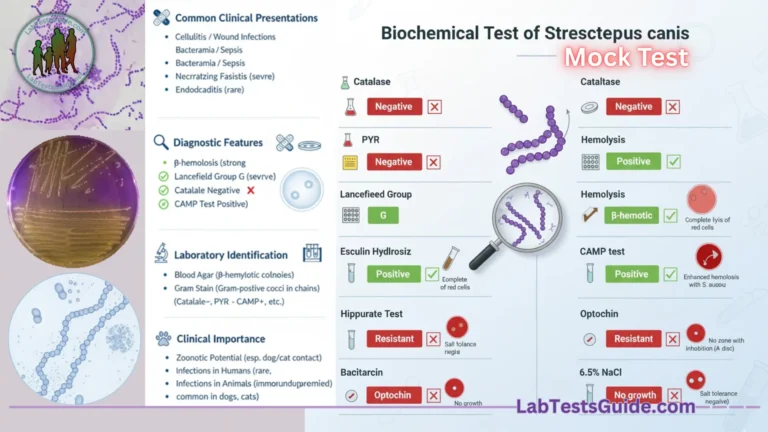
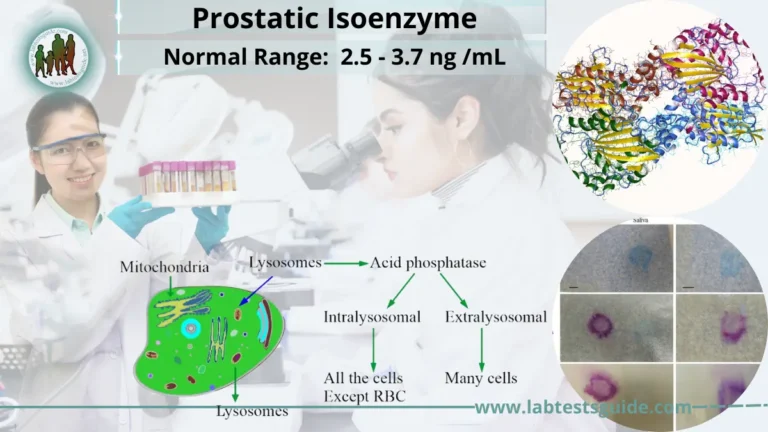
Welcome to Part 53 of the ASCP MLS Exam Practice Series, covering Liver and Kidney Function Tests. The liver and kidneys are vital organs responsible for metabolism, detoxification, and waste elimination. This section focuses on the biochemical markers, enzyme profiles, and laboratory methods used to assess hepatic and renal health. Understanding these parameters is essential for accurate diagnosis and clinical interpretation.
📘 Key Topics Covered
- Liver structure and metabolic functions
- Bilirubin metabolism and jaundice classification
- Liver enzymes and their diagnostic roles (ALT, AST, ALP, GGT)
- Serum proteins and albumin/globulin ratio
- Hepatic function tests: total bilirubin, direct bilirubin, ammonia
- Kidney physiology and function overview
- Renal function markers: urea, creatinine, uric acid
- Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) estimation
- Electrolyte and acid-base abnormalities in renal disease
- Interpretation of liver and kidney test panels
🧠 Learning Objectives
By the end of this part, you should be able to:
- Identify key biochemical markers for liver and kidney function.
- Explain the metabolic processes of bilirubin and nitrogenous waste products.
- Interpret enzyme patterns associated with liver disease.
- Evaluate renal test results and correlate with clinical conditions.
60 MCQs (4121-4180):
- In which of the following disease states is conjugated (direct) bilirubin a major serum component?
a) Hemolysis
b) Neonatal Jaundice
c) Biliary Obstruction
d) Erythroblastosis Fetalis - The expected blood gas results for a patient in chronic renal failure would match the pattern of:
a) Metabolic Acidosis
b) Respiratory Acidosis
c) Metabolic Alkalosis
d) Respiratory Alkalosis - A patient has the following lab results: total bilirubin 9.5 mg/dL, unconjugated bilirubin 8.5 mg/dL, urine bilirubin negative, urine urobilinogen increased. This jaundice is classified as:
a) Prehepatic
b) Viral Hepatic
c) Cirrhotic Hepatic
d) Posthepatic - The best test for monitoring glomerular function, due to its high sensitivity, is:
a) Urine Sodium
b) BUN/Creatinine Ratio
c) Creatinine Clearance
d) Urea Clearance - In the liver, bilirubin is conjugated to form:
a) Urobilinogen
b) Urobilin
c) Bilirubin-Albumin Complex
d) Bilirubin Diglucuronide - A patient with glomerulonephritis is most likely to present with which of the following serum results?
a) Creatinine decreased
b) Calcium increased
c) Phosphorous decreased
d) BUN increased - Kernicterus is an abnormal accumulation of bilirubin in which tissue?
a) Heart Tissue
b) Brain Tissue
c) Liver Tissue
d) Kidney Tissue - The principle excretory form of nitrogen is:
a) Amino Acids
b) Creatinine
c) Urea
d) Uric Acid - Which of the following enzyme patterns is most consistent with acute hepatitis?
a) Marked increase in ALT and AST, slight increase in ALP and GGT
b) Marked increase in ALP and GGT, slight increase in ALT and AST
c) Slight increase in all liver enzymes (ALT, AST, ALP, GGT)
d) Isolated increase in GGT - A blood creatinine value of 5.0 mg/dL is most likely to be found with which of the following blood values?
a) Urea Nitrogen: 80 mg/dL
b) Osmolality: 292 mOsm/kg
c) Uric Acid: 8 mg/dL
d) Ammonia: 80 μg/dL - In which condition does decreased activity of glucuronyl transferase result in increased unconjugated bilirubin and kernicterus in neonates?
a) Gilbert Disease
b) Rotor Syndrome
c) Dubin-Johnson Syndrome
d) Crigler-Najjar Syndrome - The Jaffe reaction is used to measure creatinine and involves the reaction with:
a) Alkaline Picrate Solution
b) Diazotized Sulfanilic Acid
c) Paradimethylaminobenzaldehyde
d) Cupric Sulfate - A patient has these findings: total serum bilirubin 8.5 mg/dL, conjugated bilirubin 6.1 mg/dL, increased urine urobilinogen, decreased fecal urobilinogen, positive urine bilirubin, AST 300 U/L. This best represents:
a) Unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia due to hemolysis
b) Unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia due to toxic liver damage
c) Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia due to hepatocellular disease
d) Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia due to biliary obstruction - Creatinine clearance is used to estimate the:
a) Tubular Secretion Rate
b) Glomerular Filtration Rate
c) Renal Blood Flow
d) Urine Concentrating Ability - Which of the following enzymes is the most sensitive indicator of cholestasis or biliary obstruction?
a) Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT)
b) Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST)
c) Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP)
d) Lactate Dehydrogenase (LD) - The most important buffer pair in plasma is:
a) Phosphate/Biphosphate
b) Hemoglobin/Imidazole
c) Bicarbonate/Carbonic Acid
d) Sulfate/Bisulfate - A critically ill patient becomes comatose. The physician suspects hepatic failure. The most helpful initial assay is:
a) Ammonia
b) ALT
c) AST
d) GGT - The most common cause of respiratory alkalosis is:
a) Vomiting
b) Starvation
c) Asthma
d) Hyperventilation - In the Jendrassik-Grof method for bilirubin, alkaline tartrate is added to:
a) Form the colored diazo bilirubin complex
b) Eliminate spectrophotometric interferences
c) Act as an accelerator for the reaction
d) React specifically with delta-bilirubin - A patient’s lab results show: Na+ 137 mEq/L, glucose 100 mg/dL, BUN 18 mg/dL, anion gap 19, osmolality 301 mOsm/Kg. This indicates a need to investigate for:
a) Chronic Respiratory Disease
b) Milk-Alkali Syndrome
c) Methanol or other organic poisoning
d) Renal compensation for respiratory alkalosis - Which of the following enzyme patterns is most consistent with obstructive jaundice?
a) Slight increase in ALP, marked increase in AST and ALT
b) Marked increase in ALP and GGT, slight increase in AST and ALT
c) Marked increase in AST and ALT, slight increase in GGT
d) Isolated increase in AST - The most sensitive enzymatic indicator for liver damage from chronic ethanol intake is:
a) Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT)
b) Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST)
c) Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase (GGT)
d) Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) - The first enzyme to become elevated after a myocardial infarction is:
a) Lactate Dehydrogenase (LD)
b) Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST)
c) Creatine Kinase (CK)
d) Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) - A stool specimen that appears black and tarlike should be tested for the presence of:
a) Occult Blood
b) Fecal Fat
c) Trypsin
d) Excess Mucus - The most widely used method for bilirubin measurement is based on the:
a) Jaffe Reaction
b) Schales and Schales Method
c) 8-Hydroxyquinoline Reaction
d) Jendrassik-Grof Method - In respiratory acidosis, a compensatory mechanism is:
a) Increased Respiratory Rate
b) Decreased Ammonia Formation
c) Increased Blood pCO2
d) Increased Plasma Bicarbonate Concentration - A patient with a normal BUN and serum creatinine but increased serum and urinary uric acid levels most likely has:
a) Dehydration
b) Gout
c) Nephrotic Syndrome
d) Renal Failure - The different forms of hemoglobin (e.g., HbA, HbS) can be separated and identified based on their charge using:
a) Immunoassay
b) Electrophoresis
c) Mass Spectrometry
d) Ion-Selective Electrode - The most common cause of a falsely increased LD1 fraction on electrophoresis is:
a) Liver Disease
b) Specimen Hemolysis
c) Congestive Heart Failure
d) An Older Specimen - The most important buffer system in the blood is:
a) Phosphate buffer system
b) Bicarbonate buffer system
c) Protein buffer system
d) Hemoglobin buffer system - The primary function of the liver is to:
a) Regulate blood pressure
b) Filter blood and produce bile
c) Produce insulin
d) Store minerals - Bilirubin is produced from the breakdown of:
a) Hemoglobin
b) Albumin
c) Creatinine
d) Urea - The conjugation of bilirubin occurs in the:
a) Spleen
b) Liver
c) Kidney
d) Bone marrow - Conjugated bilirubin is also known as:
a) Indirect bilirubin
b) Unconjugated bilirubin
c) Direct bilirubin
d) Total bilirubin - The enzyme most specific for liver cell damage is:
a) AST (aspartate aminotransferase)
b) ALP (alkaline phosphatase)
c) ALT (alanine aminotransferase)
d) GGT (gamma-glutamyl transferase) - Which enzyme is most sensitive for detecting cholestasis?
a) AST
b) GGT
c) LDH
d) ALT - The normal pathway for bilirubin excretion is through the:
a) Urine
b) Sweat glands
c) Bile and feces
d) Saliva - Which of the following conditions shows elevated unconjugated bilirubin?
a) Hemolytic anemia
b) Bile duct obstruction
c) Hepatitis
d) Cirrhosis - In obstructive jaundice, which fraction of bilirubin is predominantly increased?
a) Indirect bilirubin
b) Conjugated bilirubin
c) Delta bilirubin
d) Both indirect and delta - A high ALP level with normal AST and ALT suggests:
a) Hepatocellular damage
b) Bone disease
c) Alcoholic liver disease
d) Acute hepatitis - The De Ritis ratio (AST/ALT) greater than 2 is indicative of:
a) Viral hepatitis
b) Alcoholic liver disease
c) Cirrhosis
d) Fatty liver - The major plasma protein synthesized by the liver is:
a) Transferrin
b) Albumin
c) Globulin
d) Fibrinogen - Hypoalbuminemia is most commonly associated with:
a) Dehydration
b) Liver disease or nephrotic syndrome
c) Hemolysis
d) Polycythemia - Which test is used to measure total bilirubin?
a) Jendrassik–Grof method
b) Biuret method
c) Bromocresol green method
d) Kjeldahl method - The conversion of ammonia to urea occurs in the:
a) Kidney
b) Liver
c) Pancreas
d) Intestine - The major nitrogenous waste product in urine is:
a) Creatine
b) Uric acid
c) Urea
d) Ammonia - Urea is produced as the end product of:
a) Carbohydrate metabolism
b) Fat metabolism
c) Protein metabolism
d) Nucleic acid metabolism - Creatinine is formed from:
a) Creatine phosphate
b) Amino acids
c) Glucose
d) Fatty acids - The creatinine clearance test is used to estimate:
a) Liver function
b) Kidney glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
c) Uric acid level
d) Electrolyte balance - The normal reference range for serum creatinine in adults (mg/dL) is approximately:
a) 0.1–0.5
b) 0.6–1.2
c) 1.5–2.5
d) 2.5–4.0 - The normal blood urea nitrogen (BUN) level (mg/dL) is approximately:
a) 1–5
b) 5–20
c) 25–40
d) 50–60 - An increased BUN and creatinine level is typically seen in:
a) Liver failure
b) Renal failure
c) Hypoglycemia
d) Dehydration only - The BUN/creatinine ratio helps differentiate:
a) Liver from kidney failure
b) Pre-renal, renal, and post-renal causes of uremia
c) Bone disease from muscle disease
d) Acute from chronic liver injury - Uric acid is the end product of:
a) Protein metabolism
b) Fat metabolism
c) Purine metabolism
d) Pyrimidine metabolism - Elevated serum uric acid is seen in:
a) Gout and renal failure
b) Hypoglycemia
c) Liver cirrhosis
d) Vitamin deficiency - A low urine specific gravity indicates:
a) Concentrated urine
b) Dilute urine
c) Dehydration
d) Glycosuria - Which of the following tests best assesses tubular function?
a) Creatinine clearance
b) Urine osmolality
c) Bilirubin test
d) Serum ALP - Azotemia refers to:
a) High blood sugar
b) High nitrogenous waste in blood
c) Low urea level
d) Increased albumin - In pre-renal azotemia, the BUN/creatinine ratio is typically:
a) Normal
b) Increased (>20:1)
c) Decreased (<10:1)
d) Unchanged - Which of the following is used as a marker of early renal damage in diabetes?
a) Total protein
b) Microalbuminuria
c) Uric acid
d) BUN
📌 How to Use This Practice Set
- Answer each question before checking the key.
- Focus on why the correct answer is right and the others are wrong.
- Use this set as timed practice to simulate the real exam environment.
Answer Key
Answer Key:
- c) Biliary Obstruction
- c) Metabolic Alkalosis
- a) Prehepatic
- c) Creatinine Clearance
- d) Bilirubin Diglucuronide
- d) BUN increased
- b) Brain Tissue
- c) Urea
- a) Marked increase in ALT and AST, slight increase in ALP and GGT
- a) Urea Nitrogen: 80 mg/dL
- b) Marked increase in ALP and GGT, slight increase in AST and ALT
- c) Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase (GGT)
- c) Creatine Kinase (CK)
- a) Occult Blood
- d) Jendrassik-Grof Method
- d) Increased Plasma Bicarbonate Concentration
- b) Gout
- b) Electrophoresis
- b) Specimen Hemolysis
- b) Bicarbonate buffer system
- b) Alcoholic liver disease
- b) Albumin
- b) Liver disease or nephrotic syndrome
- a) Jendrassik–Grof method
- b) Liver
- c) Urea
- c) Protein metabolism
- a) Creatine phosphate
- b) Kidney glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
- b) 0.6–1.2
- d) Crigler-Najjar Syndrome
- a) Alkaline Picrate Solution
- c) Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia due to hepatocellular disease
- b) Glomerular Filtration Rate
- c) Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP)
- c) Bicarbonate/Carbonic Acid
- a) Ammonia
- d) Hyperventilation
- b) Eliminate spectrophotometric interferences
- c) Methanol or other organic poisoning
- b) Filter blood and produce bile
- a) Hemoglobin
- b) Liver
- c) Direct bilirubin
- c) ALT (alanine aminotransferase)
- b) GGT
- c) Bile and feces
- a) Hemolytic anemia
- b) Conjugated bilirubin
- b) Bone disease
- b) 5–20
- b) Renal failure
- b) Pre-renal, renal, and post-renal causes of uremia
- c) Purine metabolism
- a) Gout and renal failure
- b) Dilute urine
- b) Urine osmolality
- b) High nitrogenous waste in blood
- b) Increased (>20:1)
- b) Microalbuminuria
Top 8 Medical Laboratory Scientist (MLS) Exams:
Top 8 Medical Laboratory Scientist (MLS) Exams that are recognized globally and can help professionals validate their credentials and enhance their career opportunities:
1. ASCP – American Society for Clinical Pathology (USA)
- Exam Name: MLS(ASCP)
- Eligibility: Bachelor’s degree with clinical laboratory experience.
- Global Recognition: High
- Purpose: Certifies Medical Laboratory Scientists in the United States and internationally.
2. AMT – American Medical Technologists (USA)
- Exam Name: MLT(AMT) or MT(AMT)
- Eligibility: Academic and/or work experience in medical laboratory technology.
- Global Recognition: Moderate
- Purpose: Credentialing for medical technologists and technicians.
3. AIMS – Australian Institute of Medical and Clinical Scientists
- Exam Name: AIMS Certification Exam
- Eligibility: Assessment of qualifications and work experience.
- Recognition: Required for practice in Australia.
- Purpose: Certification and registration in Australia.
4. CSMLS – Canadian Society for Medical Laboratory Science
- Exam Name: CSMLS General or Subject-specific Exams
- Eligibility: Graduation from a CSMLS-accredited program or equivalent.
- Recognition: Canada
- Purpose: Entry-to-practice certification in Canada.
5. IBMS – Institute of Biomedical Science (UK)
- Exam Name: Registration and Specialist Portfolio Assessment
- Eligibility: Accredited degree and lab experience.
- Recognition: UK and some Commonwealth countries.
- Purpose: Biomedical Scientist registration with the HCPC (UK).
6. HAAD / DOH – Department of Health, Abu Dhabi (UAE)
- Exam Name: DOH/HAAD License Exam
- Eligibility: Degree in medical laboratory science and experience.
- Recognition: UAE (Abu Dhabi)
- Purpose: Licensure for medical laboratory practice in Abu Dhabi.
7. DHA – Dubai Health Authority (UAE)
- Exam Name: DHA License Exam for Medical Laboratory Technologists
- Eligibility: Relevant degree and experience.
- Recognition: Dubai, UAE
- Purpose: Professional license for clinical laboratory practice in Dubai.
8. MOH – Ministry of Health (Gulf Countries like UAE, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait)
- Exam Name: MOH License Exam
- Eligibility: BSc/Diploma in Medical Laboratory + experience.
- Recognition: Varies by country.
- Purpose: Required for practicing in public and private sector labs.
Tags:
#ASCPMLS #MLSexam #LabTech #MedicalLaboratory #BOCexam #FreePracticeQuestions #QualityControl #LaboratorySafety