori usually acquired?
Typically acquired in childhood.
What are the main routes of H. pylori transmission?
Oral-Oral route and Fecal-Oral route.
What does Oral-Oral transmission involve?
Spread via saliva, shared utensils, or oral contact.
What does Fecal-Oral transmission involve?
Spread via contaminated food, water, or poor hygiene.
Who discovered H. pylori and when?
Australian scientists Barry Marshall and Robin Warren in 1982.
Why is H. pylori globally significant?
Due to its high prevalence and association with serious gastrointestinal diseases (gastritis, ulcers, cancer).
Is H. pylori only harmful?
While primarily pathogenic, some research explores potential co-evolutionary roles in immune regulation/gut microbiota, though benefits are unconfirmed.
What is the cell wall structure of H. pylori?
It has a Gram-negative cell wall with an outer membrane containing lipopolysaccharides.
Why is the flagella structure important?
Multiple flagella provide the motility needed to navigate thick stomach mucus.
What does ‘microaerophilic’ mean for H. pylori?
It requires oxygen, but at lower concentrations than found in the atmosphere, matching the stomach environment.
What role does urease play beyond acid neutralization?
The ammonia produced also potentially damages host cells.
How does penetrating the mucus benefit H. pylori?
It allows access to the less acidic environment near the epithelial cells and facilitates adhesion.
Biochemical Test of Helicobacter pylori 30 MCQs
- What is the Gram stain characteristic of H. pylori?
a) Gram-positive
b) Gram-variable
c) Gram-negative✔ - Which enzyme is CRITICAL for H. pylori‘s survival in stomach acid?
a) Catalase
b) Oxidase
c) Urease✔. - What shape does H. pylori exhibit?
a) Cocci
b) Spiral (helical)✔
c) Bacilli - Which biochemical test is POSITIVE for H. pylori?
a) Nitrate reduction
b) Hippurate hydrolysis
c) Catalase✔ - At what temperature does H. pylori NOT grow?
a) 35°C
b) 40°C
c) 45°C✔
- What is H. pylori‘s oxygen requirement?
a) Obligate aerobe
b) Microaerophilic✔
c) Anaerobic - H. pylori grows in NaCl concentrations up to:
a) 0.75%
b) 1.25%✔
c) 1.5% - Which structure enables H. pylori motility?
a) Pili
b) Flagella✔
c) Capsule - H. pylori is:
a) Spore-forming
b) Non-sporing✔
c) Capsulated
- Chronic H. pylori infection is a risk factor for:
a) Lung cancer
b) Gastric cancer✔
c) Colon polyps - What disease involves stomach lining inflammation due to H. pylori?
a) Hepatitis
b) Gastritis✔
c) Enteritis - H. pylori causes peptic ulcers by:
a) Increasing acid secretion
b) Eroding the protective mucus layer✔
c) Invading bloodstream - Which cancer is linked to H. pylori-induced MALT?
a) Adenocarcinoma
b) Lymphoma✔
c) Sarcoma
- A positive urease test is key for diagnosing:
a) Salmonella
b) H. pylori✔
c) E. coli. - Which test is NEGATIVE for H. pylori?
a) Oxidase
b) Nitrate reduction✔
c) Catalase - H. pylori ferments:
a) Lactose
b) Glucose✔
c) Sucrose
- H. pylori is primarily transmitted via:
a) Airborne droplets
b) Fecal-oral route✔
c) Sexual contact - Infection typically begins in:
a) Adulthood
b) Childhood✔
c) Adolescence
- Ammonia produced by H. pylori:
a) Enhances acid production
b) Neutralizes stomach acid✔
c) Digests mucus - Adhesins in H. pylori help in:
a) Evading antibiotics
b) Binding to stomach cells✔
c) Flagellar movement
- Who discovered H. pylori?
a) Louis Pasteur
b) Robert Koch
c) Barry Marshall & Robin Warren✔ - H. pylori is NOT associated with:
a) Chronic gastritis
b) Gastric ulcers
c) Appendicitis✔
- Growth at 30°C is:
a) Positive
b) Negative✔
c) Variable - H. pylori is sensitive to NaCl concentration above:
a) 1.0%
b) 1.25%
c) 1.5%✔ - Which enzyme test is negative?
a) Alkaline Phosphatase
b) Hippurate✔
c) Catalase
- A patient with recurrent peptic ulcers should be tested for:
a) H. pylori✔
b) Clostridium difficile
c) Staphylococcus aureus - A positive urease breath test indicates:
a) H. pylori infection✔
b) Lactose intolerance
c) Kidney failure
- H. pylori can grow at 25°C:
a) True
b) False✔ - It produces H₂S:
a) True✔
b) False - Glycine tolerance is positive:
a) True
b) False✔